![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
pharmacogenetics |
effect on individual due to genetics i.e. metabolism, DNA |
|
|
pharmacogenomics |
effect on population - genetics, lifestyle factors, polypharmacy, diet, sex, age |
|
|
agonist |
bind to and activates receptor in place of endogenous ligand (protein binding to receptor) can be partial or allosteric (creates some effect due to receptor binding vs effect due to non-receptor binding |
|
|
antagonist |
blocks access to the receptor site to the endogenous ligand competitive reversible or irreversable & non-competitive |
|
|
affinity (attraction of the drug to the receptor |
high affinity = low concentrations of drug required low affinity = high concentrations of the drug req to bind any to the receptor no affinity = no binding |
|
|
efficacy - intrinsic activity |
no effect = no efficacy = antagonist (affinity) at higher concentrations can have same effect as endogenous compount = efficacy = agonist |
|
|
maximal drug efficacy |
maximum response a drug can produce |
|
|
competitive (reversible) antagonist |
bind to receptor site blocking agonist - competitive and so the agonists may still work if in high enough concentrations - degree of inhibition depends on plasma ratio |
|
|
irreversible antagonist |
target receptor becomes permanantly unvaliable - until receptor is replaced |
|
|
non competitive antagonist |
bind to some other site such as ion channel to inhibit electrostatic binding of receptor and endogenous compound/agonist |
|
|
pharmacokinetics of drug administration |
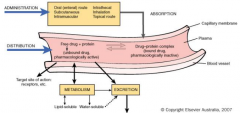
|
|
|
plasma protein binding and affinity |
Acidic drugs bind mainly to albumin
Basic drugs bind mainly to a glyco-protein |
|
|
lipophillic drugs |
have a high affinity to fat, are toxic and are distributed slowly |
|
|
BBB |
Blood Brain Barrier - lipid membrane protecting brain and cerebrospinal fluid from toxins |
|
|
routes of administration |
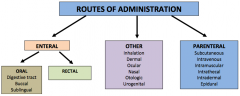
|
|
|
oral drug administration |
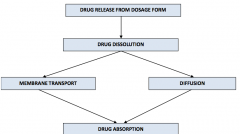
|
|
|
sublingual admin (bypassing 1st pass) |
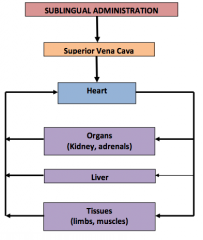
|
|
|
comparison of bioavaliability |
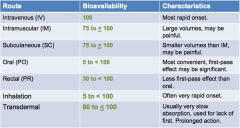
|
|
|
plasma protein binding and avaliability |
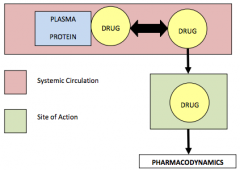
|

