![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
"broken function"
|
dysfunction
|
|
|
shortness of breath
|
dyspnea
|
|
|
heart can't pump enough blood to meet tissue needs
|
heart failure
|
|
|
fluid congestion in the lungs
|
pulmonary edema
|
|
|
"heart muscle disease"
|
cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
urine in blood
|
uremia
|
|
|
"know before"; a prediction of the course of a disease
|
prognosis
|
|
|
"know between" possible causes
|
diagnosis
|
|
|
a model in which the causes and the effects are all chemical or physical changes
|
mechanistic paradigm
|
|
|
cause --> effect
|
causality
|
|
|
the process in which physicians are presented with a effect (dysfunction) and must infer the cause
|
differential diagnosis
|
|
|
a form of negative feedback in which the product of a reaction down regulated an upstream reaction
|
product inhibition
|
|
|
model that describes the purpose served by the bodily response and implies (inappropriately) that this purpose causes the response
|
teleology
|
|
|
from the air to a rbc list the boundary layers and fluid spaces an O2 molecule would cross
|
1.) alveolar epithelium
2.) interstitial fluid (basement membrane) 3.) capilary endothelium 4.) plasma 5.)RBC |
|
|
cause always precedes the effect
|
temporality
|
|
|
when one event influences the magnitude of an earlier event in the same sequence
|
feedback
|
|
|
counteracts the consequence of a disturbance- leads to compensation, stabiliy, return to normal
|
negative feedback
|
|
|
exaggerates the consequence of a disturbance- leads to decompensation (going toward an extreme), which may or may not be desirable
|
positive feedback
|
|
|
when a "side-branch' in a cause-and-effect sequence influences the magnitude of a subsequent event in the same sequence
|
feed-forward
|
|
|
breakdown of aveolar walls
|
emphysema
|
|
|
fluid retention
|
edema
|
|
|
low oxygen in the blood
|
hypoxemia
|
|
|
resolution of the unaided eye
|
0.2 milimeters
|
|
|
resolution of light microscope
|
0.2 micrometers
|
|
|
resolution of an electron microscope (practical for biological tissues)
|
1-2 nanometers
|
|
|
size of object in picture/size of object in nature
|
magnification
|
|
|
average diameter of a RBC
|
7.5 micrometers
|
|
|
type of signalling in which the secreted signal acts on the same cell that secreted it (or neighboring cell of the same type)
|
autocrine signalling
|
|
|
a type of signalling in which the secreted signal carried by diffusion and acts on nearby cells of a different cell type
|
paracrine signalling
|
|
|
a special case of paracrine signalling in which the signalling cell is a neuron
|
neurotransmission
|
|
|
a types of signalling in which the secreted signal (hormone) is carried cia blood stream and acts on distant cells
|
endocrine signalling
|
|
|
high glucose in the blood
|
hyperglycemia
|
|
|
cell lined "pockets" of extracellular fluid
|
transcellular compartments
|
|
|
What separates inside the body from outside the body
|
epithelium
|
|
|
What separates inside the cell from outside the cell
|
cell membrane
|
|
|
What is the sodium and potasium concentration between intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid?
|
sodium is higer in extracellular fluid and potassium is higher in intracellular fluid
|
|
|
What separates blood and interstitial fluid?
|
endothelium
|
|
|
fraction of cells in the blood
|
hematocrit
|
|
|
What is the cellular portion of blood composed of?
|
erythrocytes, leukocytes, and thrombocytes
|
|
|
What is the difference between plasma and interstitial fluid?
|
plasma has proteins
|
|
|
What is the body fluid distribution between intracellular and extracellular fluid?
|
intracellular fluid= 2/3
extracellular fluid= 1/3 |
|
|
What is the body fluid distribution of extracellular fluid between interstitial and plasma?
|
interstitial= 3/4
plasma= 1/4 |
|
|
What makes up the extracellular fluid?
|
interstial fluid + plasma + lymph + transcellular compartments
|
|
|
What is the average percent body fluid for men? women?
|
men = 60%
women = 50% |
|
|
cm/in conversion factor
|
2.54 cm = 1 inch
|
|
|
What is the medical percent unit?
|
g/100mL or g/dL
|
|
|
What is the medical percent unit?
|
g/100mL or g/dL
|
|
|
fatty acids with no double bonds
|
saturated FA
|
|
|
fatty acids with 1+ double bonds
|
unsaturated FA
|
|
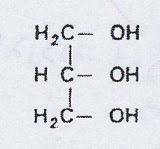
|
glycerol
|
|
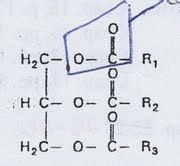
glycerol + 3 FA
|
triacylglycerol (triglycerol)
|
|
|
phospholipid w/ -H as it's OH head group
|
phosphatidic acid
|
|
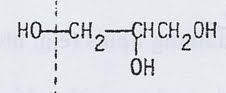
phospholipid with this as it's alcohol head group
|
phosphatidyl glycerol (PG)
|
|
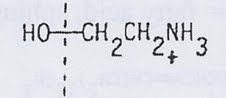
phospholipid with this as it's alcohol head group
|
phosphatidyl ethanolamine (PE)
|
|
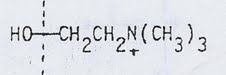
phospholipid with this as it's alcohol head group
|
phosphatidyl choline (PC)
|
|
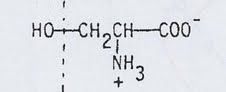
phospholipid with this as it's alcohol head group
|
phosphatidy serine (PS)
|
|
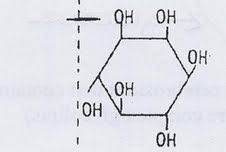
phospholipid with this as it's alcohol head group
|
phosphatidyl inositol (PI)
|
|
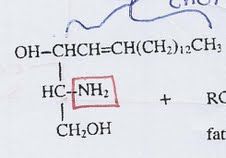
glycerol + hydrocarbon + amino group
|
sphingosine
|
|
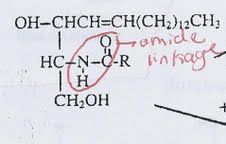
sphingosine + FA
|
ceramide
|
|
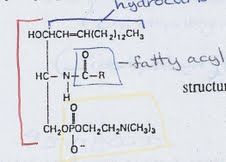
ceramide + phosphate group w/ an alcohol head group
|
sphingolipid
|
|
|
ceramide + carbohydrate (NO PHOSPHATE)
|
glycolipid
|
|
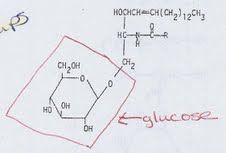
glycolipid w/ a simple sugar
|
cerebroside
|
|
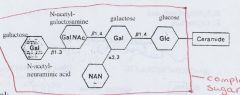
cerebrosides that contain more than one simple sugar linked to ceramide
|
gangliosides
|
|
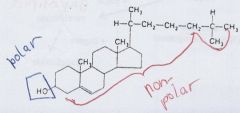
|
cholesterol
|
|
|
carbohydrate + protein
|
glycoprotein
|
|
|
Which leaflet has more PC?
|
outer leaflet
E-face (external) |
|
|
Which leaflet always contains carbohydrate groups of glycoproteins
|
outer leaflet
E-face (external) |
|
|
protein embedded in the membrane that can only be released by agents that compete for non-polar interactions (detegents)
|
integral proteins
|
|
|
membrane proteins that can be released w/o detergent
|
peripheral
|
|
|
P-face
|
inner leaflet
|
|
|
Which leaflet is associated w/ more integral proteins?
|
inner leaflet
P-face |
|

|
lateral motion
|
|
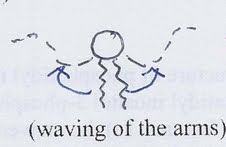
|
segmental motion
|
|
|
What is the average diameter of microfilaments? (actin)
|
6-8nm
|
|
|
What is the average diameter of intermediate filaments?
|
8-10nm
|
|
|
What is the average diameter of microtubules?
|
20-25nm
|
|
|
IF (organelle-specific) skeletal elements of the nucleus
|
Lamin
|
|
|
DNA + protein
|
chromatin
|
|
|
less condensed DNA; actively expressed
|
euchromatin
|
|
|
condensed DNA; silent
|
heterochromatin
|
|
|
RNA + protein; site of rRNA synthesis and regulatory cell cycle protein
|
nucleolus
|
|
|
space between inner and outer nuclear membranes
|
perinuclear cisterna
|
|
|
nuclear localization signal (NLS): chemical nature, receptors, and activity
|
chemical nature= basic residue
receptors= importin activity= import proteins into nucleus |
|
|
nuclear export signal (NES): chemical nature, receptors, and activity
|
chemical nature= leucine rich
receptors= exportin activity= export proteins from nucleus |
|
|
mitochondrial signal peptide: chemical nature, receptors, and activity
|
chemical nature= amphipathic helix
receptors= various/ peptidases etc activity= import proteins into the matrix |
|
|
signal sequence: chemical nature, receptors, and activity
|
chemical nature= stretch of hydrophobic AA
receptors= signal recognition particle activity= import into the ER |
|
|
lysosome targeting signal: chemical nature, receptors, and activity
|
chemical nature= mannose 6 phosphate
receptors= mannose 6 phosphate receptor activity= import proteins into lysosome |
|
|
specific proteins on the vesicle that dock onto complementary receptors on the target membrane --> fusion
|
v-SNARE
|
|
|
specific receptors on the target membrane that bind to complementary to proteins on the vesicles --> fusion
|
t-SNARE
|
|
|
cell drinking; small molecules; clathrin independent
|
pinocytosis
|
|
|
cell eating; actin dependent; clathrin independent
|
phagocytosis
|
|
|
clathrin dependent endocytosis
|
receptor mediated endocytosis
|
|
|
exocytosis in which contents are excreted continuously
|
constitutive pathway
|
|
|
exocytosis in which contents are stored in cesicles and excreted when signal is recieved.
|
regulated secretory pathway
|
|
|
type of 1st messenger that needs cell-surface receptor and doesn't need carier in the blood
|
hydrophilic
|
|
|
type of 1st messenger that needs a carrier in blood and doesn't require cell surface receptor
|
hydrophobic
|

