![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is light |
Light is a form of energy that travels in rays (straight lines) away from the source producing it at 3x10^8 m/s, and is a wave-partical duality |
|
|
Self luminous |
Self luminous objects give out their own light eg. The sun |
|
|
Non luminous |
Objects that do not give out their own light eg. The moon |
|
|
Transparent |
Allows light tonpass through it and can be seen through clearly |
|
|
Translucent |
Allows light to pass through it but cannot be seen through clearly |
|
|
Opaque |
Does not alow light to pass through it |
|
|
List the electromagnetic spectrum in decreasing wavelength |
- radiowaves - microwaves - infrared radiation - Visible light - ultra violet radiation - x-rays - gamma rays |
|
|
What is ionizing radiation? |
Gamm rays, x-rays and UV rays are all forms of ionizing radiation, it is extremely damagining, can cause cancer |
|
|
Who discover X-rays? |
Wilhelm Röntgen in 1895, the first x-ray was off his wifes hand |
|
|
Draw a diagram of a light ray hitting a plane mirror |
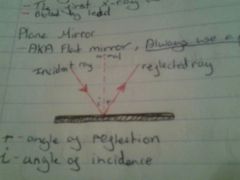
|
|
|
Name the two laws of reflection |
1. The incident ray, normal and reflected ray all lie on the same plane 2. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection (i=r) |
|
|
Define reflection, and the difference between regular and difuse reflection |
Reflection is when light bounces off of a surface Difuse reflection occurs when light bounces off regular bodies-those without smooth surfaces Regular reflection occurs when light bounces off a smooth surface, eg. Plane mirrors |
|
|
What is avirtual image? |
In a virtual image the rays of light only appear to intersect therefore the image cannot be displayed on a screen, the image is also erect as opposed to inverted |
|
|
What is a real image |
In a real image the rays of light really do intersect, so the image can be displayed on a screen, however the image is laterally inverted compared to the object |
|
|
Give three uses of plane mirrors |
- Periscopes - Wing mirrors on a car - bathroom mirrors |
|
|
Wht is the difference between a Concave mirror and a Convex mirror |

The reflective surface of a concave mirror ""caves in" and the reflective surface of a convex mirror "bulges out" |
|
|
Draw a diagram for the image of an object placed outside the centre of curvature of a concave mirror |
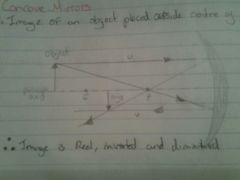
|
|
|
Draw a diagram for the image of an object placed on the centre of curvature of a concave mirror |
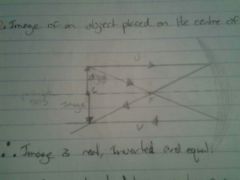
|
|
|
Draw a diagram for the image of an object placed between the centre of curvature and the focus of a concave mirror |
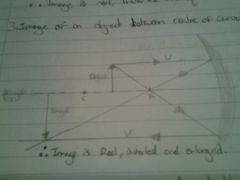
|
|
|
Draw a diagram for the image of an object placed at the focus of a concave mirror |
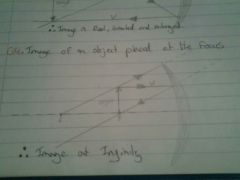
|
|
|
Draw a diagram for the image of an onject placed inside the focal length of a concave mirror |
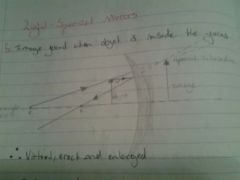
|
|
|
Give three uses of concave mirrors |
- Spotlights - reflectors in car headlights - shaving mirrors |

