![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Conduction vs. convection vs. radiation |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Uniform motion |
Motion at a constant speed and direction |
|
|
|
Velocity |
Speed and direction |
M/s ➡️ |
|
|
Acceleration |
Change of velocity over time |
M/s^2 ⬅️ |
|
|
Centripetal force |
A force inward towards the center |
|
|
|
Net force |
The sum of all the forces acting in a system. Net force creates motion while no net force means no change. |
ΣF |
|
|
Weight |
A measure of the force of gravity pulling on an object with mass |
W = mg |
|
|
The second law of motion |
F = ma |
|
|
|
The third law of motion |

Back (Definition) |
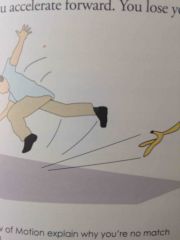
|
|
|
One ball is dropped off a cliff while another is thrown at an initial velocity of 15 m/s. Ignoring air friction, which ball will hit the ground first. |
Same time |
|
|
|
A marble and cannonball are dropped in a vacuum. Which ball will hit the ground first? |
Same time |
|
|
|
True/false The force of Earth's gravity on the moon is essentially perpendicular to the moons velocity |
True |
|
|
|
True/False The force of gravity increases as the distance increases |
False |
F = GMm/d^2 |
|
|
Law of Gravity |
Every object in the universe attracts every other object. The strength varies with the masses and the distance of the two objects |
|
|
|
General theory of relativity |
States that gravity is an effect that arises from a relationship between space, time, and matter |
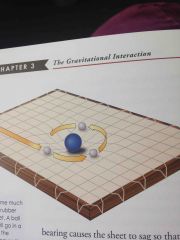
|
|
|
Electric force law |
Pairs of objects with similar charges repel and those with different charges attract. The strength varies with the net charges and the distance. |
F = kQq/d^2 |
|
|
Electrons |
Negative particle in an atom |
|
|
|
Proton |
Positive charges particle in an atom |
|
|
|
Neutron |
Neutral particle in an atom |
|
|
|
Which particle in an atom can be transferred? |
Electrons |
|
|
|
Insulator vs. conductor |
Does not allow electrons to flow through it vs. allows electrons to pass through |
|
|
|
Ferromagnetism |
When metal alloys that are attracted to magnets or are capable of being transformed into permanent magnets. |
|
|
|
Curie temperature |
The temp above which a metal is no longer magnetized |
|
|
|
Contact force |
The force between objects when they touch. Caused by the repulsion of the electrons in the objects. |
|
|
|
What does a scale measure? |
The force of contact between you and the floor. If you aren't accelerating, this force equals your weight. |
|
|
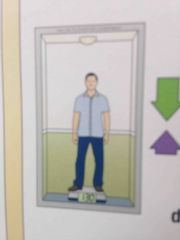
How is the reading of the scale effected when you are moving upwards in an elevator and slow down to stop? |
The reading is lower than when you are in uniform motion. |
|
|

Who experiences the greatest force? |
Neither |
|
|

Who experiences the greatest change in acceleration? |
The fly |
|
|
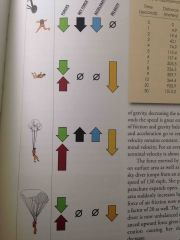
Explain what is happening here |
Answers may vary |
|
|
|
Free fall |
The act of always falling under the pure influence of gravity |
|
|

Who gon' win? |
Left? |
|
|
|
Pressure |
The force of an object divided by the area over which that force is spread. |

P = F/A |
|
|
True/false Pressure depends on depth and is less at greater depths |
False |
|
|
|
True/False Pressure is the same for all points at the same depth |
True |
|
|
|
True/False Pressure at a given depth is independent of direction |
True |
|
|
|
True/False Pressure is always parallel to the surface of a submerged object |
False |
|
|
|
Buoyant force |
The weight of the fluid that the object displaces |
|
|
|
Density |
D = m/v |
|
|
|
Why does ice float with only a small part actually above the water? |
Ice is 90% the density of liquid fresh water. This makes it so about 90% of the ice is below the surface while the remaining 10% is above the surface. |
|
|
|
Why do boats sink? |
If water gets into the boat, then the contents of the boat have the same density of the surrounding water and therefore gradually ceases to float. |
|
|
|
Explain sea breezes |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Relativity |
Motion is only defined relative to other objects |
|
|
|
Inertial frame of reference |
A state of motion that is experiencing no acceleration. |
|
|
|
Galilean relativity |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
True/False The speed of light varies depending on the perspective of the observer |
False |
Michelson-Morley experiment |
|
|
Special theory of relativity |
-Laws of nature are the same for all observers in inertial frames of reference -the speed of light is always 300,000 km/sec regardless of the device speed or observer speed |
|
|
|
Gadanken experiment |
A thought experiment |
|
|
|
Is simultaneity unaffected by high speeds? |
Ner |
|
|
|
Is time unaffected by high speeds? Why? |

Ner |
|
|
|
Length contraction |
The shortening of an object along its direction of motion as its speed approaches the speed of light, as measured by the observer not moving with the object |
|

