![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
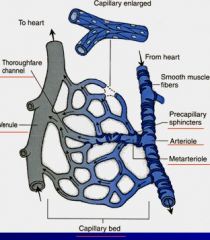
Fill in the blanks
|
|
|
|
What is the main neural control of the peripheral circulation?
|
sympathetic alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction (arterioles, metarterioles)
|
|
|
What is the main local control of the peripheral circulation?
|
local metabolic control of precapillary sphincters
|
|
|
what amino acid is involved in NO synthesis?
|
arginine
|
|
|
What effect does NO have on vascular tone?
|
vasodilator
|
|
|
what are the factors of Fick's law, involved in nutrient transfer?
|
permeability and surface area * concentration difference
|
|
|
under normal conditions, what type of transport do O2 and CO2 undergo? in pneumonia?
|
flow limited, diffusion limited
|
|
|
How do burns effect the capillary filtration coefficient?
|
burns destroy capillary integrity, increasing permeability
|
|
|
Of the four pressures driving water, which two are negligible at equilibrium?
|
THP and TOP
|
|
|
Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure due to heart failure would cause fluid to shift to the ____________
|
interstitium (edema)
|
|
|
Low plasma proteins due to a severe burn would cause fluid to shift to the ______________
|
interstitium (edema)
|
|
|
What would you expect to go along with a sinus infection that has plugged lymph drainage?
|
increased interstitial fluid (edema)
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of organ blood flow autoregulation?
|
metabolic control, myogenic control, Nitric oxide
|
|
|
What are the areas of special circulations?
|
coronary, cerebral, pulmonary, skeletal muscle, skin
|
|
|
How does the coronary blood flow meet its high O2 demand?
|
increased blood flow
|
|
|
when is left main coronary artery blood flow the highest?
|
diastole
|
|
|
when is the blood flow in the coronary arteries the lowest?
|
during intraventricular contraction
|
|
|
What effect does chronic hypertension have on cerebral blood flow? Why is this relevant to treating a chronic hypertensive patient?
|
Chronic hypertension causes a downshift of the autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. So if you drop a chronic hypertensive patient's BP too quickly, you will cause hypoxia in the brain and trigger rebound hypertension
|
|
|
Why does hypoxia cause vasoconstriction in the lungs?
|
to shunt blood away from poorly ventilated areas
|
|
|
What controls pulmonary circulation?
|
O2 concentration
|
|
|
Why is the degree of vasoconstriction in the skeletal muscle so significant to the TPR?
|
The amount of muscle mass makes this resistance a significant portion of the total peripheral resistance
|
|
|
At rest, what is the primary regulation of skeletal muscle circulation?
|
sympathetic innervation to alpha-1 adrenergic receptors (Norepi)
|
|
|
What is the primary control of skeletal muscle circulation during exercise?
|
Local Metabolic Control
|
|
|
What is the primary control for cutaneous circulation?
|
sympathetic innervation (alpha-1 adrenergic)
|
|
|
What is the triple response of histamine?
|
line, flare, wheal
|

