![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Integrated Rate Law - 0 Order
|
[A] = [A]o - Kt
Concentration = inital concentration - (rate constant * time (sec)) |
|
|
Integrated Rate Law - 1st Order
|
[A] = [A]0 *e^-kt
|
|
|
Integrated Rate Law - 2nd Order
|
1/[A] = kt + 1/[A]o
|
|
|
Rate = ?
In terms of concentration |
Rate = k[A]^n
Where n = the order of the reactant |
|
|
Units for 0 order reactants
|
Ms^-1
or M/s |
|
|
Units for 1st order reactants
|
s^-1
or 1/s |
|
|
Units for 2nd order reactants
|
s^-1M^-1
or 1/sM |
|
|
Rate / Concentration relationship
0 order, concentration doubles. |
Rate remains unchanged.
|
|
|
Rate / Concentration relationship
1st order, concentration doubles. |
Rate doubles
|
|
|
Rate / Concentration relationship
2nd order, concentration doubles. |
Rate quadruples
|
|
|
Arrhenius equation
|
k = Ae^-Ea/RT
Or ln(k) = ln(A) - Ea/RT |
|
|
0 Order straight line graph
|
[A] vs t
|
|
|
1st Order straight line graph
|
ln([A]) vs t
|
|
|
2nd Order straight line graph
|
1/[A] vs t
|
|
|
Straight line graph, temperature change
|
ln(k) vs 1/T(Temp)
|
|
|
Henderson Hasselbalch equation
|
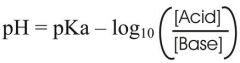
|
|
|
Factors that facilitate reactions (Kinetics)
|
Molecules must collide to react
Molecules must collide with sufficient energy Molecules must react with the correct orientation. |

