![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Speed
|
Average speed is calculated in m/s using TOTAL DISTANCE/TIME
|
|
|
Velocity
|
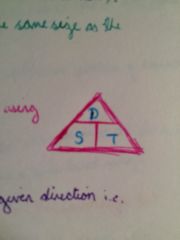
•Velocity is an objects speed in a give direction
•A change in velocity is called acceleration •Change in velocity= Change - Original Velocity |
|
|
Acceleration
|
acceleration= change in velocity/time taken
Acceleration= force (n) / mass (g) A negative acceleration (deceleration) means that the object slows down |
|
|
Resultant Force
|
•The single force that would make an object move in exactly the same way as all the original forces acting together
• If there is no resultant force, forces are balanced. It remains stationary. • If there is a resultant force, the object accelerates in the direction of the unbalanced force |
|
|
Energy transfer and Waste
|
• The Law of Conservation of Energy States that energy cannot be created or destroyed when it is transferred. All energy is usefully transferred, dissipated, or stored
• Energy=Power x Time |
|
|
Efficiency
|
Efficiency = Useful Energy / Total energy in
The answer is always a decimal less than 1 |
|
|
Refraction
|
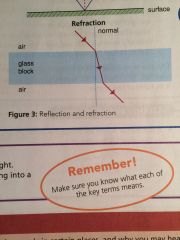
•Waves can be refracted (change direction)
• They change speed in different materials. |
|
|
Reflection
|
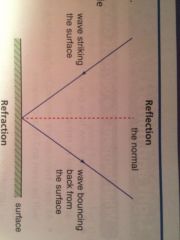
•Waves can be reflected
• The angle reflected is the same as the angle between an incoming Ray and the normal |
|
|
Diffraction
|

• Waves can be diffracted (Spread out through a gap or round an obstacle)
• Diffraction is greatest when the wavelength is about the same size as the gap or obstacle. |
|
|
Electromagnetic Spectrum
|
• Electromagnetic radiation is a continuous spectrum of transverse waves carrying energy
• Velocity can be calculated with; Speed=frequency x wavelength • The shorter the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave, the higher the frequency • Electromagnetic waves with a short wave length & high frequency carry most energy |
|
|
The National Grid
|
• Power (watts) = Voltage (v) x Current (amp)
• Step up transformers- increase the voltage to 400,000V • Increasing voltage in power cables reduces the current. Wires heat up less, so thinner cables are needed and less energy is wasted • Step down transformers in substations reduce reduce the voltage. Electricity is supplied at 230 V in homes |
|
|
Sound
|
• Vibrating objects creates sound waves are longitudes mechanical waves and cannot pass through a vacuum
• All sounds can reflected, refracted or diffracted • Loud sound waves have a large amplitudes; quiet sound waves have a small amplitude • High pitched notes have a short wavelength and high frequency; low pitched sounds have a long wavelength and low frequency. High frequencies carry more energy |
|
|
Ohms Law
|

• For some materials, voltage is proportional to current, and resistance is constant
• A voltage-current graph can be used to find the current in wire at a certain voltage. These values are used to calculate resistance. |
|
|
Resistance
|
• Resistance is calculated using;
Resistance= voltage / current |

