![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Translational motion:
|
The motion of a body as a whole through space
|
|
|
Which of these three equal-magnitude forces is most likely to loosen the tight bolt?
|
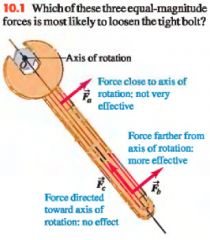
|
|
|
Torque:
|
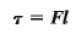
The quantitative measure of the tendency of a force to cause or change a body's rotational motion. [ moment of the force F, w/ respect to 0 as the product F1L1]
|
|
|
Line of action:
|
The line along which the force vector lies
|
|
|
The torque of a force about a pt. is the product of the force magnitude and the lever arm of the force.
|
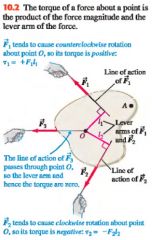
|
|
|
There are 3 ways to cal. the torque of the force:
|
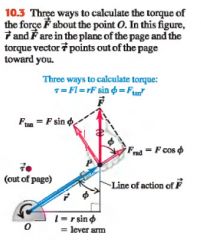
1. find the lever arm l and use T=Fl
2. determine the angle between the vectors r and F; the lever arm is rsin(angle), so T=rFsin(angle). 3. represent F in terms of radical component F(rad) along the direction of r and tangential component F(tan) at right angles, perpendicular to r. |
|
|
magnitude of torque:
|

|
|
|
Definition of torque vector:
|
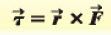
When a force F acts at a pt. having a position vector r w/respect to an origin 0, the torque T of the force w/respect to 0 is the vector quantity.
- the direction of T (torque) is perpendicular to both r & F. |
|
|
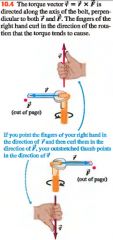
The torque vector T= r x F is directed along the axis of the bolt, perpendicular to both r & F. The fingers of the right hand curl in the direction of the rotation that the torque tends to cause.
|
|

