![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
how do fast neutrons dissipate energy in tissue?
|
elastic collisions with hydrogen nuclei
|
|
|
What is the attenuation of a 6MV beam (per cm)?
|
3.5% per cm
|
|
|
What is the difference between FDD and TMR?
|
TMR represents the attenuation of d-cm of tissue, while FDD represents attenuation and inverse square falloff between dmax and depth d
|
|
|
The maximum distance an electron can travel in tissue can be approximated by
|
the value of its energy (in MeV)/2 cm
|
|
|
Which process produces clinical electrons in a medical linear accelerator?
|
Thermoionic emission
|
|
|
What is the wavelength of a photon capable of ionization?
|
0.1 um
|
|
|
The energy of the x-rays exiting the head of a linear accelerator can be changed by
|
changing the amplitude of the electric field of the microwaves in the waveguide
|
|
|
Excess risk per Gy of childhood cancer following in utero exposure to x-rays is
|
6%
(although I've seen other estimates are as high as 14%) |
|
|
How do Gy and Sv relate?
|
Sv = Gy x W (quality factor)
|
|
|
A Lucite screen is placed in front of patients during total body irradiation procedures to:
|
increase superficial dose (it produces low energy scatter)
|
|
|
How much dose should you limit a pacemaker to?
|
2 Gy
|
|
|
According to AAPM TG-51, electron beam quality is characterized by
|
depth at which the absorbed dose falls to 50% (R50) of its maximum value.
|
|
|
What is the use factor?
|
use factor is defined as the fraction of time the x-ray falls on a given barrier
|
|
|
What are the dose limits for controled and uncontrolled areas outside a treatment vault?
|
controlled (P = 0.1 mSv/wk) or uncontrolled (P = 0.02 mSv/wk)
|
|
|
How do KERMA and absorbed dose quantities vary beyond the depth of maximum dose?
|
Both dose and KERMA fall off equally (and kerma is slightly lower)
|
|
|
IGRT refers to imaging ____ treatment
|
during
|
|
|
What happens to the angle in which isodose lines are tilted due to the presence of a wedge in a photon beam as a function of depth?
|
decreases. The presence of scattered radiation decreases with increasing depth in a phantom, thus causing the angle in which isodose lines are tilted to decrease.
|
|
|
According to AAPM TG 51, a thin lead sheet should be used in the calibration of an x-ray beam to determine the depth dose curve for all photon energies greater than
|
10 MV
|
|
|
What does the profile of a 20-MeV electron beam look like?
|
For high-energy electrons, the low isodose levels bulge out, whereas the high isodose levels laterally constrict.
|
|
|
How does using the wrong beam energy affect the dose delivered (what is the % error)?
|
~1.5% per cm
|
|
|
How does changing the setup distance (accidentally using SSD instead of SAD) affect the dose delivered (what is the % error)?
|
2% per cm
|
|
|
What is an issue with using film for dosimetry at low energies?
|
Overresponds because of the high Z silver (Z=47)
|
|
|
How does GafChromic film differ from radiographic film?
|
No chemical processing required
|
|
|
The anisotropy function in the brachytherapy dose calculation for a line source accounts for the difference in the dose around the source due to
|
self-absorption
|
|
|
According to the NRC, a female radiation worker is considered pregnant when she
|
when she declares her pregnancy in writing to her employer
|
|
|
How do protons usually interact with the patient to produce a biological effect?
|
Direct ionization (not by compton)
|
|
|
What is the typical dose rate of an 192Ir source?
|
5-10 Ci (3-8 Gy/min)
Remember HDR is 12 Gy per HOUR |
|
|
For a 10 MV photon beam, what is the attenuation per cm of water?
|
about 3%
|
|
|
the surface dose for a 9-MeV beam is in what percentage range of the maximum absorbed dose, dmax?
|
80-100%
|
|
|
According to the NRC, the annual total effective dose limit to an individual member of the general public is
|
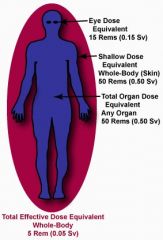
1 mSv (2% of the annual occupational limit)
|
|
|
Neutrons may interact within the medium they are traversing by
|
the Knockout reaction
|
|
|
Which type of ionization chamber is best for measuring surface dose?
|
parallel plate
|
|
|
What change in air pressure will result in a 1% change in the ionization chamber reading?
|
7 mm Hg
k (correction factor) proportional to T and 1/P |
|
|
The exposure rate limit to an unposted, unrestricted radiation area from a temporary implant must be limited to
|
2 mR/hr (0.02 mSv/hr)
|
|
|
Which of the following personnel must be present during an HDR procedure after the procedure begins?
|
Any approved MD trained in HDR procedures and the authorized HDR medical physicist
|
|
|
One Hounsfield unit represents what percent change in the linear attenuation coefficient of water?
|
0.1%
|
|
|
The International Commission on Radiation Units (ICRU) defines a HDR as
|
>12 Gy/hr.
|
|
|
For 6 MV beams what are the relative contributions of attenuation and inverse square law for radiation falloff?
|
2% per cm for inverse square law
3% per cm for attenuation |
|
|
What is the energy of an Auger electron?
|
EAuger = ETransition - EB = (69.5 keV – 11 keV) – 11 keV = 47.5 keV
|
|
|
Which decay pathways is dependent on the amount of energy available for decay?
|
positron: an energy equivalent to twice the rest mass of an electron (2m0c2 = 1.022 MeV) must be available for positron emission to occur.
|
|
|
What do physicists mean when they talk about workload of a linac?
|
The number of MU's used
|
|
|
For a 6-MV x-ray beam, what is the most appropriate specification for flatness in the radial and transverse directions?
|
Within +/-3% over 80% of the maximum field size at a depth of 10 cm
|
|
|
For a 6-MV x-ray beam, what is the most appropriate specification for symmetry in the radial and transverse directions?
|
Within +/-2% over 80% of the maximum field size at a depth of 10 cm
|
|
|
How many mrem in a mSv?
|
100
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a circulator in a linear accelerator?
|
Absorb reflected microwaves
|
|
|
What property of a radiation source for brachytherapy makes it more anisotropic?
|
Low energy - I125 has anisotropy for this reason
|
|
|
A measurement is performed using an air ionization chamber. An increase in 3°C has what effect on percent change in the reading?
|
-1%
|
|
|
Task Group No. 43 (TG-43) dose calculation formalism can be applied to which type of treatment?
|
Small encapsulated sources
|
|
|
Which type of ionizing radiation is produced when low-energy (thermal) neutrons bombard a boron-containing compound during boron-neutron capture therapy?
|
Alpha particles and gammas (0.48 MeV)
|
|
|
What is the conversion of Kelvin to Celcius
|
K = C + 273
|
|
|
What property allows for deeper penetration of ultrasound waves?
|
Low wavelength (but low wavelength is also low res)
|
|
|
Attenuation and inverse square: What do TMR and PDD account for?
|
TMR: attenuation
PDD: attenuation and inverse square |
|
|
The average surface anterior air kerma rate at the symphysis pubis from patients receiving 1-125 seed implantation in the prostate is about:
|
25 uGy/h
|
|
|
In the shielding formula B = W·UT/d 2 the symbol U represents:
|
The fraction of the total machine workload during which the beam is pointed at the barrier in question.
|
|
|
How does I125 decay?
|
Iodine-125 decays by electron capture to an excited state of 125Te. From this it decays to the ground state by emission of 35.5 keV gammas. Internal conversion gives rise to characteristic x-rays that have energies in the range of 27-35 keV
|
|
|
In an xray tube, do electrons travel from cathode or anode?
|
cathode to anode
|
|
|
Neutrons have a higher Quality Factor than electrons because:
|
They transfer energy to low energy protons, which have a high LET.
|
|
|
What are the units for exposure?
|
rotentgen (R)
Si unit is C/kg |
|
|
How often must ion chambers and electrometers be calibrated?
|
every 2 years.
|
|
|
How do you calculate the wedge angle given some hinge angle?
|
90-(hinge/2)
|
|
|
How do you approximate dose to fetus in a pregnant patient getting RT?
|
at 10-20 cm distance from the fetus at 10 cm depth the dose is 0.6-2% of the dose at beam axis
|
|
|
Average dose to a member of the U.S. population from natural background radiation (excluding radon).
|
1 mSv
|
|
|
Average dose to a member of the U.S. population from medical x-rays.
|
0.4 mSv
|
|
|
What is the possitioning error after IGRT?
|
1-5 mm
|
|
|
Can paterson-parker tables be used for seeds of equal activities?
|
no - designed for Ra needles with lower activity at the center
|
|
|
What are the new guidelines for when a patient with permanent brachy seeds can be released?
|
When the expected total effective dose to people around the patient will be < 5 mSv
|

