![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
energy that exists over a wide range is called
|
continuum
|
|
|
|
smallest quantity of any type of electromagnetic energy
|
photon
|
|
|
|
does visible light have electric and magnetic properties
|
yes ( electromagnetic)
|
|
|
|
do photons have mass
|
no
|
|
|
|
photons are energy disturbances that move through __________
|
space
|
|
|
|
the velocity of all electromagnetic radiation is
|
the speed of light
|
|
|
|
what does the electric field govern
|
interactions of electrostatic charges
|
|
|
|
what does the magnetic field govern
|
magnetic poles
|
|
|
|
variation in wave type is called a what wave
|
sine wave
|
|
|
|
sine waves are variations of what over time
|
amplitude
|
|
|
|
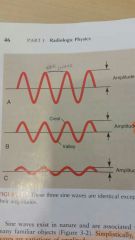
what is one half the range from crest to valley over which the sine wave varies
|
amplitude
|
|
|
|
the rate of rise and fall is
|
frequency (usually identified as cycles per second)
|
|
|
|
what is the unit of measurement for frequency
|
Hertz (Hz)
|
1 Hertz is equal to one cycle per second
|
|
|
the frequency is equal to the number of ______ or the number of ______ that pass the point of an observer per unit of time
|
crests valleys
|
|
|
|
how high or low a sine wave goes is called
|
amplitude
|
|
|
|
the number of wavelengths that pass a point of observation per second is
|
frequency
|
|
|
|
the distance from one crest to another, from one valley to another, from any point on the sine wave to the next corresponding point
|
wave length
|
|
|
|
what is not related to wavelength or frequency
|
amplitude
|
|
|
|
as the ______ is increased, the ______ is reduced
|
frequency, wavelength
|
|
|
|
what are the three wave parameters needed to describe electromagnetic energy
|
velocity, frequency, and wavelength
|
|
|
|
does a change in the velocity, frequency and wavelength affect the values of the other
|
yes ( velocity is constant)
|
|
|
|
at a given velocity, wavelength, and frequency are inversely proportional
|
true
|
|
|
|
what are the three regions most important to radiologic science in the electromagnetic spectrum
|
visible light, xray radiation, radio frequency
|
|
|
|
visible light can be deviated when it passes through one transparent medium to another, this deviation of light is called
|
refraction
|
|
|
|
what occupies the smallest segment of the electromagnetic spectrum
|
visible light (only portion that we can sense directly)
|
|
|
|
sun light contains two types of visible light what types
|
infrared and ultraviolet
|
|
|
|
radio frequency has a relatively _____ energy and relatively _____ wavelength
|
low, long
|
|
|
|
what is the only difference between x and gamma rays
|
their origin
|
|
|
|
these rays are emitted from the electron cloud of an atom and are stimulated artificially
|
x rays
|
|
|
|
come from inside the nucleus of a radioactive atom
|
gamma rays
|
|
|
|
visible light is identified by ______?
|
wavelength
|
|
|
|
radio frequency is identified by _____?
|
frequency
|
|
|
|
xrays are identified by its ______?
|
energy
|
|
|
|
a photon of x radiation and a photon of visible light are fundamentally the same except that x radiation has a much higher _______, and hence a shorter ______, than visible light
|
frequency, wavelength
|
|
|
|
the shorter the photons _____ , the the higher the photons _____
|
wavelength, energy
|
|
|
|
the reduction in intensity that results from scattering and absorption
|
attenuation
|
|
|
|
passage of an xray beam through an anatomical part with no interaction with atomic structures
|
transmission
|
|
|
|
surface that allows light to be transmitted but greatly alters and reduces its intensity
|
translucent
|
|
|
|
surface that allows light to be permitted almost unaltered
|
transparent
|
|
|
|
transfer of energy from an electromagnetic field to matter
|
absorption
|
|
|
|
when light is absorbed the energy deposited reappears as
|
heat
|
|
|
|
what are three degrees of interaction between light and an absorbing material
|
transparency, translucency, and opacity
|
|
|
|
glass is roughened with sand paper, light is still transmitted through the glass but its greatly scattered and reduced in intensity
|
translucent
|
|
|
|
glass is painted black and no light can pass through
|
opaque
|
|
|
|
structures that absorb xrays are called
|
radiopaque
|
|
|
|
structures that transmit xrays are called
|
radiolucent
|
|
|
|
law that states that the intensity of radiation at a location is inversely proportional to the square of its distance from the source of radiation
|
inverse square law
|
|
|
|
matter can neither be created or destroyed what law is this
|
law of conservation of matter
|
|
|
|
energy can neither be created nor destroyed what law is this
|
law of conservation of energy
|
|
|
|
the longer the wavelength of _______ energy. the lower the energy of each _____
|
electromagnetic, photon
|
|
|
|
two glands attached to reach lateral thyroid lobe
|
parathyroid glands
|
|
|
|
located inferior to the thyroid gland
|
thymus
|
|
|
|
which bronchus is wider, shorter, more vertical, more likely to clog from foods particles and foreign objects
|
right primary bronchus
|
|
|
|
which bronchus is smaller in diameter, twice as long, more horizontal,
|
left primary bronchus
|
|
|
|
specific prominence or ridge, where it divides into right and left bronchi
|
Carina
|
|
|
|
how many lobes and bronchus does the right lung have
|
3
|
|
|
|
how many lobes and bronchus does the left lobe have
|
2
|
|
|
|
what is the light spongy highly elastic substance of the lung called
|
parenchyma
|
|

