![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the Bones of the Skull
|
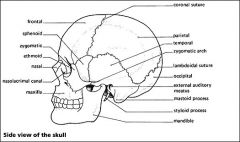
-Frontal Bone-Lacrimal Bone-Nasal Bone-Maxilla- Zygomatic Bone-Mandible-Temporal Bone-Parietal Bone-Occipital Bone-Mastoid Process
|
|
|
What are fontanels?
|
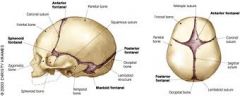
Areas of the skull that have not closed in newborns.
-Anterior: Diamond shaped and closes between 4 and 26 months -Posterior: Triangle shaped and closes by 2 months -normal-soft/flat -full, bulging, or sunken |
|
|
What are the important muscles of the face?
|
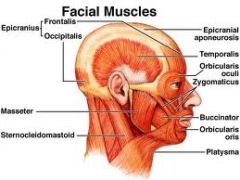
Masseter, Temporalis, Nasolabial folds, sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, Palpupil fissure (measure when lips are closed)
|
|
|
Structures of the external eye
|
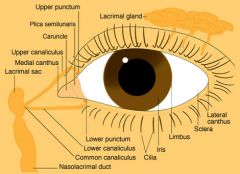
-Palpebral Fissure (space between upper and lower lid)
-Pupil -Sclera -Limbus -Canthus -Caruncle |
|
|
What should you consider when examining a child's head?
|
Did the mother drink alcohol?
What the birth vaginal? Did the head grow and fontanels close on schedule? At what age did the baby achieve head control? |
|
|
What should you look for during inspection and palpation of the head, face and scalp?
|
-Symmetry
-general size and shape -quantity and distribution of hair -lice? -normocephalic: normal size -macrocephaly: >90% size -caused by hydrocephaly -microcephaly: < 10% size -caused by chromosomal abnormalities, intrauterine infection, maternal drug/alcohol use |
|
|
What is acromegaly?
|
Pituitary abnormality that causes brow and jaw prominence. Soft tissue is enlarged
|
|
|
What is characteristic of fetal alcohol syndrome?
|
thin upper lip
|
|
|
What is Cranial Nerve VII and what does it mediate?
|
Facial Nerve
-Mediates the facial muscles -expression should be symmetrical -palpebral fissures should be equal bilaterally -nasolabial folds should be symmetric |
|
|
What is the Tarsal Plate of the Eye?
|
The Connective Tissue that gives the eye its shape.
|
|
|
What is the Meibomian glands of the eye?>
|
They give oil to the eye and an air tight seal
|
|
|
What is the Bulbar conjunctiva?
What is the Palpebral conjunctiva? |
PC: lines the lid
BC: lines the cornea -with conjunctivitis the conjunctiva looks swollen and the Bulbar moves away |
|
|
What is the Tarsal Plate of the Eye?
|
The Connective Tissue that gives the eye its shape.
|
|
|
What is the Meibomian glands of the eye?>
|
They give oil to the eye and an air tight seal
|
|
|
What is the Bulbar conjunctiva?
What is the Palpebral conjunctiva? |
PC: lines the lid
BC: lines the cornea -with conjunctivitis the conjunctiva looks swollen and the Bulbar moves away |
|
|
What is the Lacrimal Apparatus?
|
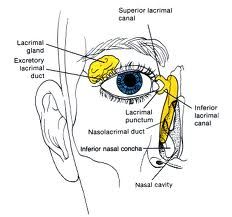
-Provides constant irrigation
-Secretes tears which flow across the eye and drain into the puncta -Tears then drain into the nasolacrimal sac and then to the nose |
|
|
What is the internal eye anatomy?
|
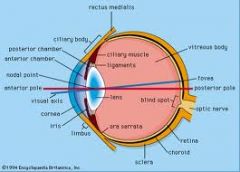
Three layers
-Sclera -Choroid -Retina Ciliary Body Anterior Compartment Posterior Compartment |
|
|
What should you be able to see with an opthalmoscope?
|
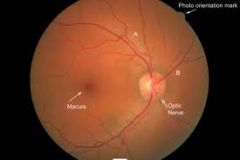
-Four sets of retinal vessels
-Retinal field and background should be clear -Optic disk should be bright yellow and is always on the nasal side -Macula is the same size as the optic disk and about 2 diameters away |
|
|
What is our visual field limited by?
|
Our eyebrows, cheeks and the side of our eyes
|
|
|
What is binocular and monocular vision?
|
Binocular: looking straight ahead
Monocular: looking sideways |
|
|
How is an image seen on the receptors?
|
upside down and reversed
|
|
|
Where do visual fibers cross?
|
The optic chiasm
|
|
|
Where does a visual impulse have to travel to be interpreted by the brain?
|
Conducted through the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract on each side and then through a curving tract called the optic radiation
|
|
|
What are direct and consensual reflexes?
|
Direct: the pupil that is exposed to light will constrict
Consensual: the pupil not exposed to direct light will constrict along with the one exposed |
|
|
What is accommodation?
|
The adaptation of the pupils to focus on images close up or far away.
-As an image gets closer the pupils will constric |
|
|
Where should the eyelid sit?
|
the upper iris should be covered by the lid, but not the pupil
|
|
|
What is strabismus?
|
Lazy eye
|
|
|
What is the snellen test?
|
Test for visual acuity
-20/20 vision means that an object 20 feet away can be seen at 20 feet away -20/50 means that what is read at 20 ft away and person with 20/20 can read at 50ft away. |
|
|
What is myopia?
What is hyperopia? What is presbyopia? |
-Myopia: nearsighted, focal point is in front of the retina
-Hyperopia: farsighted, focal point falls behind the retina -Presbyopia: changes in the eye sight over time |
|
|
What is a possible reason for 1/3 of an eyebrow missing?
|
Thyroid problem
|
|
|
What is ptosis of the eye?
|
Drooping of the upper eyelid
|
|
|
What is anisocoria?
|
one pupil is bigger than the other
|
|
|
What test is used to determine strabismus?
|
Corneal light reflex test
|
|
|
What occurs in an optic nerve cut?
|
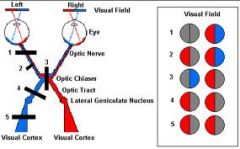
Blindness in the eye effected
#1 |
|
|
What happens in an Optic Chiasm cut?
|
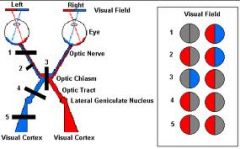
Bitemporal hemianopsia: involves the fivers crossing over to the opposite side. Since these fibers originate in the nasal half of each retina, visual loss involves the TEMPORAL half of each field.
-#3 |
|
|
Right Optic Tract Cut?
|
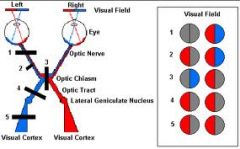
Left homonymous hemianopsia: lesion in the right optic tract interrupts fiber originating on the same side of the both eyes. Visual loss involves half of each eye. #4
|
|
|
What is Cranial Nerve I and its function?
|
Olfactory
-Smell |
|
|
What is cranial nerve II and what is its function?
|
Optic
-Visual Acuity, visual fields, and ocular fundi |
|
|
What is cranial nerve III and function?
|
Ocularmotor
-Pupillary reactions -extraocular movements Test using the 6 cardinal positions of gaze |
|
|
What is cranial nerve IV and function?
|
Trochlear
-Extraocular movements Test using 6 cardinal positions of gaze |
|
|
What is cranial nerve V and what is its function?
|
Trigeminal
-Corneal reflexes, facial sensation and jaw movements |
|
|
What is cranial nerve VI and what is its function?
|
Abducens
-Extraocular movements |
|
|
What is cranial nerve VII and what is its functions?
|
Facial
-Facial movements |
|
|
What is cranial nerve VIII and function?
|
Vestibulocochlear
-Hearing |
|
|
What is cranial nerve IX and function?
|
Glossopharyngeal
-Swallowing, rise of the palate, gag reflex |
|
|
What is cranial nerve X and function?
|
Vagus
-Swallowing, rise of the palate, gag reflex, and parasympathetic function |
|
|
What is cranial nerve XI and function?
|
Accessory Nerve
-Movement of the Trapezius muscle |
|
|
What is cranial nerve XII and function
|
Hypoglossal
-with trigeminal, vagus and facial it helps with voice and speech, tongue movements |
|
|
What function does the medial rectus have and which CN innervates it?
|
Adduction (eye moves nasally)
-Ocularmotor (III) |
|
|
What does the interior rectus do and what CN innervates it?
|
Depression (eye moves downward)
-Ocularmotor (III) |
|
|
What does the superior rectus do? What CN innervates it?
|
Elevation (eye moves upward)
Abduction -Ocularmotor (III) |
|
|
What does the Inferior Oblique do and what CN innervates it?
|
-Elevation
-Adduction -Extorsion -Ocularmotor (III) |
|
|
What does the Superior Oblique do and what CN innervates it?
|
-Depression
-Intorsion -Adduction -Trochlear (IV) |
|
|
What does the Lateral Rectus do and what CN innervates it?
|
Abduction (eye moves temporally away from the nose
-Abducens (VI) |
|
|
What is Papilledema?
|
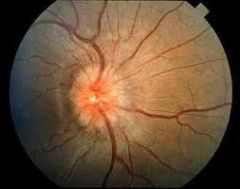
Choking of the Optic disk due to an increase in intracranial pressure.
-The disk will appear fuzzy -it will look like the disc is coming towards you. -usually accompanied by a headache or following an injury |
|
|
What is nystagmus?
|
A shuttering of the eye during the 6 cardinal fields of gaze test.
-it is normal at the end-points |

