![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Formula for water balance & relevance...
|
Input-Output=balance
=1100 steady state greater>1000= Negative Water Balance less <1000 = Positive Water Balance |
|
|
|
Filtration Fraction=
|
Golmular Filtration Rate/Renal Plasma Flow
|
|
|
|
What factor allows you to calculate renal plasma flow?
|
Calculate the Clearance of Para-aminohippurate
= C PAH = (U PAH )(V) / P PAH |
|
|
|
What is the formula for Renal Plasma Flow?
|
(1-Hct) x Renal blood flow
or Caluclatw PAH clearance |
|
|
|
What is the formula for renal blood flow?
|
RBF=Renal Plasma Flow/(1-Hct)
|
|
|
|
Glomular Filtation Rate is equal to what other factors?
|
creatinine clearance or inulin clearance
|
|
|
|
Glomular Filtration Rate =
(Frank Starling Equations) |
= Kf [(P GC - P BC ) - (iiGC - iiBC )]
or = Kf x net filtration pressure (NFP) |
|
|
|
Net filtration pressure (NFP)=
|
[(P GC - P BC ) - (iiGC - iiBC )]
|
|
|
|
Filtered Load=
|
Glomular Filtration rate x Plasma Concentration
|
|
|
|
Excretion rate= (What units?)
|
mg/min
Urine Concentration(U) x Urine rate(V) or Filtered Load + (Secretion Rate-Resorption Rate) |
|
|
|
Glomular Filtration Rate in relation to Excretion Rate...
|
GFR=(Ux)(V)/P
|
|
|
|
Creatine Clearance
|
C(cr) = Ucr x Urine Rate/Pcr
(Which is also = to GFR!) |
|
|
|
Clearance Equation and Result interpretation
|
Cx= (Ux)(V)/Px
If Cx > GFR then molecule is secreted If Cx < GFR then molecule is Reabsorbed |
|
|
|
Clearance Ratio and significance
|
Cx/Cinulin
1.0= Good GFR Marker <1.0=not filtered, or filtered and reabsorbed >1.0 filtered and secreted |
|
|
|
Transport Rate Equation, Units, and significance
|
Tx= Filtered Load - Excretion Rate
+indicates reabsorption -indicates secretion |
|
|
|
Fractional Excretion and result interpretation
|
excretion rate/filtered load
FE<1 Reabsorption FE>1 secretion |
|
|
|
TF/Px Ratio Interpretation
|
1=reabsorption proportional to H20 reabsorption
<1= reabsorption of substance greater than water >1=reabsorption of substance has been less than water of there is net secretion of the substance |
|
|
|
Tm Interpretation
|
Tm=tubular Maximum (mg.min)
Max rate of solute transport below Tm-FL is reabsorbed portion above Tm= excreted |
|
|
|
Free Water Clearance
|
C(h2o)= V-C(osm)
|
|
|
|
What is Osmolar Clearence (def?)
|
Osmolar clearance (C osm ) is the ml/min
of blood plasma cleared of osmotically active particles. |
|
|
|
What is the formula for Osmplar Clearance?
What is the normal range? |
C osm = U osm V /P osm
Normal C osm = 1 to 2 ml/min |
Reduced C osm
– Positive osmolar balance - gaining osmoles Increased C osm – “Dumping” osmolytes, leads to a loss of ECF. |
|
|
What is the The Henderson-Hasselbalch eq to calculate blood pH?
|
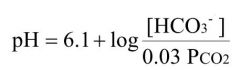
|
|
|
|
normal plasma values (acid base)
|
pH: 7.4 ± 0.05
HCO 3-: 24 ± 2 mEq/L PCO 2 : 40 ± 5 mmHg |
|
|
|
Anion gap Formula and Normal Range
|
AG = [Na+] - ([Cl-] - [HCO 3-]) Know the normal range (8-16 mM).
|
|
|
|
Law of Mass Action
|
o For each 10 mmHg decrease in PCO 2 , HCO 3- will decrease 2 mEq/L
o For each 10 mmHg increase in PCO 2 , HCO 3- will increase 1 mEq/L |
|
|
|
What is the significance of the Anion Gap Measurement?
|
The anion gap is a calculation method used to aid in the differential diagnosis of metabolic acidosis.
|
|
|
|
Causes of Metabolic Acidosis
|
KUSSMAL
Ketones: (Vomiting, high protein, diabetic ketoasidos, alcoholoc KA, Starvation Uremea: (from renal failure) S:Salicylate S: Septic M: Methanol A: Aldehyde or All others L: lactica Acid |
|
|
|
Causes of Metabolic Alkalosis
|
H+ Loss of HCO3-Gain
Ingestion of alkali (e.g., antacids). Hyperaldosteronism (e.g., Conn’s syndrome high aldosterone levels stimulate H + loss (next panel). ECF volume contraction: |
|
|
|
What are some causes of ECF volume contraction? What can it result in?
|
• Vomiting: lose HCl, fluid and K + ,
• Nasogastric suction: as above, • Loop or thiazide diuretics: lose fluid and K + Metabolic Alkalosis |
|
|
|
How do you calculate MAP?( 2)
|
diastolic + 1/3 pulse pressure
MAP=CO x TPR |
|
|
|
C H2O=
|
V - C osm
|
|
|
|
If C H2O is negative=
|
solute-free water is
being conserved by the body. |
|
|
|
C H2O is positive=
|
then solute-free water is
being lost from the body and a dilute urine is being formed |
|

