![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is carbon fixation
|
the process of converting CO2 to sugars, endothermic process regulates the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere and the oceans |
|
|
what is the compensation point
|
the point at which the rate of photosynthesis and the rate of respiration is the same no net gain or loss of carbohydrates |
|
|
which have a shorter compensation period shade plants or sun plants
|
shade plants can utilise the light intensity better so reach there compensation period quicker
|
|
|
what are the enzymes used in photosynthesis
|
ATP synthase- light dependent stage, in the non-cyclic photophosphorylation stage Rubisco used in the krebs cycle |
|
|
what are in the centre of the photosystems in the thylakoid membrane |
primary pigment reaction centre chlorophyll a- p680 in photosystem 2 p700 in photosystem 1 |
|
|
Name the components of a chloroplast |
envelope thylakoids making a grana stroma circular DNA Carbohydrates that are produced photosynthesis may form starch grains |
|
|
what are the two components of the light dependent stage of photosynthesis what does each one produce |
cyclic photophosphorylation- produces ATP, uses photosystem 1(p700) non cyclic photophosphorylation, produces ATP reduced NADP, O2 |
|
|
describe the stages in non cyclic photophosphorylation
|
1)light hits photosystem 2 2)excites a pair of electrons, electrons escape but are captured by an electron carrier 3)the electrons from the photosystem are replaced by the process of photolysis 2H20= 4H+ 4E-+O2 4)electrons lose energy as they move along the electron transfer chain 5)the energy is used to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane into the thylakoid space- causes a proton gradient 6)electrons are captured by photosystem 2 7)the protons difuse back into the stroma through special channels associated with ATP synthase this causes the formation of ATP 8)finally the electrons are accepted by NADP to become reduced NADP |
|
|
draw the calvin cycle for one CO2
|
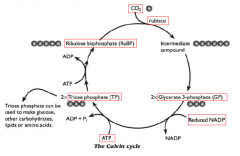
|
|
|
how many cycles of the Calvin cycle are needed to make one molecule of glucose
|
6 turns, every three turns produced one tp, two TP are needed to make one molecule of glucose
|
|
|
what is the effect of water stress on the rate of photosynthesis
|
plant roots produce abscisic acid which causes the stomata to close, leading to less CO2 entering the Calvin cycle
|

