![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Molecules that collect light energy
|
Pigments
|
|
|
What colors do chlorophyll a and b absorb best?
|
Blue-violet and red
|
|
|
Main light absorbing pigment
|
Chlorophyll
|
|
|
Organisms that can make their own food
|
Autotrophs
|
|
|
Gel-filled space inside chloroplast
|
Stroma
|
|
|
What contains chlorophyll and absorbs light energy during light dependent reactions?
|
Photo systems II and I
|
|
|
Which molecule stores more than 90x the energy in an ATP molecule?
|
Glucose
|
|
|
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
|
Stroma
|
|
|
Stacks of thylakoids
|
Grana
|
|
|
Another name for light independent reactions
|
Calvin cycle
|
|
|
What are caretenoids?
|
Orange and yellow colored pigments
|
|
|
3 factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis:
|
1. Temperature
2. Light intensity 3. Water |
|
|
What pushes H+ ions from the stroma across the membrane into the thylakoid space?
|
Chemiosmosis
|
|
|
Which of the following is true about glucose?
A. Atp consists of ribose sugar, adenine, and 3 phos. groups B. ADP forms from ATP C. Used ATP is discarded by the cell as waste D. ATP provides energy for active transport cells |
A b d
|
|
|
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
|
Stroma
|
|
|
What is made during light dependent reactions and carry energy and high energy electrons?
|
Atp and nadph
|
|
|
During light dependent reactions, H+ ions build up in the _______space when ______is split.
|
Thylakoid; water
|
|
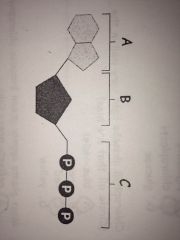
What are the parts that make up this molecule? What is this molecule?
|
Adenine, ribose, tri-phosphate chain.
ATP |
|
|
What does ATP stand for?
|
Adenosine triphosphate
|
|
|
Carbon and oxygen from ________end up as part of ________following Calvin cycle
|
Carbon dioxide; glucose
|
|
|
Proteins in living things that help chemical reactions
|
Enzymes
|
|
|
Plants gather the sun's energy with light absorbing molecules called
|
Pigments
|
|
|
How many molecules of carbon dioxide are there used to make 1 molecule of glucose?
|
6
|
|
|
Where are photosystems I and II found?
|
Thylakoid membrane
|
|
|
Why does the space inside the thylakoid membrane because positively charged during light-dependent reactions?
|
H+ ions build up in the space as water is split
|
|
|
First step of photosynthesis
|
Pigments in photosystem II absorbs light
|
|
|
Oxygen produced in light-dependent reaction
|
Is released into the atmosphere
|
|
|
Label A B and C
|
A= thylakoid
B= stroma C= granum |
|
|
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
|
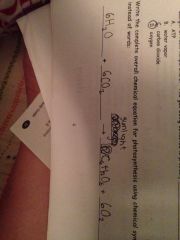
|
|
|
What is the first step of cellular respiration?
|
Glycolysis
|
|
|
Carriers for energy and high energy electrons during glycolysisw
|
NADH
|
|
|
If oxygen is not present glycolysis is followed by
|
Fermentation
|
|
|
What is the 3-carbon molecule when glucose is broken in half?
|
Pyruvic acid
|
|
|
If a reaction does not require oxygen it is
|
Anaerobic
|
|
|
How many ATP molecules are added to start glycolysis? What is the net gain?
|
Needs 2 and gains 2
|
|
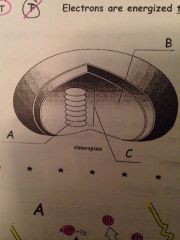
Label A B and C
|
A= thylakoid
B= stroma C= granum |
|
|
What is the formula for cellular respiration?
|
C6H12O6+ 6O2---> 6H2O+ 6CO2+ energy (ATP)
|
|
|
Another name for light independent reactions
|
Calvin cycle
|
|
|
Carbon and oxygen from ________end up as part of ________following Calvin cycle
|
Carbon dioxide; glucose
|
|
|
What is made during light dependent reactions and carry energy and high energy electrons?
|
Atp and nadph
|
|
|
Proteins in living things that help chemical reactions
|
Enzymes
|
|
|
Equation for alcoholic fermentation
|
NADH+ pyruvic acid---> 2NAD+ + 2CO2+ ethanol
|
|
|
Equation for lactic acid fermentation
|
NADH+ pyruvic acid---> 2NAD+ + lactic acid
|
|
|
Correct sequence of cellular respiration
|
Glycolysis--> Krebs cycle--> ETC
|
|
|
How many total ATP molecules are produced by 1 molecule of glucose completing cellular respiration?
|
36
|
|
|
What is produced during the Krebs cycle
|
ATP, NADH, FADH2, CO2
|
|
|
What molecule is the final acceptor at the end of the ETC?
|
Oxygen
|
|
|
The stage of cellular respiration that produces the most ATP
|
Electron transport
|
|
|
What is the 6-carbon molecule formed when acetyl-coa joins its 2 carbons to a 4-carbon molecule during the Krebs cycle?
|
Citric acid
|
|
|
Where are enzymes for ETC located?
|
Inter membrane space
|
|
|
Carbon atoms in pyruvic acid end of as what in the atmosphere following the Krebs cycle?
|
CO2
|
|
|
Folded inner membrane inside mitochondria
|
Cristae
|
|
|
This molecule reacts with pyruvic acid to release CO2 produce NADH and acetyl-CoA
|
Coenzyme-A
|
|
|
_______forms when coenzyme-A attaches to 2 carbons from pyruvic acid.
|
Acetyl-CoA
|
|
|
What is the storage form of glucose?
|
Glycogen
|
|
|
Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
|
Matrix
|
|
|
What is produced from ETC?
|
Water and ATP
NET ATP: 32-34 |
|
|
What gas is needed for ETC?
|
Oxygen
|
|
|
What is the place that is filled with H+ as electrons move down ETC?
|
Intermembrane space
|
|
|
Place where ADP and P join to make ATP
|
Matrix
|
|
|
Molecule used by cells to store and transfer energy
|
ATP
|
|
|
What happens when oxygen is present and includes glycolysis, krebs, and ETC?
|
Cellular respiration
|
|
|
High energy electron carrier produces fewer ATPs than NADH as its electrons pass through the ETC because it enters farther down the chain
|
FADH2
|
|
|
What is the atmospheric gas required for aerobic respiration?
|
Oxygen
|
|
|
The _____cycle breaks down pyruvic acid into CO2 and produces NADH, FADH2, and ATP
|
Krebs
|
|
|
Passage of H+ ions through ________________ causes it to spin and produce ATP.
|
ATP synthase
|
|
|
C6H12O6
|
Glucose
|

