![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the features of the eye.
|
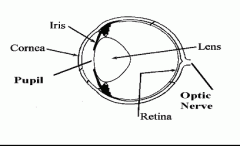
|
|
|
What is long sight?
|
When you can only see things that are far away from you.
|
|
|
What is short sight?
|
When you can only see things that are close to you.
|
|
|
How does long sight work? Draw a diagram.
|
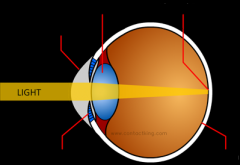
|
|
|
How does short sight work? Draw a diagram.
|
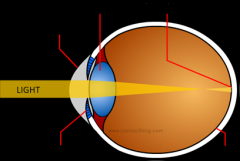
|
|
|
What about the lens of a long-sighted person causes their sight impairment?
|
Their lens is not thick enough, which means that the rays of light that enter their eye have not met before they reach the retina as they does not bend inwards enough.
|
|
|
What about the lens of a short-sighted person causes their sight impairment?
|
Their lens is not thin enough which means that the rays of light which have entered their eye are converged before they reach the retina.
|
|
|
What is light?
|
Light is a transverse wave that causes oscillations in the electric and magnetic fields as it travels.
|
|
|
How does one calculate speed?
|
Speed = Wavelength x Frequency
|
|
|
What happens when the wavelength increases? Why?
|
The frequency decreases. Because there must remain a balanced ratio.
|
|
|
Name the electromagnetic spectrum.
|
Radio waves
Microwaves Infrared radiation Visible light Ultraviolet light X-Rays Gamma Rays |
|
|
What are the colours of the electromagnetic spectrum?
|
Red
Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet |
|
|
What are the names of the subatomic particles?
|
Electrons (-1)
Protons (+1) Neutrons (n) |
|
|
What determines the atomic mass of an element?
|
No. of neutrons + no. of protons
|
|
|
What determines the atomic number of an element?
|
No. of protons
|
|
|
What determines the group of an element?
|
The number of electrons on the outer shell.
|
|
|
What is the maximum number of electrons that can be fund on the first shell and thereafter?
|
1st shell: 2,
2nd shell and thereafter: 8 |
|
|
What is the mass and charge of a proton?
|
Mass: 1
Charge: +1 |
|
|
What is the mass and charge of a neutron?
|
Mass: 1
Charge: 0 |
|
|
What is the mass and charge of an electron?
|
Mass: 0
Charge: -1 |
|
|
What are protons and neutrons categorised as?
|
Nucleons.
|
|
|
What must the number of protons equal?
|
The number of neutrons.
|
|
|
What is an isotope?
|
A variation of an element; an atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons.
|
|
|
What is strong nuclear force?
|
A force that binds the nucleons closer together.
|
|
|
What is radioactive decay?
|
When an unstable nucleus becomes stable.
|
|
|
What would happen if there was no strong nuclear force?
|
The protons in the nucleus would repel as they have the same charge.
|
|
|
Is strong nuclear force or the repellant force of the protons stronger?
|
Strong nuclear force is stronger.
|
|
|
What happens when the nucleus is too large?
|
The electric force of the protons overcomes the string nuclear force and radioactive decay occurs.
|
|
|
What is an α (alpha) particle?
|
2 protons and 2 neutrons that are ejected out of the nucleus at 0.1 x speed of light
|
|
|
What are the atomic number and atomic mass of the alpha particle? What is α (alpha) decay?
|
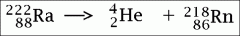
Atomic number: 2
Atomic Mass: 4 |
|
|
What is a β (beta) particle?
|
It is one electron (originally one neutron decaying into a proton and an electron).
|
|
|
What is β (beta) decay? Why is this the case?
|
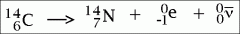
The atomic number increases by 1 because 1 neutron creates 1 proton and 1 electron. There is no change in atomic mass as the mass of a neutron is replaced by the mass of a proton.
|
|
|
What is a γ (gamma) ray?
|
It is radiation.
|
|
|
What is γ (gamma) decay?
Why is this the case? |
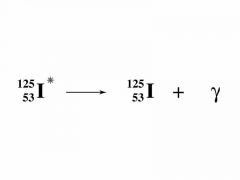
The atomic mass and number of the element remain unchanged as gamma radiation has no mass (no nucleus).
|
|
|
What is ionisation?
|
When an atom loses an electron and becomes positively charged.
|
|
|
What role does an alpha particle play in the process of ionisation?
|
The alpha particle may come into contact with an electron and thus eject the electron out of the atom.
|
|
|
What are two characteristics of radioactive decay?
|
1) It is completely random (we cannot predict when it will occur)
2) It is spontaneous (we cannot influence the chances of decay occurring) |
|
|
What is half-life?
|
Half-life is the time taken for the number of undecided nuclei to be reduced by half.
|
|
|
Does each element have it's own specific half-life?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What is the result of radioactive decay in terms of the nucleus?
|
1 mother nucleus = 1 daughter nucleus +1 particle (or just energy in the case of gamma decay).
|
|
|
What are two characteristics of nuclear fission?
|
1) It is random
2) It can be both spontaneous and induced |
|
|
What is the result of nuclear fission?
|
1 mother nucleus = 2 (or 3) daughter nuclei + particles
|
|
|
How can nuclear fission be induced?
|
A neutron can be shot at the mother nucleus which creates 2 daughter nuclei.
|
|
|
How can nuclear fission create a chain reaction?
|
If there is a critical mass of a nuclear fuel (e.g - Uranium), the neutrons created in the first nuclear fission (splitting of mother nucleus into 2 daughter nuclei) can collide with more Uranium which will cause a chain reaction to occur.
|

