![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is recorded on an EKG?
|
The wave of repolarization and depolarization.
|
|
|
What does a long QT interval warn of?
|
Patient if vulnerable to rapid ventricular rhythms
|
|
|
What is the span on the EKG that represents ventricular contraction?
|
QRS to the end of T.
|
|
|
What is a normal time for the PR interval?
|
< 0.2 secs
|
|
|
< 0.8 secs is normal for what portion of the EKG?
|
the ORS complex
|
|
|
What is the time of a normal QT segment?
|
< 0.4 seconds
|
|
|
When is it normal for the line on the EKG to be isoelectric?
|
-PR segment
-ST segment |
|
|
What is a possible diagnosis for a PR interval > 0.2 seconds?
|
First degree block, possibly from too much Digoxin
|
|
|
How would a Bundle of HIs problem show up on the EKG?
|
The QRS segment is > 0.8seconds
|
|
|
What do the limb heads of the EKG do?
|
They record activity in the coronal and frontal plane of the body
|
|
|
What type of configuration do leads I, II and III have?
Describe this configuration. |
Bipolar configuration
-THey have one positive pole electrode and one negative pole electrode |
|
|
What direction does energy move in the electrodes? What does this mean?
|
From negative to positive
-Will record as a positive inflection on the EKG |
|
|
What the the chest leads record?
|
Activity in the axial (horizontal plane of the body
|
|
|
Where are chest leads V1 and V2 placed?
|
4th Intercostal either side of the sternum
|
|
|
V4-V5 chest leads are placed where on the chest
|
Intercostal space, Mid-clavicular line
|
|
|
Where do we put lead V3
|
between V2 and V4
|
|
|
State where V6 chest lead placed
|
at the 5th intercostal MCL (mitral area)
|
|
|
V5 lead is placed where on the chest?
|
5th ICS between V4 and V6
|
|
|
What will electrical activity moving towards the positive record as?
|
Will be viewed as upright complexes on the monitor
|
|
|
What does a downward deflection of the EKG indicate?
|
That the electrical activity is moving from + to -
|
|
|
What occurs when Lead II is used in particular?
|
Both the flow of negative to positive impulses of the ECG machine and that of the heart are traveling in the same direction.
|
|
|
What lines on the EKG grid is darker and Why?
|
Every 5th to help you count
|
|
|
What does each small box on the EKG grid represent?
|
0.04 seconds in time
|
|
|
The large block on the EKG grid corresponds to what time?
|
0.2 seconds (5 small boxes)
|
|
|
What is the regular heart rate for an adult?
|
60-100 bpm
|
|
|
What HR described bradycardia?
|
< 60 bpm
|
|
|
What is tachycardia?
|
> 100 bpm
|
|
|
What are the methods of rate calculation?
|
-Count RR interval and large boxes
-Count RR interval and tic marks |
|
|
What are the HRs when you are using the method of counting RR interval and large boxes?
|
300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50
|
|
|
What does it mean to count RR interval and tic marks?
|
3-second tic marks - count for 6 seconds and multiply by 10
|
|
|
What is the rate that the EKG paper rolls out?
|
25mm or 1inch/second
|
|
|
What is Rhythm of HR?
|
Is the quality of timing as one heart beat is compared to the next, regardless of rate
|
|
|
How do you determine the heart rhythm?
|
By comparing the length of several adjacent RR intervals
|
|
|
How do you describe regular rhythm?
|
All RR intervals of equal length
|
|
|
What is regular irregular rhythm?
|
RR intervalsof different lengths but overall pattern is present
|
|
|
What is irregular irregular rhythm?
|
No overall pattern
|
|
|
What can cause a premature atrial beat?
|
-adrenaline
-increased sympathetic stimulation -beta-1 receptor stimulants -caffeine -cocaine -amphetamines -excess digitalis (digoxin) -hyperthyroidism |
|
|
Describe a premature atrial beat.
|
The atrial foci become irritable due to many factors
|
|
|
What are the signals on the EKG that would indicate a premature atrial beat?
|
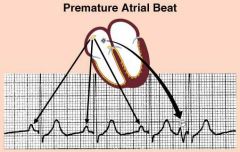
Pause following the premature atrial contraction (PAC) that is longer than the normal PP interval, but shorter than twice the normal PP interval and the different shape of the P wave
|
|
|
Does a premature atrial beat indicate a problem with the SA node?
|
No, it is working perfectly fine, but it irritable and triggers extra beats
|
|
|
What is Sinus bradycardia?
|
Normal sinus rhythm at a slower pace
|
|
|
What is sinus tachycardia?
|
Normal Sinus Rhythm at an accelerated rate
|
|
|
What is sinus tachycardia?
|
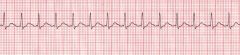
Normal Sinus Rhythm at an accelerated rate
|
|
|
Describe Sinus Arrhythmia
|
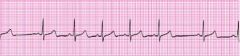
HR may be faster when inspiring. May be a normal finding
|
|
|
Describe Sinus Arrhythmia
|
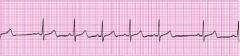
HR may be faster when inspiring. May be a normal finding
|
|
|
Describe Sinus Arrhythmia
|
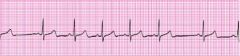
HR may be faster when inspiring. May be a normal finding
|
|
|
What occurs in an atrial flutter? How would you describe the describe the EKG?
|
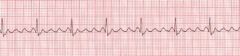
Single, strong ECTOPIC focus in an atria start to beat fast 240-360 bpm.
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is an atrial flutter?
|
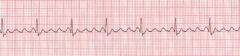
Regular Irregular
|
|
|
What does the AV node do in Atrial Flutter?
|
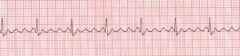
They act as the gatekeeper, blocking some of the impulses to the ventricle
|
|
|
What occurs in atrial fibrillation?
|
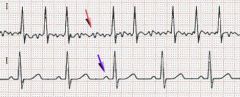
Many weak ectopic foci in the atria beat in an uncoordinated pattern, resulting in an uneven baseline of many tiny P waves.
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is atrial fibrillation?
|
Irregular Irregular
|
|
|
How fast do the atria beat in atrial fibrillation?
|
up to 300 bpm
|
|
|
How fast is the HR in atrial fibrillation? Why?
|
Can be 80 or up to 120, can have variable response from the ventricles
-Eventually the ventricles receive enough electrical stimulation to contract or they contract on their own |
|
|
What can occur due to atrial fibrillation? How is this counteracted?
|
Clots can form
-Patients go on coumadin |
|
|
Define Premature Ventricular Contractions
|
VENTRICULAR FOCI made irritable by LOW CO2 and LOW K
|
|
|
What pathologies cause premature ventricular contractions?
|
-airway obstruction
-absence of air -low O2 -reduced cardiac output -poor or absent coronary blood supply -hypokalemia |
|
|
What can Premature ventricular contractions trigger?
|
V-Tach
|
|
|
Describe the EKG of Premature Ventricular Contraction
|
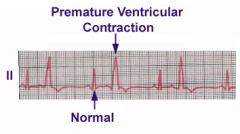
Premature beat that produces a giant ventricular complex on EKG
-QRS is WIDER! |
|
|
Describe the EKG of Premature Ventricular Contraction
|
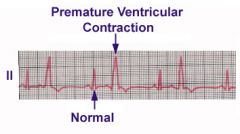
Premature beat that produces a giant ventricular complex on EKG
-QRS is WIDER! |
|
|
What is Ventricular Tachycardia?
Can it sustain life? |
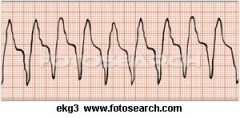
-Result of one strong Vent Ectopic Focus that hijacks the conduction system of the heart
-Cannot sustain life |
|
|
What causes ventricular fibrillation?
|
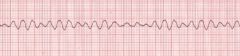
Beating of many weak ectopic foci in the ventricles, resulting in uncoordinated contractions
|
|
|
What occurs in the body during V-fib?
|
The blood cannot circulate to the brain or organs and cannot sustain life.
|
|
|
What are the conduction abnormalities?
|
-1st degree Atrioventricular Block
-2nd Degree Atrioventricular Block (Type I) -2nd Degree Atrioventricular Block (Type II) -Third Degree Ventricular Block |
|
|
What does the EKG look like in a first degree AV block?
|
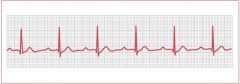
PR interval >.20 and always constant
|
|
|
What is a First Degree AV block?
|
-Increased PR interval
-The impulse within the AV node is delayed making a longer than normal pause before ventricular contraction |
|
|
How would you describe 2nd degree AV block type I?
|
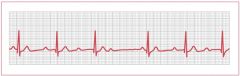
-Progressively longer PR duration until non-conducted PR
-Going, Going, GONE! |
|
|
Describe 2nd degree AV block Type II
What are the possible rhythm patterns? |
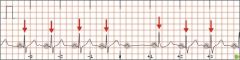
Consistently normal PR interval but then a normal, punctual P wave with no QRS Complex
-Can be 2:1 or 3:1 |
|
|
Describe a Complete or 3rd degree block
|
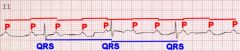
No relationship between the P waves and the QRS complex
-AV node is completely blocked -Not associated at all |
|
|
What is the sympathetic response in the heart?
|
NE binds on B1
-Increases SA node pacing -Increases force of myocardial contraction -Constricts arteries, increases BP |
|
|
What is the parasympathetic response on the heart?
|
-Ach activate cholinergic
-Decrease SA pacing -Decrease force of contraction -Dilates arteries - |
|
|
Where does an MI occur in the heart?
|
In the Coronary arteries
|
|
|
When do coronary arteries fill?
|
during Diastole
|
|
|
What is bypass surgery?
|
Take a vein from the leg and replace the blocked part of the artery.
|

