![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Unpleasant feeling that often precedes vomiting |
Nausea |
|
|
Forcible emptying of gastric, and occasionally, intestinal contents |
Emesis (vomiting) |
|
|
Used to relieve nausea and vomiting |
Antiemetic drugs |
|
|
Both located in the brain Once stimulated, cause the vomiting reflex 2 |
Vomiting center (VC) Chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) |
|
|
Antiemetics and Antinausea Drugs 5 |
Anticholinergic drugs Antihistamines (histamine 1 [H1] receptor blockers) (Respiratory) Antidopaminergic drugs Prokinetic drugs Serotonin blockers Tetrahydrocannabinoids |
|
|
Antiemetics and Antinausea Drugs: Mechanism of Action 2 |
Many different mechanisms of action
Most work by blocking one of the vomiting pathways, thus blocking the stimulus that induces vomiting |
|
|
Antiemetics and Antinausea Drugs Picture |
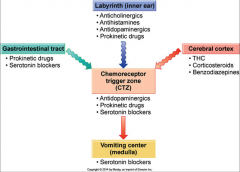
|
|
|
____ : Bind to and block ___ in the inner ear labyrinth Block transmission of nauseating stimuli to CTZ Also block transmission of nauseating stimuli from the reticular formation to the VC Patches are 72 hour doses and changed every 3 days |
Anticholinergic drugs (ACh blockers)
acetylcholine (ACh) receptors |
|
|
Anticholinergic drugs (ACh blockers) 1 |
scopolamine (Transderm-Scōp, Scopace) |
|
|
The nurse is preparing to administer scopolamine to a patient. It is most important for the nurse to determine if the patient has a history of which condition? |
Narrow-angle glaucoma |
|
|
commonly administered in patch form to prevent motion sickness, is the contraindication to its use in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma. |
scopolamine (Transderm-Scōp, Scopace) |
|
|
Prevent cholinergic stimulation in vestibular and reticular areas, thus preventing nausea and vomiting Also used for motion sickness, nonproductive cough, allergy symptoms, sedation Inhibit ACh by binding to H1 receptors
|
Antihistamine drugs (H1 receptor blockers) |
|
|
Antihistamine drugs (H1 receptor blockers) 4 |
dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) diphenhydramine (Benadryl) meclizine (Antivert) Hydroxyzine (Vistaril) – IM only due to tissue damage (NO IV)
|
|
|
Block dopamine receptors in the CTZ Also used for psychotic disorders, intractable hiccups |
Antidopaminergic drugs |
|
|
Antidopaminergic drugs 3 +1 |
prochlorperazine (Compazine) promethazine (Phenergan) droperidol: Use is controversial because of associated cardiac dysrhythmia
|
|
|
Block dopamine receptors in the CTZ (chemoreceptor trigger zone) Cause CTZ to be desensitized to impulses it receives from the GI tract Also stimulate peristalsis in GI tract, enhancing emptying of stomach contents Also used for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), delayed gastric emptying |
Prokinetic drugs |
|
|
Prokinetic drugs 1 +2 |
metoclopramide (Reglan)
Long-term use may cause irreversible tardive dyskinesia Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to procaine or procainamide
|
|
|
____promotes the movement of substances through the gastrointestinal tract and increases gastrointestinal motility. This action is helpful in preventing aspiration in those receiving tube feedings. |
metoclopramide (Reglan) |
|
|
Used for nausea and vomiting in patients receiving chemotherapy and for postoperative nausea and vomiting Can cause headache, diarrhea, prolonged QT interval* Block serotonin receptors in the GI tract, CTZ, and VC
|
Serotonin blockers |
|
|
Serotonin blockers 4 |
dolasetron (Anzemet) granisetron (Kytril) ondansetron (Zofran)* palonosetron (Aloxi)
|
|
|
Major psychoactive substance in marijuana
Inhibitory effects on reticular formation, thalamus, cerebral cortex
Alter mood and body’s perception of its surroundings, which may help relieve nausea and vomiting
|
Tetrahydrocannabinoids
|
|
|
____ is used as an appetite stimulant in patients who are experiencing nutritional wasting due to cancer and cancer treatment.
|
Dronabinol |
|
|
Tetrahydrocannabinoids (THC)
Used for nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy, and anorexia associated with weight loss in AIDS patients |
dronabinol (Marinol) |
|
|
Mint-flavored oral solution Used off label for treatment of morning sickness* Safe for pregnants Miscellaneous Class used to relieve nausea
|
phosphorated carbohydrate solution (Emetrol) |
|
|
Used for the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy regimens |
aprepitant (Emend) |
|
|
Vary according to drug used Stem from their nonselective blockade of various receptors |
Adverse Effects |
|
|
_____ have the potential to cause prolonged QTc interval. |
The serotonin blockers |
|
|
Used for nausea and vomiting, including that caused by chemotherapy, morning sickness, and motion sickness Adverse effects Anorexia, nausea and vomiting, skin reactions Clinicians question safety during pregnancy Drug interactions May increase absorption of oral medications Increase bleeding risk with anticoagulants
|
Herbal Products: Ginger |
|
|
Use of ginger can increase absorption of all oral medications and may theoretically __2__ |
increase bleeding risk with anticoagulants
or antiplatelet drugs |
|
|
Assess complete nausea and vomiting history, including precipitating factors Assess current medications Assess for contraindications and potential drug interactions |
Nursing Implications |
|
|
Many of these drugs cause severe drowsiness (Benadryl); warn patients about driving or performing any hazardous tasks Taking antiemetics with alcohol may cause severe CNS depression Teach patients to change positions slowly to avoid hypotensive effects
|
Nursing Implications |
|
|
For chemotherapy, antiemetics are often given 30 to 60 minutes before chemotherapy begins Monitor for therapeutic effects Monitor for adverse effects
|
Nursing Implications |

