![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
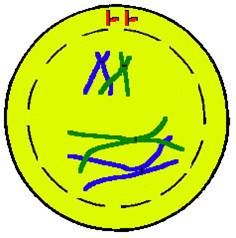
Prophase 1:
|
Chromosomes form and each chromosome pairs with its homologous chromosome; called a tetrad – four chromatids
In a tetrad, homologous chromosomes can exchange portions of their chromatids; called crossing-over Occurs at the chiasma Creates recombinant chromatids (“recombined”) Provides genetic variation – that’s how each one of us is very different from the other Sexual reproduction creates genetic variation |
|
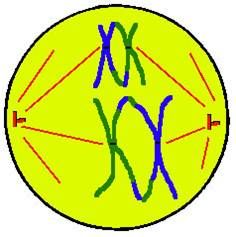
Metaphase 1:
|
Tetrads line up in the middle, equatorial plane, of the cell
|
|
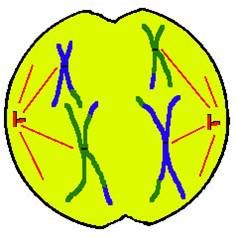
Anaphase 1:
|
Tetrads line up in the middle, equatorial plane, of the cell
|
|
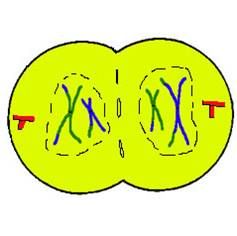
Telophase and Cytokineses 1:
|
Nuclear envelope forms
Cytokinesis occurs resulting in two daughter cells Daughter cells are NOT identical due to crossing-over in prophase I |
|
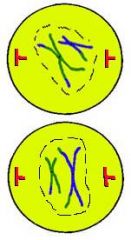
Prophase 2:
|
Chromosomes form
Nuclear envelope disappears |
|
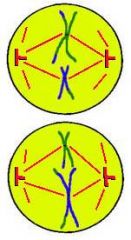
Metaphase 2:
|
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell at the equatorial plate
|
|
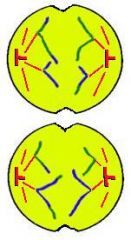
Anaphase 2:
|
Sister chromatids separate and move away from each other to opposite poles of the cell
|
|
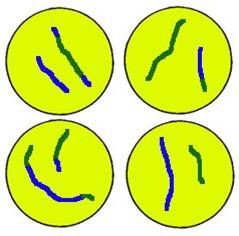
Telophase and Cytokineses 2:
|
Nuclear envelope forms
Cytokinesis occurs resulting in four genetically different gametes |

