![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ohms Law |
Ohms Law states that when the physical factors remain constant voltage is proportional to current in a wire |
|
|
How to reverse the effect of a thermistor as a potential divider |
Measure the voltage over the other resistor instead, or use the other type of thermistor |
|
|
Resistance equation |
V/I=R V=IR I=V/R |
|
|
Kirchoff's first law |
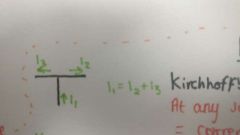
At any junction (node) the Σcurrent'in' = Σcurrent'out' |
|
|
Kirchoff's second law |
ΣP.D's in a closed circuit = 0
Or put another way
Σemf's = ΣP.D drops |
|
|
Coulomb Definition |
1 Coulomb is the amount of charge which flows past a point when 1A flows for 1 second Q=Ixt |
|
|
Resistance Definition |
Resistance is the ratio of voltage to current. It is the limiting factor for the current, it limits the flow of current through a point R=V/I |
|
|
Resistivity definition |
A measure of the resisting power of a material of a uniform (constant) cross sectional area per metre of length R=ρl/A ρ=RA/l |
|
|
Potential Difference |
The difference in potential electrical energy between two point shows the amount of energy the charge is losing or gaining Voltage = Work done ÷ Charge Units (V) ( J) (c) |
|
|
Power definition |
Power is the rate energy is transfered Power = Work done ÷ Time (w) ( J) (s) |
|
|
Superconductor |

A superconductor is a wire or component made of a material that has a zero resistivity below a certain temperature, called its critical temperature. |

