![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Class Agnatha |
Jawless fish |
|
|
Class Chondrichthyes |
Fish with skeleton of cartilage
Sharks |
|
|
Class Osteichthyes |
Bony ray-finned fish |
|
|
Class Amphibia |
Lack scales and claws
Frogs |
|
|
Class Reptilia |
Have dry scaly skin and lungs
Turtles |
|
|
Class Aves |
Feathers wings and legs covered in scales
Birds |
|
|
Class Mammalia |
Have hair and nourish young with milk
Bears |
|
|
Porifera |
Sponges |
|
|
Cnidarians |
Jellyfish |
|
|
Platyhelminthes |
Flatworms |
|
|
Nematodes |
Roundworms |
|
|
Annelids |
Segmented worms |
|
|
Mollusks |
Snails |
|
|
Arthropods |
Crabs, lobsters, and insects |
|
|
Echinoderms |
Starfish |
|
|
Classification |
System to name and group organisms in logical order |
|
|
Classification |
System to name and group organisms in logical order |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Classifies organisms and assigns each organism a universally known name |
|
|
Classification |
System to name and group organisms in logical order |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Classifies organisms and assigns each organism a universally known name |
|
|
Carolus Linnaeus |
Developed a method to classify organisms into groups and subgroups Each level is called a taxon |
|
|
Classification |
System to name and group organisms in logical order |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Classifies organisms and assigns each organism a universally known name |
|
|
Carolus Linnaeus |
Developed a method to classify organisms into groups and subgroups Each level is called a taxon |
|
|
Most general - Most specific |
Domain kingdom phylum class order family genus species |
|
|
Classification |
System to name and group organisms in logical order |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Classifies organisms and assigns each organism a universally known name |
|
|
Carolus Linnaeus |
Developed a method to classify organisms into groups and subgroups Each level is called a taxon |
|
|
Most general - Most specific |
Domain kingdom phylum class order family genus species |
|
|
Rules for naming an organism |
Name is italicized First word capitalized- genus Second word lower case- family |
|
|
Classification |
System to name and group organisms in logical order |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Classifies organisms and assigns each organism a universally known name |
|
|
Carolus Linnaeus |
Developed a method to classify organisms into groups and subgroups Each level is called a taxon |
|
|
Most general - Most specific |
Domain kingdom phylum class order family genus species |
|
|
Rules for naming an organism |
Name is italicized First word capitalized- genus Second word lower case- family |
|
|
Dichotomous key |
Written set of choices that leads to a name of a particular organism |
|
|
Classification |
System to name and group organisms in logical order |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Classifies organisms and assigns each organism a universally known name |
|
|
Carolus Linnaeus |
Developed a method to classify organisms into groups and subgroups Each level is called a taxon |
|
|
Most general - Most specific |
Domain kingdom phylum class order family genus species |
|
|
Rules for naming an organism |
Name is italicized First word capitalized- genus Second word lower case- family |
|
|
Dichotomous key |
Written set of choices that leads to a name of a particular organism |
|
|
Six kingdoms |
Eubacteria archaebacteria Protista fungi plantae animalia |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Smallest and most common microorganisms Single called Determined by the presence or absence of carbohydrate/peptidoglycan |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Smallest and most common microorganisms Single called Determined by the presence or absence of carbohydrate/peptidoglycan |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Single called/multicellular Larger and more complex than prokaryotes |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Smallest and most common microorganisms Single called Determined by the presence or absence of carbohydrate/peptidoglycan |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Single called/multicellular Larger and more complex than prokaryotes |
|
|
Unicellular |
Single called Typically in the kingdoms eubacteria and archaebacteria |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Smallest and most common microorganisms Single called Determined by the presence or absence of carbohydrate/peptidoglycan |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Single called/multicellular Larger and more complex than prokaryotes |
|
|
Unicellular |
Single called Typically in the kingdoms eubacteria and archaebacteria |
|
|
Multicellular |
Many called |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Smallest and most common microorganisms Single called Determined by the presence or absence of carbohydrate/peptidoglycan |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Single called/multicellular Larger and more complex than prokaryotes |
|
|
Unicellular |
Single called Typically in the kingdoms eubacteria and archaebacteria |
|
|
Multicellular |
Many called |
|
|
Autotroph & Heterotroph |
Autotrophs- make own food Heterotrophs- must consume food |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Smallest and most common microorganisms Single called Determined by the presence or absence of carbohydrate/peptidoglycan |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Single called/multicellular Larger and more complex than prokaryotes |
|
|
Unicellular |
Single called Typically in the kingdoms eubacteria and archaebacteria |
|
|
Multicellular |
Many called |
|
|
Autotroph & Heterotroph |
Autotrophs- make own food Heterotrophs- must consume food |
|
|
Ectothermic & Endothermic |
Ectothermic- organisms that rely on the outside envoi enemy to warm it's body (cold blooded) Endothermic- organisms that can maintain a constant internal temperature, homeostasis (warm blooded) |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Smallest and most common microorganisms Single called Determined by the presence or absence of carbohydrate/peptidoglycan |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Single called/multicellular Larger and more complex than prokaryotes |
|
|
Unicellular |
Single called Typically in the kingdoms eubacteria and archaebacteria |
|
|
Multicellular |
Many called |
|
|
Autotroph & Heterotroph |
Autotrophs- make own food Heterotrophs- must consume food |
|
|
Ectothermic & Endothermic |
Ectothermic- organisms that rely on the outside envoi enemy to warm it's body (cold blooded) Endothermic- organisms that can maintain a constant internal temperature, homeostasis (warm blooded) |
|
Front (Term) |
|
|
|
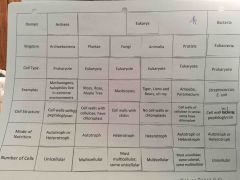
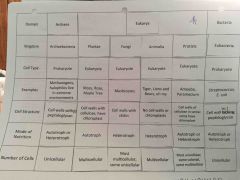
Chordates |
Made up of 7 classes Most are vertebrates (backbone)
|
|
|
Prokaryote |
Smallest and most common microorganisms Single called Determined by the presence or absence of carbohydrate/peptidoglycan |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Single called/multicellular Larger and more complex than prokaryotes |
|
|
Unicellular |
Single called Typically in the kingdoms eubacteria and archaebacteria |
|
|
Multicellular |
Many called |
|
|
Autotroph & Heterotroph |
Autotrophs- make own food Heterotrophs- must consume food |
|
|
Ectothermic & Endothermic |
Ectothermic- organisms that rely on the outside envoi enemy to warm it's body (cold blooded) Endothermic- organisms that can maintain a constant internal temperature, homeostasis (warm blooded) |
|
Front (Term) |
|
|
|
Chordates |
Made up of 7 classes Most are vertebrates (backbone)
|
|
|
Four key characteristics of chordates |
Hollow nerve chord Notochord Pharyngeal pouches for gas exchange Tail |
|
|
The two subphylas that don't have backbones but have the characteristics of a chordate |
Tonicates - lose tails as adults and become sessile filter feeders Lancelets - no true heart |
|
|
Kingdom and phylum of vertebrates |
Kingdom animalia Phylum coradata |
|
|
Virus replication - Lytic infection & Lysogenetic |
Lytic- enters cell, copies itself, and causes cell to burst Lysogenetic- inter grates DNA into host's DNA and viral genre tic information replicates |
|
|
Germ theory of disease |
Idea that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms (germs) |
|
|
Pathogen |
-Found in a sick organism and not in a healthy one (disease causing agent) -Must be isolated and grown in a lab -Cultured pathogen is placed in new host -Pathogen should be isolated from second host and should be identical to the original |
|
|
Types of organisms that cause diseases |
Viruses Bacteria Protista Worms Fungi |
|
|
Three shapes of prokaryotes |
Bacilli- rod shaped Cocci- spherical Spirilla- spiral |
|
|
Bacteria is classified by |
Cell wall structure Metabolism Respiration |
|
|
Cell wall structure Archaebacteria vs Eubacteria |
Archaebacteria doesn't contain peptidoglycan Eubacteria contains peptidoglycan |
|
|
|
|
|
Types of respiration used by prokaryotes |
Obligate aerobes: requires constant supply of oxygen Obligates anaerobes: live without oxygen Facilitative anaerobes survive with or without oxygen |
|
|
Protist is not a |
Plant animal or fungus |
|
|
Organisms in kingdom animalia are |
Eukaryotic and Heterotroph |
|
|
Characteristics of protists |
Eukaryotic Hetero or auto trophic Uni or multicellular Obtained nutrients by decomposing organic matter |
|
|
Types of protists |
Plant like - algae (red green and brown) Animal like- Protozoa |
|
|
Fungi |
Eukaryotic and Heterotrophic |
|
|
Fungi have _________ to digest food |
Extra cellular digestion |
|
|
Fungi have ______ the same as buys |
Chitin |
|
|
Fungi ______ nutrients |
Absorb |
|
|
Fungi are important for |
Decomposing food and produce antibiotics |
|
|
Asymmetrical & Symmetrical |
Asymmetrical- no symmetry Symmetrical- the same |
|
|
Two types of symmetry |
Radial- all parts of the animal are the same around the center of the body Bilateral- animal can be divided into two halves (up&down/ left&right) |
|
|
Monerans divided into two kingdoms
|
Kingdom archaebacteria and eubacteria (both contain prokaryotes) |
|
|
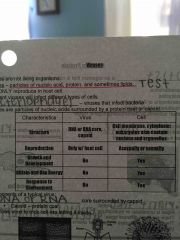
Viruses |
Non living Only reproduce in host cell |
|
|
What particles make up a virus |
Nucleic acid protein and sometimes lipids |
|
|
Fungi have ______ the same as bugs |
Chitin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Components of a typical virus |
DNA or rna core surrounded by capsid (protein coat) Allows viruses to trick cell into leering it inside |

