![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are waves caused by? |
Vibrations |
|
|
What is the difference between mechanical and electromagnetic waves? |
Mechanical waves need a medium |
|
|
What is amplitude? |
The maximum displacement of a wave from the average point. |
|
|
What is one wavelength in degrees and radians? |
360 degrees or 2pi radians |
|
|
What is one time period, half a time period and a quarter time period in degrees and radians? |
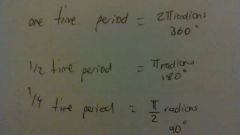
|
|
|
What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves? |
Longitudinal = parallel Transverse = perpendicular |
|
|
What is polarisation? |
Limiting a wave to one directional plane |
|
|
Give examples of practical uses of polarisation |
Fishermen to reduce water glare to see fish. Skiiers to reduce snow glare to see better. |
|
|
What happens when two polarising filters are are placed with their planes perpendicular? |
No light is observed |
|
|
What is superposition? |
When two or more waves meet the displacements are added |
|
|
Where are nodes and antinodes located on a stationary wave? |
Antinodes are the maximum displacements and nodes are the parts where the waves meet. |
|
|
Compare the amplitude of different particles in progressive and stationary waves. |
Progressive - same amplitude depending on time. Stationary - maximum displacement depends on the position of the waves. |
|
|
Compare the phase difference between two particles on progressive and stationary waves. |
Progressive - exactly the same between one cycle and the next Stationary - Dependent on the position of the waves. |
|
|
What is the equation for the speed of a wave moving along a stretched string? |
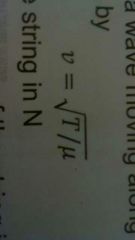
|
|
|
What is the equation for the first harmonic of a string? |
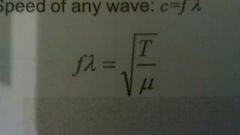
|
|
|
What is the equation for fringe separation? |
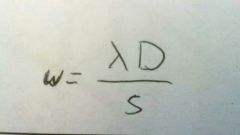
Fringe separation = (wavelength X perpendicular distance from screen to slits) / distance between slits |
|
|
What is the diffraction grating formula derivation? |
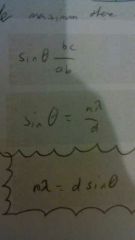
|
|
|
What is monochromatic light? |
Light of a single wavelength |
|
|
Why do optical fibres have cladding? |
To increase the critical angle within the core fibre. To prevent adjacent fibres from touching. |
|
|
What is constructive interference? |
Positive and negative displacements add to create a bigger resultant wave. |
|
|
What is destructive interference? |
Waves that are out of phase add displacements and produce a smaller resultant wave. If the waves are in antiphase there will be no resultant displacement. |
|
|
What is uncertainty? |
+ or - 1/2 of the smallest scald division. |
|
|
What is the equation for specific charge? |
Charge/Mass |
|
|
What is the unit for specific charge? |
C/kg |
|
|
Explain how a stationary wave is produced on a plucked string. |
There are two waves traveling in opposite directions. Because of reflection at the end of the string. The two waves interfere and superimpose. |
|
|
What is E=hf? |
The energy of a photon = plancks constant X frequency |
|
|
What is plancks constant? |
6.63x10^-34 Js |
|
|
What are the derivations of E =hf? |

|
|
|
What is the name given to the electrons antiparticle? |
Positron |
|
|
What happens when a particle and an antiparticle meet? |
They annihilate and two photons are produced. |
|
|
What is an electron volt? |
1.6x10^-19 |
|
|
What is specific charge? |
Charge/Mass |

