![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
273 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Solution?
|
A solution is defined as a mixture of two or more components forming a homogenous molecular dispersion.
|
|
|
For pharmaceutical preparations of binary solutions, what two components are need?
|
Solute: solid
Solvent: liquid |
|
|
What term is more appropriate when MIXING LIQUIDS?
|
Miscibility
|
|
|
What terms are not appropriate when MIXING LIQUIDS?
|
Solute
Solvent |
|
|
What are three types of SOLVENTS?
|
Polar
Non Polar Semi Polar |
|
|
What are two components of solution?
|
Solvent
Solute |
|
|
What is the general rule for dissolving solvents?
|
Like Dissolves Like
|
|
|
True or False: Solubility of a solute in a solvent purely depends on the nature of both solute and solvent?
|
True
|
|
|
Solubility of a non polar solute in a solvent is _____
|
Large
|
|
|
A polar solute has low solubility or insoluble in a ________ solvent?
|
Non polar
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
High Dielectric constant
Can dissolve polar solutes Break covalent bonds of potentially strong electrolytes by acid-base reaction Solvates the molecules through dipole interaction forces |
|
|
Give an example of POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
Water
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of NON POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
Low dielectric constants
Unable to decrease the attraction between ions Cannot break the covalent bonds and ionize weak electrolytes Can dissolve non polar solutes |
|
|
Give some examples of NON POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
Benzene
Mineral oil Carbon tetrachloride |
|
|
What are some characteristics of SEMI POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
Induce a certain degree of polarity in non-polar solvent
Acts as intermediate solvent to bring miscibility of liquids |
|
|
Give some examples of SEMI-POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
Ketones
Alcohols |
|
|
Give some examples of NON POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
Benzene
Mineral oil Carbon tetrachloride |
|
|
What are some characteristics of SEMI POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
Induce a certain degree of polarity in non-polar solvent
Acts as intermediate solvent to bring miscibility of liquids |
|
|
Give some examples of SEMI-POLAR SOLVENTS?
|
Ketones
Alcohols |
|
|
Which solvent is the most commonly used solvent?
|
Water
|
|
|
In pharmacy school, alcohol is refer to as?
|
Ethyl alcohol (ethanol)
|
|
|
Alcohol is miscible with what other solvents?
|
Water
Alcohol Glycerin Propylene Glycol Polyethylene glycol (PEG 400) |
|
|
Children younger than the age of 6, can have an intake of how much alcohol?
|
0.5 %
|
|
|
Characteristics of Water as a Solvent
|
No toxicity, compatible with body fluids
Compendial requirement for water for the preparation of syrups, elixirs, suspensions,m emulstions is purified water USP |
|
|
Children between the age of 6-12 years old, can have an intake of how much alcohol?
|
5%
|
|
|
Identify some PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS of GLYCERIN USP?
|
Clear
Colorless Viscous Liquid |
|
|
Glycerin USP is miscible with what solvents?
|
Water
Alcohol PG PEG 400 |
|
|
Glycerin USP can act as what?
|
Humectant
Preservative |
|
|
Individuals 12 years old or older, can have an intake of how much alcohol?
|
10%
|
|
|
Glycerin is compatible with what solvent?
|
Alcohol
Water |
|
|
True or False: Glycerin USP can be use both internally and externally?
|
True
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of PROPYLENE GLYCOL USP?
|
Clear, colorless, viscous liquid
Miscible with water, alcohol, PG, PEG 400 Served as a humectant and preservative Use both for internal and external use |
|
|
What is the main difference between PROPYLENE GLYCOL USP and POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL versus GLYCERIN?
|
Glycerin USP is compatible with alcohol and water, whereas Propylene Glycol USP and POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL are not
|
|
|
What are some PHYSICAL characteristics of POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 400?
|
Clear colorless
Odorless Viscous liquid |
|
|
Which solvent is the only one COMPATIBLE WITH ALCOHOL AND WATER? Which one is MISCIBLE WITH WATER AND ALCOHOL?
|
Glycerin USP
Glycerin USP Polyethylene glycol 400 Propylene Glycol USP |
|
|
Which solvent is the only that is ODORLESS?
|
Polyethylene glycol 400
|
|
|
Which solvents are MISCIBLE WITH WATER, GLYCERIN, PG, PEG 400?
|
Alcohol
Glycerin USP Propylene Glycol USP |
|
|
Which solvents are CLEAR, COLORLESS, AND VISCOUS LIQUID?
|
Glycerin USP
Propylene Glycol USP Polyethylene Glycol 400 |
|
|
Which solvents act as a HUMECTANT and PRESERVATIVES?
|
Glycerin UPS
Propylene Glycol USP |
|
|
What solvent is composed of EO and water?
|
Polyethylene Glycol
|
|
|
Which solvent is used for INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORMULATIONS?
|
Polyethylene glycol 400
|
|
|
Define SOLUBILITY?
|
The solubility of a substance at a given temperature is defined as the concentration of the dissolved solute when it is in equilibrium with the un-dissolved solute
|
|
|
What is the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a specific amount of solvent?
|
100 grams
|
|
|
Solubility Equation?
|
Solute (gm)/Solvent (100 gm)
|
|
|
The process of Dissolution involves?
|
Separation of Solute Molecules
Separation of Solvent Molecules Interactions between solvent and solute. |
|
|
What is the solubility theory equation?
|
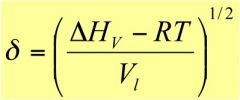
|
|
|
What are 3 types of INTERMOLECULAR FORCES?
|
Dispersive Forces
Dipolar Forces Hydrogen Bonds |
|
|
What is the difference between UNSATURATED SOLUTION and SATURATED SOLUTION?
|
Unsaturated solution contain less than the maximum amount of SOLUTE for the temperature is dissolved in the SOLVENT
Saturated solutions contains solvent that holds as much as is possible at that temperature. |
|
|
What are some characteristics of UNSATURATED SOLUTION?
|
Less than the maximum amount of solute for that temperature is dissolved in the solvent
NO SOLID REAMINS IN FLASK |
|
|
What are some characteristics of SATURATED SOLUTION?
|
Solvent holds as much solute as is possible at that temperature
UN-DISSOLVED SOLID REMAINS IN FLASK Dissolved solute is in dynamic equilibrium with solid solute particles. |
|
|
What is the main difference between SATURATED and SUPERSATURATED solutions?
|
Saturated solution contains solvent that holds as much solute as possible at the temperature.
Supersaturated solution contains solvent that holds more solute that is normally possible at that temperature. |
|
|
What are some characteristics of SUPERSATURATED SOLUTION?
|
Solvent holds more solute that is normally possible at the temperature
These solutions are UNSTABLE Crystallization can often be stimulated by adding a "seed crystal" or scratching the side of the flask. |
|
|
Look at the table?
|
Look at the lecture on Lecture 13
Slide 31 |
|
|
Dielectric constant measures what?
|
Solubility of the solvents
|
|
|
Consider an elixir made with drug A (1200 mg), ethanol (15 mL), simple syrup (40 mL), and water (40 mL). The pharmacist prepares the formulation by adding the drug to the ethanol, followed by water and finally the simple syrup.
Calculate the % w/v for drug A for this preparation? |
1.3%
Convert 1200 mg to 1.2 grams (1.2g/95mL) (100) = 1.3% |
|
|
What are some factors that can influence solubility?
|
Chemical structure
Molecular size Temperature pH Pressure Solute-Solvent Interaction |
|
|
In what ways can CHEMICAL STRUCTURE affect solubility?
|
The stronger the intermolecular attraction (Hydrogen bonding, dipole dipole, and dispersion) between solute and solvent, the more likely the solute will dissolve.
|
|
|
Ions in water have what kind intermolecular force?
|
Ion dipole
|
|
|
The presence of OH groups capable of hydrogen bonding with water enhances the ________ ______ of organic molecules?
|
Aqueous solubility
|
|
|
Between Glucose and Cyclohexane, which one is more soluble and why?
|
Glucose is more soluble in water in comparison to cyclohexane because glucose is hydrogen bonded whereas cyclohexane interact through dispersion forces.
|
|
|
What is the difference between ENDOTHERMIC PROCESS and EXOTHERMIC PROCESS?
|
Endothermic process solubility increases with the increase in temperature (direct relationship)
Exothermic process solubility decrease with the increase in temperature (indirect relationship) |
|
|
The solubility of most gases _______ with a ____________ in the temperature?
|
Decrease
Increase |
|
|
What kind of relationship does PRESSURE and SOLUBILITY have (direct or indirect)?
|
Direct
An increase in pressure increases the solubility of a gas in liquid |
|
|
How can molecular size influence solubility of a molecule?
|
The larger the molecule or the higher its molecular weight the less soluble the substance will be
|
|
|
Why would large molecule be less soluble?
|
Because large molecules are more difficult to surround with solvent molecules.
|
|
|
Branching molecules are (less or more) soluble?
|
More soluble because it will reduce the size or volume of the molecule and make it easier to solvate the molecules with solvent
|
|
|
What are some alterations that could increase the solubility of a drug?
|
Co solvent
Complexation Chemical modification (pro-drug) Solid dispersion Microemulsion |
|
|
What are some characteristics of MICRONIZATION?
|
Smaller the particle size the higher the drug reabsorption
Size reduction produces ball milling The crystalline drug may become amorphous, more solubilized, MAY DECREASE THE STABILITY, and ADJUST TIME OF MILLING. |
|
|
How can CO SOLVENT increase the solubility of a drug?
|
By disrupting the hydrophobic interactions of water at the non polar solute/water interfaces.
|
|
|
Can CO SOLVENT completely solubilized every drug?
|
Depends on the chemical structure of the drug, that is, the more non polar the solute, the greater the solubilization achieved by co solvent addition.
|
|
|
Co-solvent reduces the differences between ________ of the two components and increase the _________.
|
Polarity
Solubility |
|
|
Identify one disadvantage of using Co-solvents?
|
The use of co-solvents in the precipitation of the drug upon dilution during administration into the body, resulting in pain or tissue damage.
|
|
|
Define PRO-DRUG?
|
Pro drugs are drug that is therapeutically inactive when administered but becomes activated in the body by either chemical or enzymatic processing
|
|
|
The addition of _____ ______ can increase the aqueous solubility by increase the hydrogen bonding and other molecular interactions between the _______ and _______.
|
Polar groups
Drug Water |
|
|
Define COMPLEXATION?
|
Association of two or more molecules to form a non covalent based complex with higher solubility than the drug itself.
Structure help bind the nonpolar drug molecule inside the nonpolar cavity and encaspulate drug molecule and allow to release drug (carrier mediated transport) |
|
|
What are two types of COMPLEXATION?
|
Stacking
Inclusion |
|
|
Define SURFACTANTS or SURFACE ACTIVE?
|
Molecules and ions that are adsorbed at interfce
|
|
|
True or False: Surfactants have affinity for both polar and non polar solvents also known as AMPIPHILLE?
|
True
|
|
|
Depending on the ____ and ____ of the polar and non polar group present, the ampiphille may be predominantly _______ or ______ or ______.
|
Number
Nature Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balanced |
|
|
True or False: Some poorly soluble drugs can be solubilized in micellar solutions?
|
True
|
|
|
Why would be adjust the pH of the solvent?
|
To enhanced that stability of the drug to be dissolve.
|
|
|
What are some disadvantage of adjusting the pH of the solvent to enhance the stability of the drug?
|
There are many drugs for which pH adjustment is not an effective means of improving solubility.
Weak acidic or basic drugs may require extremes in pH that are outside accepted physiologic limits or may cause stability problems with formulation ingredients |
|
|
Define SYRUPS?
|
Syrups are concentrated aqueous preparations of sugar or sugar substitute with or without flavoring agents and medicinal susbtances
|
|
|
Between SIMPLE SYRUP, MEDICATED SYRUP, and FLAVORED SYRUP, which one uses WATER ALONE for making syrup?
|
Simple syrup
|
|
|
Between SIMPLE SYRUP, MEDICATED SYRUP, and FLAVORED SYRUP, which one contains aromatic or pleasantly flavored substances and is intended to be used as a vehicle or flavor for prescription?
|
Flavored syrup
|
|
|
Between SIMPLE SYRUP, MEDICATED SYRUP, and FLAVORED SYRUP, which one contain some added medicinal substance?
|
Medicated syrup
|
|
|
Identify the 4 Major Components of Syrup?
|
Sugar
Antimicrobial preservative Flavorants Colorants |
|
|
Between SIMPLE SYRUP, MEDICATED SYRUP, and FLAVORED SYRUP, which one uses WATER ALONE for making syrup?
|
Simple syrup
|
|
|
Between SIMPLE SYRUP, MEDICATED SYRUP, and FLAVORED SYRUP, which one contains aromatic or pleasantly flavored substances and is intended to be used as a vehicle or flavor for prescription?
|
Flavored syrup
|
|
|
Between SIMPLE SYRUP, MEDICATED SYRUP, and FLAVORED SYRUP, which one contain some added medicinal substance?
|
Medicated syrup
|
|
|
Identify the 4 Major Components of Syrup?
|
Sugar
Antimicrobial preservative Flavorants Colorants |
|
|
What are some minor components of syrups?
|
Solubilizers
Thickeners Stabilizers Active Ingredient |
|
|
What are two types of Sugar?
|
Sucrose Based
Non Sucrose Based |
|
|
Are sucrose highly or lowly WATER SOLUBLE?
|
Highly Water Soluble
|
|
|
List the characteristics of Sucrose?
|
Inherent sweetness, viscosity, and stability
Does not require addition preservative IF USED SOON When properly prepared and maintained, the syrup is inherently stable and resistant to growth of micro-organisms Pediatric formulation: chronic use could cause dental cavities Forbidden to diabetic patients |
|
|
Why does Sucrose not required additional preservative and if it is used soon?
|
Because the concentration of sucrose is so high it will be a hypertonic solution and the bacteria will shrink due to the water draining out.
|
|
|
If Syrup NF is completely saturated with sucrose
[A] More stable syrup [B] Unstable syrup [C] Resistance to crystallization [D] More favored formulation |
B. Unstable Syrup
|
|
|
If Syrup NF is completely saturated with sucrose
[A] More stable syrup [B] Unstable syrup [C] Resistance to crystallization [D] More favored formulation |
B. Unstable Syrup
|
|
|
Why is it important that the concentration of sucrose approaches but not quite reach the saturation point?
|
Does not allow the free water available for growth of micro-organisms
Help maintain the physical stability of syrups in varying temperature |
|
|
Why is it important that the concentration of sucrose approaches but not quite reach the saturation point?
|
Does not allow the free water available for growth of micro-organisms
Help maintain the physical stability of syrups in varying temperature |
|
|
Why is important not to store sucrose in a cool storage?
|
Sucrose might crystallized (nuclei formation)
|
|
|
Why is important not to store sucrose in a cool storage?
|
Sucrose might crystallized (nuclei formation)
|
|
|
Give some example of NON SUCROSE BASED SYRUP?
|
Solution of Polyol: Sorbitol
Mixture of Polyols: Sorbitol & Glycerin Others: Glycerin & Propylene Glycol, methylcellucose, hydroxy ethyl cellulose Glycerin & Propylene glycol: Glucogenetic |
|
|
Give some example of NON SUCROSE BASED SYRUP?
|
Solution of Polyol: Sorbitol
Mixture of Polyols: Sorbitol & Glycerin Others: Glycerin & Propylene Glycol, methylcellucose, hydroxy ethyl cellulose Glycerin & Propylene glycol: Glucogenetic |
|
|
What kind of syrup should you give a DIABETIC PATIENTS?
|
NON sucrose based syrups
An example is Diabetic Simple Syrup |
|
|
What kind of syrup should you give a DIABETIC PATIENTS?
|
NON sucrose based syrups
An example is Diabetic Simple Syrup |
|
|
What are three types of NON SUCROSE BASED SWEETNERS?
|
Saccharin
Aspartame Sodium Cyclamates |
|
|
What is the disadvantage of using SACCHARIN?
|
Bitter after taste
|
|
|
What is the disadvantage of using ASPARTAME?
|
Renal tubule acidosis when used in large quantities.
|
|
|
What is one CONTRAINDICATION OF USING ASPARTAME?
|
Phenylketonuria
|
|
|
What are the DISADVANTAGES OF USING SODIUM CYCLAMATES?
|
Photosensitization
Eczema and dermatitis No longer approved by FDA as sweetener due to its carcinogenic potential |
|
|
List the 3 NON SUCROSE BASED SWEETENERS, from the most sweetest to least sweetest?
|
MOST Saccharin
Aspartame LEAST Sodium Cyclamates |
|
|
Antimicrobial preservative varies with the amount of _____ ______ available for microbial growth?
|
Free Water
|
|
|
Flavorants added must be ______ soluble?
|
Water
|
|
|
What purposes does COLORANT served?
|
To enhance the appeal of the syrup, colorant must correlate with the flavor added
|
|
|
What are 4 General Requirements of Using A COLORANT?
|
Water soluble
Nonreactive with syrup components Color stable at the pH range Light stable |
|
|
What are 4 ways SYRUPS CAN BE PREPARED?
|
Solution with aid of heat
Solution by agitation Addition of sucrose to a medicated/flavored liquid Percolation |
|
|
What the steps when preparing a syrup with HEAT?
|
Sugar and Water are added together and heated until it is dissolved
Let it cooled and adjusted the volume as needed |
|
|
What is an advantage of using heat to prepare a syrup?
|
Quick preparation
|
|
|
What is a disadvantage of using heat to prepare a syrup?
|
Excessive heat could cause invert sugar resulting in microbial growth.
|
|
|
If there is presence of excessive heat, what will happen to the sugar?
|
Becomes INVERT SUGAR that breaks down in to DEXTROSE and FRUCTOSE.
|
|
|
What kind of sugar is SUCROSE?
|
Disaccharide
|
|
|
What are some possibilities if a solution is prepared with EXCESSIVE HEAT?
|
Result of INVERT SUGAR
- Sweetness of syrup is altered - Color darken - When overheated caramelization of sucrose occurs - More susceptible to microbial growth |
|
|
What is an advantage of preparing a solution by AGITATION?
|
Stability is high
|
|
|
What is a disadvantage of preparing a solution by AGITATION?
|
Time consuming
|
|
|
Identify all the steps in PERCOLATION?
|
Purified water or an aqueous solution is permitted to pass slowly through a bed of crystalline sucrose, thus dissolving it and forming a syrup.
A plug of cotton is placed in the neck of the percolator If necessary, a portion of the liquid is re-passed through the percolator to dissolve all of the sucrose. |
|
|
What method is use for the preparation of SYRUP USP?
|
Percolation
|
|
|
How should SYRUPS be STORED?
|
Well dried bottles
Tight containers Cool dry place |
|
|
At what temperature should syrups be store at? (recommended by the USP)
|
Temperature not above 25 Degree Celsius
|
|
|
What is the reason why PRESERVATIVES could be added to syrups?
|
Prevent bacterial and mold growth, particularly when the concentration of sucrose in the syrup is low.
|
|
|
The concentration of preservatives is proportional to the ____ _____.
|
Free water
|
|
|
What are the advantages of SYRUPS?
|
Pleasant tasting vehicles for medicinal substances
Patients having difficult in swallowing solid dosage forms, using syrup is a good alternative. |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of SYRUPS?
|
Stability
Difficulty in formulation of water insoluble drugs |
|
|
What is the difference between ELIXIRS and SYRUPS?
|
Elixirs are sweetened hydro-alcoholic solutions intended for oral use and are usually flavored to enhance the palatability.
Syrups areConcentrated aqueous preparations of sugar or sugar substitute with or without flavoring agents and medicinal substances. |
|
|
What are the components of ELIXIRS? components of SUGAR?
|
Elixirs
Sugar Water Alcohol Flavors SYRUPS Sugar Antimicrobial preservative Flavorants Colorants |
|
|
True or False: Elixirs should be cloudy in one phase system?
|
False: Clear one phase system
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of ELIXIRS?
|
Palatable
Alcohol 4-40% Often contain co-solvents Alcohol used to solubilized insoluble components and also acts as preservative |
|
|
What are 2 types of ELIXIRS?
|
Medicated and NON Medicated
|
|
|
How are NON Medicated Elixirs useful for Pharmacists?
|
Addition of therapeutic agent
Dilution of an existing medicated elixir |
|
|
When selecting a vehicle for NON Medicated elixirs, what should you consider?
|
Solubility and stability of drug substance in water and alcohol
|
|
|
For which VEHICLE, should the amount of alcohol be slightly above the amount needed to maintain drug solubility?
|
HYDROALCOHOLIC VEHICLE
|
|
|
What are 2 reasons why we used MEDICATED ELIXIRS?
|
Employed for therapeutic purposes
Single therapeutic agent is preferred over two or more therapeutic agents in one elixir |
|
|
What is one way we can prepared ELIXIRS?
|
Simple solution by agitation and admixture of two or more liquid ingredients
- Water soluble ingredient is dissolve in water - Alcohol soluble ingredient is dissolved in alcohol - Last, the aqueous solution is incorporated in the alcoholic solution. |
|
|
What are 4 ADVANTAGES OF ELIXIRS?
|
Less viscous and sweet compared with syrups
Able to maintain both water soluble and water insoluble ingredients in a solution Ease of preparation Formulation stability |
|
|
What are 2 DISADVANTAGES OF ELIXIRS?
|
Less efficient in masking the taste of bitter tasting drugs
Presence of alcohol |
|
|
What purpose does ALCOHOL served in liquid medications
|
Solubilize insoluble components
Preservative |
|
|
Why is alcohol incompatible with certain substances?
|
Because alcohol precipitates water soluble substance and many inorganic salts from aqueous solution
|
|
|
If an aqueous solution is added to an elixir, a partial precipitation of ingredients may occur. Why is that?
|
Reduced alcoholic content of the final preparation
|
|
|
Which of the following phrases describe the elixir dosage form?
[A] A homogeneous system [B] The solute is in a monomolecular dispersion [C] The product contains at least two components [D] All of the above [E] None of the above |
D. all of the above
|
|
|
Medicated syrups have three or more components. Which of the following could be present in a medicated syrup?
[A] A pharmacologically active chemical [B]Sucrose [C] Water [D] Artificial sweeteners & flavors [E] All of the above |
E. all of the above
|
|
|
True or False:In general, products labeled with the word elixir contain ethyl alcohol
|
True
|
|
|
True or False:Stability of Pharmaceutical syrups can be enhanced by substituting sucrose wholly or partly with some non-sucrose based sugars to prevent crystallization of syrups stored for longer period of time.
|
True
|
|
|
Test Question:In an extemporaneous dispensing facility, Simple syrup NF is kept prepared for few days as a vehicle to dispense other medications. The day after the syrup was prepared, a pharmacist noticed that the syrup was brownish. Should he dispense the medication in this syrup?
|
No. Possible because of caramelization has occurred it might be more prone to microbial growth
|
|
|
Define TINCTURES?
|
Tinctures are alcoholic or hydro-alcoholic solutions prepared from vegetable materials or from chemical substances
|
|
|
Identify components of TINCTURES?
|
Alcohol content 15-80%
Preservative Solvent Medicated tinctures taken orally include Paregoric USP or camphorated tincture of opium |
|
|
True or False: Tinctures cannot be mixed successfully with liquids too diverse in solvent character?
|
True
|
|
|
How should TINCTURE BE STORED?
|
Tightly stoppered bottles
Not exposed to high temperatures Light resistant containers |
|
|
What is the difference between TOPICAL SOLUTIONS and TOPICAL TINCTURES?
|
Topical solutions: aqueous vehicle
Topical tinctures: alcoholic vehicle |
|
|
How should topical solutions and tinctures be stored?
|
Glass containers
Plastic containers |
|
|
True or False: Topical solutions and tinctures has presence of dye and sting?
|
True
|
|
|
Define SPRAYS?
|
Sprays may be defined as aqueous or oleaginous solutions in the form of coarse droplets or as finely divided solids to be applied topically most usually to the nasopharyngeal tractor to the skin.
|
|
|
What are three types of SPRAYS?
|
Intranasally
Throat sprays Topical sprays |
|
|
What are some characteristics of SPRAY?
|
Mechanical devices to break up the particles into fine droplets.
One-way pump sprays Atomizer Solutions and sprays are mostly used as anti-infective agents All medication for external purposes: EXTERNAL USE ONLY |
|
|
Vaginal Solutions comes in 2 different forms, what are they?
|
Vaginal douche
Solution - Solutions - Powders |
|
|
In Vaginal solution, powders may be prepared in ____ or ____ _____?
|
Bulk
Unit Packages |
|
|
Douche are use as what?
|
Hygienic effects
Anti-infectives |
|
|
Rectal solutions are use in two areas, what?
|
Local Use
Systemic Use |
|
|
What are two types of ENEMAS?
|
Retention enemas
Evacuation enemas |
|
|
What are some characteristics of AROMATIC WATERS?
|
Clear aqueous solutions saturated with volatile oils or other aromatic or volatile substances
Flavor/perfuming No longer in widespread use |
|
|
What are DILUTED ACIDS?
|
Aqueous solutions prepared by diluting the corresponding concentrated acid with purified water
|
|
|
What is the difference between concentrated acids and diluted acids?
|
Concentrated acids is measure in %w/w.
Diluted acids are measured in %w/v. |
|
|
Between Concentrated acids and diluted acids, which one has LITTLE MEDICINAL USE?
|
Diluted acids
|
|
|
If you want 100 mL of diluted acid from conc. Acid, one would require 10 g of solute
|
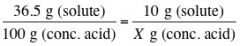
X = 27.39 g of conc. acid
|
|
|
Write down the specific gravity equation?
|
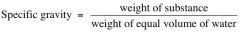
|
|
|
If sp gr is 1.17 of HCl, what is its weight?
|
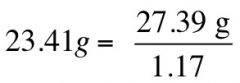
|
|
|
What are two equations you can use to for DILUTED ACIDS?
|
Specific gravity
Volume of Concentration Acid Use |
|
|
What is the equation for VOLUME CONCENTRATION ACID TO USE?
|

|
|
|
If given the same problem: if sp gr is 1.17 of HCl, what is its weight?
|
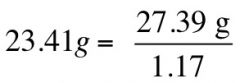
|
|
|
What are SPIRITS?
|
Spirits are alcoholic or hydro-alcoholic solutions of volatile substances
|
|
|
What are some THERAPEUTIC PURPOSES of SPIRITS?
|
Orally
Externally Inhalation |
|
|
How would you prepared SPIRITS?
|
Simple solution method
Maceration Distillation |
|
|
What is the alcoholic concentration in SPIRITS?
|
60% Alcohol
|
|
|
What are LINIMENTS?
|
Liniments are alcoholic or oleaginous solutions or emulsion of various medicinal substances intended to be rubbed on the skin.
|
|
|
What purpose does the alcoholic or hydroalcoholic content serve? Oleaginous served?
|
Hydroalcoholic
-Rubefacient -Counterirritant -Penetrating Oleaginous -Massage -Less irritating |
|
|
Lininments should not be applied to ____ _____ areas?
|
Broken skin
|
|
|
Vehicle for LINIMENTS should be selected base on what?
|
Type of action
Solubility of components External use only Light resistant containers |
|
|
What are COLLOIDIONS?
|
Colloidions are liquid preparations composed of pyroxylin dissolved in a solvent mixture usually composed of alcohol and ether with or without added medicinal substances.
|
|
|
What are some of the restriction place on COLLOIDIONS?
|
External use
Tight containers |
|
|
What are FLUID EXTRACTS?
|
Liquid preparations of vegetable drugs prepared by percolation
|
|
|
Fluids extracts are _____, ______, and self administration is possible?
|
Concentrated
Potent |
|
|
True or False: Fluid extracts are BITTER?
|
True
|
|
|
What is the difference between EXTRACTS and FLUID EXTRACTS?
|
Extracts are concentrated preparations of vegetable or animal drugs obtained by removal of the active constituents of the respective drugs with suitable menstrua
|
|
|
What are 3 forms of EXTRACTS?
|
Semi-liquid
Pilular Powdered |
|
|
What are some characteristics of EXTRACTS?
|
Potent preparations
Active constituent of crude drug Large portion of inactive ingredients |
|
|
What 2 methods of EXTRACTIONS?
|
Maceration
Percolation |
|
|
Do case study?
|
Ansel's Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems
page 381-383 |
|
|
Tonicity modifiers are influence by what?
|
Adjustment of pH of the pharmaceutical solutions that are administered to the delicate membranes
Osmotic pressure |
|
|
Define OSMOSIS?
|
The spontaneous net movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to lower water concentration
|
|
|
Identify an important factor in maintaining HOMEOSTASIS?
|
Regulating the water flow through the plasma membrane
|
|
|
True or False: Concentration of water in a solution depends upon the CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, not the NUMBER OF SOLUTE PARTICLES IN THE SOLUTION.
|
FalseConcentration of water in a solution depends upon the number of solute particles in the solution, not on their chemical composition
|
|
|
Osmotic pressure is largely influence by what factor?
|
Colligative properties
|
|
|
Define COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES?
|
Properties that depends on the number of particles in the solution
|
|
|
Define OSMOTIC PRESSURE?
|
Defined as the pressure required to offset the movement of solvent through a semi-permeable membrane from a dilute aqueous solution to a more concentrated one
|
|
|
Write down the equation for OSMOTIC PRESSURE?
|
Π V = nRT
|
|
|
What is another way to write the OSMOTIC PRESSURE using Molarity?
|
Π V = mRT
|
|
|
What is MOLARITY?
|
Molarity of the solution is the concentration of solutes in moles per liter
|
|
|
2 g of glucose, is dissolved in 150 mL of solution at 25 C. What is the π of the solution? (m.w. of glucose: 180)
|
Answer: 1.808
2g/0.15L = molarity PieVolume = nRT |
|
|
What are the differences in OSMOLAR STRENGTH: Osmoles, Osmolarity, and Osmolality?
|
OSMOLES: Number of moles of a chemical compound that contribute towards the solution’s osmotic pressure
OSMOLARITY: Number of osmoles of solute per liter of solvent (osmol/L). OSMOLALITY: Number of osmoles of solute per kilogram of solvent. |
|
|
In pharmacy, which unit is commonly use to indicated osmolar strength?
|
Milliosmole (mOsmol)
|
|
|
Write down the Milliosmole (mOsmol) formula?
|
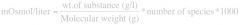
|
|
|
Calculate the mOsmol/Liter of a 0.9% NaCl solution (m.w. NaCl: 58.5 g)
|
Answer: 308 mOsmol/l
|
|
|
The USP require 4 items to state the osmolar concentration, what are they?
|
Intravenous fluids
Nutrients Electrolytes Osmotic diuretic mannitol |
|
|
What are 3 types of SOLUTION?
|
Hypertonic
Hypotonic Isotonic |
|
|
Define ISOTONIC SOLUTION?
|
The solutions having equal concentration of solute as the cells of the body.
|
|
|
What isotonic solutions commonly use for?
|
Use to replace the body fluids
|
|
|
Define HYPERTONIC SOLUTION?
|
Solutions having higher concentration of solute as compared to the cells of the body.
Water leaves a cell by osmosis, causing the cell to shrink |
|
|
What purpose does HYPERTONIC SOLUTION served?
|
Used to draw water from tissue (edema)
|
|
|
What is HYPOTONIC SOLUTIONS?
|
Solutions having lower concentration of solute as compared to the cells of the body
Water moves into the cell and cause the cell to swell up |
|
|
What HYPOTONIC SOLUTIONS use for?
|
Rehydrate tissue
|
|
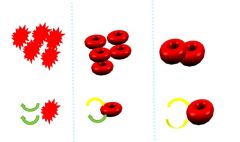
Identify which blood cell is isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic?
|
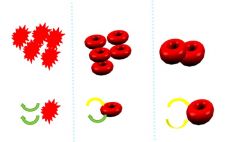
Left: hypertonic because water is moving out of the cell causing it to shrink
Middle: isotonic because of equal exchange of water coming in and out Right: hypotonic because more water is coming into the blood cell causing it to swell |
|
|
What are 4 ingredients that are used as tonicity modifiers?
|
Amino acids
Salts Weak acids Saccharides |
|
|
What are 3 types of amino acids use as TONICITY MODIFIERS?
|
Arginine
Histidine Glycine |
|
|
What the 3 salts use as TONICITY MODIFIERS?
|
Sodium chloride
Potassium chloride Sodium citrate |
|
|
Which weak acid is use as a TONICITY MODIFIER?
|
Boric acids
|
|
|
What the 3 saccharides are use as TONICITY MODIFIERS?
|
Sucrose
Glucose Mannitol |
|
|
What are 4 common methods for TONICITY ADJUSTMENT?
|
NaCl equivalent method
Freezing Point Depression Mtd White Vincent Method Sprowls Method |
|
|
Go to Lecture: Isotonic Solution and know the steps to all the method and how to calculate questions?
|
Slide 26 to Slide 41
|
|
|
The eye is an isolated and high specialized organ of _______?
|
Photoreception
|
|
|
The eye is divided in two segments, which are?
|
Anterior segment
Posterior segment |
|
|
The anterior segment of the eye is composed of what structures of the eye?
|
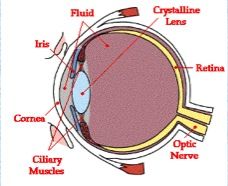
Cornea
Conjunctiva Iris Ciliary body Lens |
|
|
The posterior segment of the eye is composed of what?
|
Vitreous chamber
3 Cellular layers - Sclera - Choroid - Retina |
|
|
What are the 5 route of OCULAR DRUG DELIVERY?
|
Topical
Periocular Intraocular Transcleral Ocular iontophoresis |
|
|
Identify some factors affecting the OCULAR BIOAVAILABILITY in the PRE-CORNEAL?
|
Fluid drainage
Drug binding Conjunctival absorption Systemic absorption |
|
|
Identify some factors affecting the OCULAR BIOAVAILABILITY in the CORNEAL?
|
Hydrophilic drugs
|
|
|
What are the 3 cellular layers found in the POSTERIOR SEGMENT OF THE EYE?
|
Sclera --> outer
Choroid --> middle Retina --> inner |
|
|
Identify some factors affecting the OCULAR BIOAVAILABILITY in the POST-CORNEAL?
|
Melanin binding
Drug metabolism |
|
|
80-90% of fluid drains in the the what duct during the PRE-CORNEAL?
|
Naso-lacrymal duct
|
|
|
Drainage rate during the PRE-CORNEAL is influence by what factors?
|
Instilled volume
Viscosity pH Tonicity Drug Type |
|
|
What is the pH of tear fluid?
|
7.4
|
|
|
During the PRE-CORNEAL, drug binding to proteins (increase/decrease) the free drug concentration available for pharmacological action?
|
Decrease
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of CONJUNCTIVAL?
|
Highly VASCULARIZED mucus membrane
Highly permeable High surface area |
|
|
Between the CONJUNCTIVA and CORNEA, which one absorbed drug more?
|
Conjunctiva
|
|
|
What is the major route of entry into the systemic circulation?
|
Conjunctiva
|
|
|
What structure in the Corneal resist the passage of lipophilic drugs?
|
Corneal stroma
|
|
|
What are some strategies in penetrating the corneal stroma?
|
Liposomes
Penetration enhancers Nanoparticles |
|
|
What structure is the major barrier for hydrophilic drugs?
|
Corneal
|
|
|
Where are melanin found?
|
Iris
Ciliary body |
|
|
True or False: Melanin can affect the ocular Bioavailability?
|
True
|
|
|
What purpose does melanin served?
|
Imparts color to the eye
|
|
|
Where are most metabolic active site found?
|
Cornea
Iris Ciliary body |
|
|
How are ophthalamic drug typically delivery?
|
Topical
Systemic |
|
|
Between topical and systemic delivery, which one is considered the preferred way to achieved therapeutic levels of the drug in the eye?
|
Topical application
|
|
|
What are 4 types of topical application?
|
Solutions
Suspensions Ointments Other: includes gel, liposomes, and polymeric drug carriers |
|
|
What are some PHARMACEUTICAL REQUIREMENTS to considered for OPHTHALMIC FORMULATION?
|
Sterile
Isotonic Buffered Viscosity Ocular Bioavailability |
|
|
What are two ways to sterilized solutions?
|
Autoclaving
Filtration |
|
|
How would you maintain the sterility?
|
Preservatives
|
|
|
Identify some desirable property of an antimicrobial preservative?
|
Broad spectrum
Compatibile with other ingredients Non-toxic and non-irritant Chemical stability Rapid action |
|
|
Drug formulations topically instilled must be ISOTONIC with tears, why?
|
Because hypertonic solution could cause dehydration of corneal epithelium discomfort and irritation and hence reflex tears and reflex blinks leading to loss of drugs
|
|
|
What are some pharmaceutical requirement when considering Buffering agents?
|
Comfort
Stable Solubility Bioavailability Preservative efficacy |
|
|
True or False: Tears have buffer capacity?
|
True
|
|
|
Eyes are more likely to tolerate (alkaline or acidic solution)?
|
Alkaline solution
|
|
|
What purpose does the viscosity enhancers served?
|
Prolong the residence time in the pre-corneal area
|
|
|
What kind of polymers are found in viscosity enhancers?
|
Water soluble polymers
|
|
|
PAA and HA interacts with the mucus layer to?
|
Improve the drug retention
|
|
|
Viscosity is determine by what Equation?
|
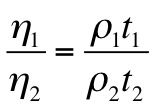
Ostwald' Viscometer
|
|
|
True or False: Suspension are lipophilic drugs
|
True
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of SUSPENSIONS?
|
Increase in duration of action
Decrease irritation due to small particles Decrease stimulation of lacrimation |
|
|
What are some advantageous of Ointments?
|
Enhance drug availability
Increase the ocular contact time |
|
|
What are some disadvantage of Ointments?
|
Greasiness
Patient in compliance |
|
|
What are some mandatory tests on finished products?
|
Leaker test
Clarity test Sterility test |
|
|
Quality control tests are conducted on ________ _____, manufacturing, and _____ _____.
|
Incoming stock
Manufacturing Finished products |
|
|
What are the steps in proper administration of ophthalmic solutions?
|
Wash hands
Inspection for any chip/crack Inspection for color, clarity, particles. If suspension the shake well before use Cap of the dropper should be removed and returned immediately |
|
|
Do all homework on Lecture Ophthalmic solution?
|
Slide 33 to Slide 38
|

