![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Photon
|
Small packet of light energy
Has wave and particle properties Moves very fast in a straight line Sun gives light so there is no need for a medium or material Can't be measured Transferred by radiation |
|
|
Visible light spectrum
|
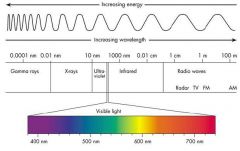
VL is seen as white but is all colors together (ROY G BIV)
Long wave length = high frequency (slower) |
|
|
Luminous
Non-luminous |
Must get hot to give off light
Produces light by reflecting light rays |
|
|
Reflection
|
The bouncing back of light rays from a reflective surface
|
|
|
Light rays
|
Light passes through transparent objects
Light can go through or around translucent objects Opaque objects absorb or reflect light |
|
|
Colour
|
Wave lengths being reflected and absorbed
|
|
|
Mirrors
|
Transparent glass with reflective metal behind it
|
|
|
The law of reflection
|
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal are all on the same plain |
|
|
Specular reflection
|
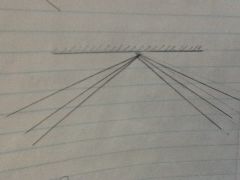
Reflection of light off a smooth surface (mirror)
|
|
|
Diffuse reflection
|
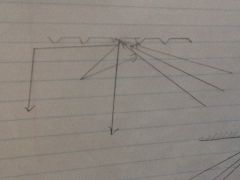
Reflection of light off an irregular or dull surface (wavy lake)
|
|
|
Locating images in a plain mirror
|
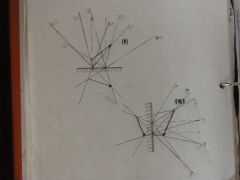
|
|
|
Curved mirrors
|
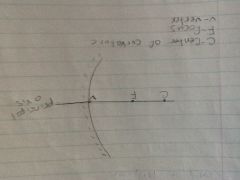
|
|

|
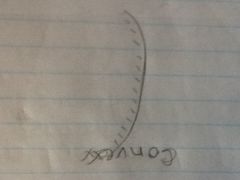
|
|
|
Salt
|
Size
Attitude Location Type |
|
|
Refraction
|
The bending or change of light direction when it travels from one medium to another
|
|
|
Rules of refraction
|
1) incident ray, refracted ray, and normal are on the same plane. Incident ray and refracted ray are on opposite sides of the line that divides the two medium
2) light bends towards the normal when the speed of light is less then the first medium and bends away when the second medium I'd greater then the first |
|
|
Critical angle
|
The minimum angle all light will be reflected
|
|
|
Ray diagrams for refraction
|

|
|

The flattened sun
|
When the sun is closer to the horizon the light slowest to the bottom is refracted more then the top
|
|
|
Mirage
|
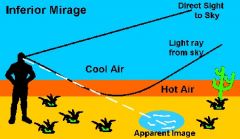
|
|

Rainbows
|
Light enters a rain drop and white light separates in to the seven colors of the rainbow
*you can only see a rainbow if the sun is behind you |
|
|
Dispersion
|
The separation of white light into the seven colors of the rainbow (ROY G BIV)
|
|
|
Rules for converging lenses
|
A ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted through the principal focus
A ray through the secondary principal focus is refracted parallel to the principal axis A ray through the optical center continues straight without being refracted |
|
|
Rules for diverging lenses
|
A ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted as it it had come through the principal axis
A ray that appears to press through the principal focus is refracted parallel to the principal axis A ray through the optical center continues straight through on its path |
|
|
incandescence
|
production of light as a result of high temperature
ex. stove, incandescent light bulbs |
|
|
electric discharge
|
the process of producing light by passing an electric current through gas
ex. lightning, neon glow signs |
|
|
phosphorescence
|
ultra violet light is absorbed and then visible light is emitted per a period of time
ex. glow in the dark stickers, glow watches |
|
|
fluorescence
|
immediate emission of visible light because ultra violet light was absorbed
ex. brightening laundry detergent, highlighters, florescent lights |
|
|
chemiluminescence
|
the production of light as a result of of a chemical reaction with little or no heat
ex. glow sticks |
|
|
bioluminescence
|
visible light in a living organism because of a chemical reaction
ex. glow worms, fireflies, angler fish |
|
|
triboluminescence
|
emission of light due to friction
ex. candied or plain hard sugar broken in the dark |

