![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is cardiac imaging synchronized
|
The methods used to synchronize with cardiac motion essentially rely on the electrocardiogram (ECG)
|
|
|
What are the 2 methods by which the ECG is messed up
|
Induced currents
The magneto-hydrodynamic effect |
|
|
What does the magneto-hydodynamic effect do
|
the motion of the blood (electric conductor) in the magnetic field produces an electric current which adds on to the cardiac conduction signal. This effect appears on the trace as an increase in the T wave
|
|
|
What are some causes of current induced ECG changes
|
Currents induced by gradient variation, RF pulses and breathing, which alter the ECG trace.
|
|
|
What is the result of a poor ECG signal when trying to gate a study
|
ECG signal degradation will result in a lack of synchronization, lack of diagnostic value of the ECG monitoring trace. Indeed it is vital to have an R wave that clearly stands out from the rest of the trace to be machine-detectable.
|
|
|
What r 2 types of cardiac gating
|
prospective gating
retropective gating |
|
|
What is prospective cardiac gating
|
R wave serves to trigger MRI acquisitions, which will then all occur at the same moment in the cardiac cycle: this is prospective gating
|
|
|
In Cardiac MR what is the length of the TR determined by
|
The TR is a multiple of the length of the cardiac cycle (1 or 2 cardiac cycles).
|
|
|
How long is the TR
|
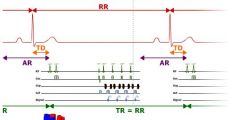
a cardiac cycle
|
|
|
What is AR
|
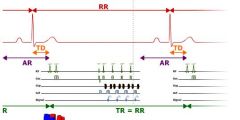
Not sure what AR stands for but its the time not being recorded
|
|
|
What is TD in this image
|
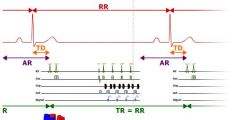
trigger delay
|
|
|
What is the TR equivalent to if it is 1 cardiac cycle
|
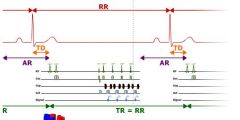
the RR interval
|
|
|
What is the benefit of cardiac imaging
|
Cardiac synchronization limits the artifacts linked to the motion of the heart and blood flow
|
|
|
What is the advantage of retrospective gating
|
The advantage of retrospective gating is the possibility of imaging the entire cardiac cycle, whereas in prospective gating, there is a lapse of time at the end of the diastole
|
|
|
What is flash artifact
|
the first image has a stronger signal, (flash artifact) because longitudinal magnetization has had an added interval in which to recuperate. Partial saturation and the balancing of longitudinal magnetization only occur in the subsequent images
|
|
|
How is flash artifact prevented
|
This drawback can be overcome by continuing to apply radiofrequency pulses and gradients during the lapse of free time at the end of the diastole, without recording a signal, to keep longitudinal magnetization in equilibrium
|
|
|
Does retrospective imaging get flash artifact
|
no, retrospective gating is not subject to flash artifacts as there is no lapse of free time in the cardiac cycle.
|
|
|
What is retrospective gating in cardiac imaging
|
Or MRI acquisition is continuous, with a simultaneous ECG recording to reorganize the data during image reconstruction: this is retrospective gating.
|
|
|
What occurs with each R wave in retrospective gating
|
With each R wave, the phase encoding gradient changes.
|
|
|
What is the advantage of retrospective cardiac gating
|
The advantage of retrospective gating is the possibility of imaging the entire cardiac cycle, whereas in prospective gating, there is a lapse of time at the end of the diastole.
|
|
|
What happens with each RR interval in retrospective gating
|
With each R wave, the phase encoding gradient changes
|
|
|
What does that mean that the phase encoding gradient changes
|
|
|
|
What are the MR sequences of choice for cardiac imaging
|
Fast MRI sequences will be the technique of choice in cardiac exploration (ultrafast spin echo, fast gradient echo)
|
|
|
What are other options which may accelerate cardiac imaging
|
Single-shot sequences
|
|
|
What is another name for dark blood imaging
|
“dark blood” contrast (PRESTO dark-blood / black-blood)
|
|
|
What is the main function of dark blood imaging
|
In morphological cardiac MRI, the main priority is to clearly delineate the heart chambers and vascular lumen
|
|
|
What is dark blood imaging a variation of
|
This imaging is based on spin echo sequences, in their fast and ultrafast variants, with prospective gating and diastole acquisition
|
|
|
What is the cause of dark blood contrast
|
contrast results from the outflow effect of the moving spins in the blood, and suppression of the blood signal prior to acquisition
|
|
|
How fast is the spin echo sequences, combined with the multiplane technique
|
can be carried out in breath-hold (5 to 15 seconds depending on the machine).
|
|
|
How many heartbeats to a slice in ultrafast sequence
|
Ultrafast spin echo sequences can acquire a slice in a single R-R interval (a heartbeat).
|

