![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
136 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
most hormones use which M/A
|
Gs: ACTH, LH, FSH, TSH, V2, HCG, MSH, CRH, b1, b2, calcitonin, PTH, glucagon
|
|
|
Gq hormones 7
|
GnRH, TRH, GHRH, AII, V2, oxytocin, a1
|
|
|
steroid hormones 7
|
cortisol, estrogen, tesosterone, progesterone, aldosterone, vit D, thyroid hormone
|
|
|
tyr kinase hormones 2
|
insulin, IGF
|
|
|
cGMP hormones 3
|
ANP, EDRF, NO
|
|
|
ant pit hormones 7
|
TSH, LH, FSH, ACTH, MSH, GH, PRL
|
|
|
post pit hormones 2
|
ADH, oxytocin
|
|
|
gp fam ant pit hormones 3
|
TSH, LH, FSH
|
|
|
POMC ant pit hormones 3
|
ACTH, MSH, b-endorphin
|
|
|
GH homologous hormones 3
|
GH, PRL, HPL
|
|
|
how GH secreted
|
pulsatile
|
|
|
factors that inc GH secretion 6
|
sleep, puberty, stress, starvation, exercise, hypoglycemia
|
|
|
hormone stim GH secretion
|
GHRH
|
|
|
hormone inh GH secretion
|
SMST
|
|
|
Neg feedback of GH 4
|
somatomedins dec GH secretion, somatomedin inc SMST secretion, GHRH inh itself, GH inc SMST secretion
|
|
|
direct GH axn 4
|
dec glucose uptake, inc lipolysis, inc protein synth, inc IGF production
|
|
|
IGF axn 3
|
inc linear growth, in lean body mass, in organ size
|
|
|
neg feedback of PRL 2
|
PRL stim dopa release from hypothal
|
|
|
hormone that stim PRL
|
TRH
|
|
|
PRL axn 4
|
stim milk production, stim breast development, dec synth & release of GnRH (inh ovulation & spermatogenesis)
|
|
|
ADH originate in
|
supraoptic nuclei
|
|
|
oxytocin originate in
|
paraventricular nuclei
|
|
|
major stim oxytocin release
|
suckling
|
|
|
oxytocin axn 2
|
contraction myoepithelium in breast, uterus
|
|
|
thyroglobulin synth from
|
tyr
|
|
|
thyroglobulin synth in
|
thyroid follicular cells
|
|
|
I- pump present in
|
follicular cells facing blood
|
|
|
I- pump inh by 2
|
thiocyanate, perchlorate
|
|
|
I- oxidation by
|
peroxidase enzyme
|
|
|
reactive form iodine
|
I2
|
|
|
peroxidase enzyme inh by
|
propylthiouracil
|
|
|
peroxidase enzyme located in
|
follicular cell membrane facing lumen
|
|
|
I2 organification
|
add to tyr -> MIT, DIT
|
|
|
Wolff-Chaikof effect
|
high I- level inh organification
|
|
|
T4 formed by
|
DIT + DIT
|
|
|
T3 formed by
|
MIT + DIT
|
|
|
most abundant thyroid hormone
|
T4
|
|
|
most reactive thyroid hormone
|
T3
|
|
|
inactive thyroid hormone
|
rT3
|
|
|
leftover MIT, DIT deiodinated by
|
thyroid deiodinase
|
|
|
thyroid hormone release req
|
lysosomal degradation of thyroglobulin
|
|
|
in circ, thyroid hormone bound to
|
TBG (thyroxine binding globulin)
|
|
|
hepatic failure fx on thyroid hormone
|
dec TBG, norm free hormone levels
|
|
|
preg fx on thyroid hormone
|
inc TBG, norm free hormone levels
|
|
|
T4 inactivated by
|
5'-iodinase
|
|
|
hypertrophy of thyroid caused by
|
chronic TSH elevation
|
|
|
thyroid fx on bone 2
|
req bone formation; ossification & fusion of growth plates
|
|
|
thyroid fx on CNS 2
|
req for CNS maturation; hypothyroidism cause irreversible MR
|
|
|
hyperthyroidism CNS fx 2
|
hyperexcitability, irritability
|
|
|
hypothyroidism CNS fx 5
|
listlessness, slowed speech, somnolence, impaired memory, dec mental capacity
|
|
|
thyroid fx on Na/K
|
inc synth Na/K ATPase
|
|
|
thyroid fx on CVS/Resp 4
|
upregulate b1-R, inc HR, inc SV; inc vent
|
|
|
thyroid metabolic fx 6
|
inc glucose absorption, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, glucose oxidation, lipolysis, protein catabolism
|
|
|
zona glomerulosa produce
|
aldo
|
|
|
zona fasciculata produce
|
cortisol
|
|
|
zona reticularis produce
|
androgens
|
|
|
progesteron, deoxycorticosterone, aldo, cortisol are
|
21-C steroids
|
|
|
19-C steroids are
|
androgens
|
|
|
18-C steroids are
|
estrogens
|
|
|
androstenedion to testosterone in
|
testes
|
|
|
aromatization of androgens in 2
|
ovaries, placenta
|
|
|
corticosterone to aldo by
|
aldo synthase
|
|
|
aldo synthase reg by
|
AII
|
|
|
chol to pregnenolone by
|
chol desmolase
|
|
|
chol desmolase reg by
|
ACTH, LH
|
|
|
glucocorticoid secretion
|
circadian rhythm
|
|
|
cortisol levels highest in
|
kmron just before waking
|
|
|
CRH originate in
|
paraventricular nuclei
|
|
|
ACTH reg on adrenals
|
upreg own receptor
|
|
|
adrenal cortex hypertrophy caused by
|
chronic ACTH elevation
|
|
|
neg feedback of cortisol
|
cortisol inh CRH secretion; cortisol inh ACTH secretion
|
|
|
dexamethasone test
|
should SUPPRESS ACTH
|
|
|
Aldo most tightly reg by
|
RAAS
|
|
|
3 main fx of cortisol
|
stim gluconeogenesis, anti-infl, maintain vasc response to cats
|
|
|
how cortisol stim gluconeogenesis 3
|
inc protein catabolism, dec glucose utilization, inc lipolysis
|
|
|
how cortisol anti-infl 4
|
induce lipocortin, IL-2, hist, 5HT
|
|
|
how cortisol maintain vasc response to cats
|
upreg a1-R on arterioles
|
|
|
primary adrenal insufficiency patho
|
low aldo, cortisol, androgens; Addisons
|
|
|
secondary adrenal insufficiency patho
|
low ACTH
|
|
|
cortisol xs
|
Cushing's
|
|
|
aldo xs
|
Conn's
|
|
|
21b-hydroxylase def
|
dec cortisol, dec aldo, inc androgens
|
|
|
17a-hydroxylase def
|
dec androgen, dec cortisol, inc aldo
|
|
|
central islet cells
|
beta cells
|
|
|
outer rim islet cells
|
alpha cells
|
|
|
delta cells secrete
|
SMST, gastrin
|
|
|
how much Ca bound to plasma proteins
|
40%
|
|
|
biologically active Ca is
|
free, ionized
|
|
|
positive Ca balance seen in
|
growing children
|
|
|
neg Ca balance seen in 2
|
preg/lactation
|
|
|
PTH synth & secreted by
|
chief cells
|
|
|
stim PTH
|
Ca-sensing R of parathyroid membrane
|
|
|
Mg fx on PTH
|
mild dec -> stim; severe dec -> inh
|
|
|
PTH axn 4
|
inc bone resorption, inh renal phsophate reabsoprtion, inc renal Ca reabsorption, inc intestinal Ca reabsorption
|
|
|
bone resorption inc what in urine
|
hydroxyproline
|
|
|
pseudohypoparthyroidism type 1a is
|
Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy
|
|
|
defect in Albright's
|
Gs protein in kidney & bone -> resistance to PTH
|
|
|
2o hyperparthyroidism caused by
|
chronic renal failure
|
|
|
familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) genetics
|
auo dom
|
|
|
FHH patho
|
incativation mutations of Ca-sensing receptor -> less sensative
|
|
|
active form vit D
|
1,25-dihydroxycolecalciferol
|
|
|
1a-hydroxylas activity inc by 3
|
hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, inc PTH
|
|
|
vit D axn 2
|
inc intestinal & renal Ca & phosphate absorption, inc bone resportion (old bone -> new bone)
|
|
|
calcitonin synth & secreted by
|
parafollicular cells (thyroid)
|
|
|
LH axn in male
|
stim chol desmolase to inc testosterone synth (Leydig cell)
|
|
|
5a-reductase in
|
accessory organs
|
|
|
GnRH originate in
|
arcuate nuc
|
|
|
FSH axn in male
|
stim spermatogenesis in Sertoli cells
|
|
|
neg feedback of FSH 2
|
Stertoli secrete inhibin -> inh FSH at ant pit; testosterone inh GnRH at hypothal
|
|
|
testosterone axn 8
|
epididymis/vas deferens/seminal vesicle differentiation, growth spurt, epiphyseal closure, libido, spermatogenesis, voice deepening, muscle mass inc, penis/seminal vesicle growth
|
|
|
DTH axn 4
|
penis/scrotum/prostate differentiation, male hair pattern, sebaceous gland, prostate growth
|
|
|
GnRH secretion is
|
pulsatile
|
|
|
Neg feedback of LH 2
|
testosterone inh LH at ant pit; testosterone inh GnRH at hypothal
|
|
|
LH > FSH when
|
puberty, reproductive years
|
|
|
FSH > LH when
|
childhood, senescence
|
|
|
LH axn in female
|
stim chol desmolase to inc testosterone synth (theca cell)
|
|
|
estrogen made by
|
granlosa cells
|
|
|
FSH axn in female
|
stim androstenedione -> testosterone -> 17b-estradiol
|
|
|
FSH & LH fx on ovaries 4
|
steroidogenesis, follicular development past antral stage, ovulation, luteinization
|
|
|
estrogen axn 6
|
mature/maintain vagina->uterus, female 2o sex characteristics, breast development, prolif granulosa, maintain preg, lower uterine contraction threshold, stim PRL
|
|
|
hormone of follicular phase
|
estrogen
|
|
|
hormone of midcycle
|
estrogen
|
|
|
hormone of luteal phase
|
estrogen & progesterone
|
|
|
progesterone axn 3
|
breast development, raise uterine contraction threshold, maintain preg
|
|
|
primordial follicle progress to
|
graafian stage
|
|
|
estradiol levels inc cause
|
uterus proliferation
|
|
|
estradiol levels inc b/c
|
LH & FSH R inc in theca & granulosa cells
|
|
|
estrogen fx on LH & FSH
|
initially neg feedback, then positive
|
|
|
regardless of cycle length, when is ovulation
|
14 days before menses
|
|
|
ovulation fx on body temp
|
inc basal body temp
|
|
|
ovulation caused by
|
burst estradiol synth -> LH surge
|
|
|
cervical changes during ovulation 2
|
less viscous, more penetrable for sperm
|
|
|
corpus luteum secrete
|
estrogen, progesterone
|
|
|
uterus during luteal phase
|
secretory
|
|
|
endometrial sloughing due to
|
abrupt dec estrogen, progesterone
|
|
|
Adrenocortical hormone synth
|
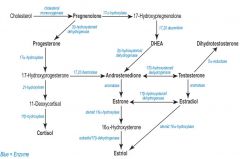
|

