![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do the pairs of pharyngeal arches surround? |
rostral end of foregut |
|
|
What arches are above the larynx? |
I , II , III |
|
|
What arches are below the larynx? |
IV and VI |
|
|
What is the pharyngeal groove? |
shallow external groove separating arches from adjacent arch |
|
|
What is the pharyngeal pouch? |
internal groove of pharyngeal arch |
|
|
How are the pharyngeal grooves and pouches named? |
for pharyngeal arch superior to it |
|
|
What is the pharyngeal membrane? |
membrane between each pharyngeal groove |
|
|
What cell layers are the pharyngeal arches made of? |
ectoderm - lines external surface of each arch - associated with groove middle is mesenchyme endoderm - lines deep side of each arch - associated with pouch |
|
|
Where is the mesenchyme that makes up the pharyngeal arches derived from? |
paraxial and lateral plate mesoderm and neural crest cells |
|
|
What is contained within each pharyngeal arch? |
aortic arch cartilaginous rod muscular component nerve |
|
|
What does the aortic arch come from? |
truncus arteriosus of primordial heart |
|
|
What does the cartilaginous rod form? |
skeleton of arch |
|
|
What is the nerve of the pharyngeal arch derived from? |
neuroectoderm of primordial brain |
|
|
What nerves are associated with which pharyngeal arches? |
arch I - trigeminal n. arch II - facial n. arch III - glossopharyngeal n. arch IV - pharyngeal branches and superior laryngeal n. of vagus arch VI - recurrent laryngeal n. of vagus |
|
|
What are the vascular elements associated with which arches? |
arch I - maxillary a. arch II - hyoid and stapedial aa. arch III - common carotid, internal carotid, external carotid arch IV - aortic arch between l. common carotid and l. subclavian, right subclavian arch VI - right pulmonary a. , ductus arteriosus |
|
|
What bones are associated with arch I? |
bones of face: - maxilla - zygoma - mandible - palatine - vomer - squamus part of temporal - incus - malleus |
|
|
What bones are associated with arch II? |
- styloid process - lesser horn and superior 1/2 of hyoid and stapes |
|
|
What bones are associated with arch III? |
greater horn and inferior 1/2 of body of hyoid |
|
|
What bones are associated with arch IV and arch VI? |
laryngeal cartilages |
|
|
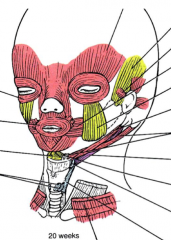
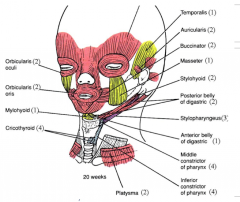
What muscles does arch I form? |
innervated by CN V3 - muscles of mastication - mylohyoid - ant. belly digastric - tensor veli palatini - tensor tympani |
|
|
What muscles form from arch II? |
innervated by CN VII - muscle of facial expression - stylohyoid - post. belly digastric - stapedius |
|
|
What muscles come from arch III? |
innervated by CN IX stylopharyngeus |
|
|
What muscles come from arch IV? |
vagus n. - levator veli palatini - palatoglossus - palatopharyngeus - salpingopharyngeus - pharyngeal constrictors - cricothyroid |
|
|
What muscles come from arch VI? |
vagus n. - intrinsic muscles of larynx EXCEPT cricothyroid |
|
|
|
|
|
Which pharyngeal groove isn't lost during development? |
first pharyngeal groove |
|
|
What does the first pharyngeal membrane become? |
tympanic membrane |
|
|
What does the first pharyngeal groove become? |
external auditory meatus |
|
|
What cell layers is the tympanic membrane derived from? |
ectoderm - skin covering outer surface mesoderm - actual membrane endoderm - skin covering inner surface |
|
|
What obliterates the caudal grooves of the pharyngeal arches? |
overgrowth of second pharyngeal arch and fusion with mesenchyme |
|
|
What happens if the pharyngeal sinus persists? |
becomes a cyst to be removed |
|
|
What causes a cervical cyst? |
failure of pharyngeal grooves 2-3 to be resorbed |
|
|
What is the clinical relevance of a cervical cyst? |
mostly benign, may become infected excision is common but must be careful |
|
|
What does the first pharyngeal pouch become? |
middle ear cavity/mastoid antrum auditory tube |
|
|
What does the second pharyngeal pouch become? |
epithelium of palatine tonsils |
|
|
What does the third pharyngeal pouch become? |
superior - inferior parathyroids inferior - thymus |
|
|
What is the function of the parathyroid gland? |
increase calcium levels in blood via parathyroid hormone |
|
|
What does the fourth pharyngeal pouch become? |
superior - superior parathyroids inferior - C- cells of thyroid |
|
|
What is the function of C-cells of the thyroid? |
secrete calcotonin to decrease calcium levels |
|
|
How does the thyroid develop? |
invagination of endoderm (foramen cecum) at midline of terminal sulcus migrates caudally until reaches larynx thyroglossal duct regresses - sometimes stays as pyramidal lobe |
|
|
What is the tongue formed by? |
contributions from pharyngeal arches I - IV |
|
|
What forms the anterior 2/3 of the adult tongue? |
medial and lateral tongue buds from 1st pharyngeal arch |
|
|
What forms the posterior 1/3 of the tongue? |
hypobranchial eminence from 2nd - 4th pharyngeal arches (mostly 3rd) |
|
|
What does the junction of the two parts of the tongue form? |
sulcus terminalis |
|
|
What forms the intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles? |
mesoderm from occipital somites |
|
|
What causes Treacher Collins syndrome? |
failure of neural crest cells to properly migrate into 1st arch |
|
|
What are symptoms of Treacher Collins syndrome? |
underdeveloped zygomatic bones mandibular hypoplasia malformed ears hearing loss no significant cognitive defect |
|
|
What does the face develop from? |
5 prominences that surround stomodeum (opening of oropharyngeal region) |
|
|
What are the prominences that make up the face? |
frontonasal prominence 2 maxillary prominences - pharyngeal arch I 2 mandibular prominences - pharyngeal arch I |
|
|
What are the thickenings on the lateral edges of the frontonasal prominence called? |
nasal placodes |
|
|
What is the nasal pit? |
depression in center of nasal placode |
|
|
What does the nasal pit form? |
anterior nasal openings and nasal cavity |
|
|
What is the lateral nasal process? |
part of nasal placode lateral to nasal pit |
|
|
What is the medial nasal process? |
part of nasal placode medial to nasal pit |
|
|
What is formed at the junction of the maxillary prominence and lateral nasal process? |
nasolacrimal furrow |
|
|
What forms the nasolacrimal duct? |
ectoderm cells from nasolacrimal furrow that form a solid rod of cells and detach from groove and sink deep to skin |
|
|
What happens if the maxillary prominence and lateral nasal process don't fuse? |
oblique facial cleft - nasolacrimal duct becomes an open groove |
|
|
What does the merging of the 2 medial nasal processes form? |
intermaxillary segment |
|
|
What is the intermaxillary segment a precursor to? |
philtrum of the lip |
|
|
What arises from a failure of the medial nasal processes to fuse? |
median cleft lip - often associated with brain anomalies |
|
|
What forms from the fusion of the intermaxillary segment with the maxillary prominences? |
upper lip and jaw architecture |
|
|
What happens if the intermaxillary segment fails to fuse with the maxillary prominences? |
cleft lip |
|
|
What happens if the mandibular and maxillary process halt fusion early? |
macrostomia - far extended mouth |
|
|
What happens if there is excessive merging of the maxillary and mandibular processes? |
microstomia - small mouth |
|
|
What does the palate develop from? |
mesenchyme tissue deep to intermaxillary segment of maxillary processes |
|
|
What forms the primary palate? |
portion from intermaxillary process |
|
|
What forms the secondary palate? |
tissue deep to maxillary process |
|
|
What forms from the intermaxillary segment? |
portion of hard palate rostral to incisive foramen source of incisor teeth |
|
|
What is the secondary palate formed from? |
two palatine shelves - extensions of maxillary prominences |
|
|
What is the nasal septum formed from? |
frontonasal prominence's underlying mesenchyme that invaginates in the midline meets secondary plates at midline |
|
|
What forms the frontonasal prominence? |
secondary plates from maxillary prominence and nasal septum |
|
|
What does incomplete fusion of the palatine shelves lead to? |
bifid uvula - incomplete fusion of soft palate OR cleft palate - incomplete fusion of some part of hard and soft palate |

