![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Which cells produce Renin?
2. What is the function of Renin? 3. What is the function of ACE? 4. When is Renin released? |
1. Juxtaglomerular Cells of the afferent and efferent arterioles
2. Converts Angiotensinogen to AT1 3. Converts AT1 --> AT2 4. When stretch receptors at the JGA sense decreased perfusion When the Macula Densa receptors detect low Na+ SANS innervates the JGA --> NE --> B1 --> Renin |
|
|
How do the following affect Renin release?
1. Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors, Caffeine, Methylxanthines 2. Angiotensin II 3. ACE inhibitors and ARBs |
1. Block Na+ recovery --> Mild diuresis
Caffeine blocks ADG release from the Posterior Pituitary 2. Negative Feedback on Renin 3. Block the feedback of ATII on Renin --> Increase Renin |
|
|
1. What receptors do ARBs block?
2. How does this receptor normally become stimulated and what happens after the initial stimulation? 3. What effects does ATII have on the AT2 receptor? 4. Who has the most AT2 receptors? |
1. AT1 receptors
2. ATII --> Gq --> PLC --> Smooth Muscle Contraction --> Vasoconstriction Aldosterone synthesis and secretion ADH secretion Cardiac Hypertrophy Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell proliferation Augmentation of peripheral SANS activity Renal renin inhibition Reset Vasomotor center to higher "Normal" BP 3. Vasodilation, Cardiac hypertrophy 4. Fetuses and Neonates |
|
|
1. Functions of Aldosterone
|
1. Na+ absorption at DCT/Cortical Collecting Duct
HypoK+ Alkalosis Increased Plasma volume HTN |
|
|
1. What kind of enzyme is ACE?
2. What does it do? |
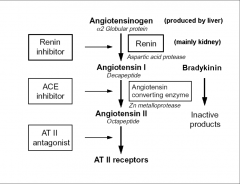
1. PDP - Peptidyl Dipeptidase (aka Kinase II)
2. Converts ATI --> ATII Converts Bradykinin into inactive fragments |
|
|
1. Effects of Bradykinin
2. What are the consequences of ACE Inhibition? |
1. VAsodilator (Bradykinin II Receptor --> G-protein --> NO --> Decreased arterial resistance and increased venous capacitance)
Proinflammatory (B1 --> Mediates pain, swelling, angioedema Gq --> PLC --> Bronchoconstrictor --> Induce airway irritability, COUGH, Airway obstruction 2. Captopril Cough (bradykinin) Hyperk+ Acute Renal Failure Hypotension (first-dose phenomenon) Bronchial hyperresponsiveness, ANGIOEDEMA PAIN |
|
|
How do the following cause Indirect decreases in Renin?
1. Clonidine 2. Beta Blockers |
1. CNS-active Alpha-2 Agonist --> Decreases SANS --> Decreases NE effect on JGA --> No renin
2. Block NE at the B1 receptor of the JGA --> No renin |
|
|
Renin Antagonist - Aliskerin
1. MOA: 2. Use: 3. What drug is Aliskerin combined with for first line use in HTN? 4. Tox; |
1. Binds renin
2. HTN Combo with Diuretics, ACE Inhibitors, ARBs because they increase renin as a side effect 3. Amlodipine (dihydropyridine type Ca2+ channel blocker) --> More effective than either drug alone 4. Pregnancy caution Mild Diarrhea Allergy Cough, Dizzy w/ Hydrochlorothiazide Dizzy w/ Valsartan or Amlodipine |
|
|
ACE Inhibitors - Captopril, Lisinopril
Prodrugs - Enalapril, Ramipril, Quinapril, Benazepril, Fosinopril Active Metabolites - Enalaprilat, Ramiprilat 1. Why are ACE Inhibitors used in diabetic patients? 2. MOA: 3. Use: 4. Tox: 5. Contraindications: |
1. Renal protection
2. Blocks ATI-->ATII 3. HTN, CHF, Diabetes 4. PREGNANCY --> Fetal Renotox Angiotensin Absence --> Hypotension (first dose phenomenon) --> Acute renal failuer Aldosterone Absence --> HyperK+ Bradykinin Presence --> Cough, resp irritability, angioedema (swelling throat, lips tongue) Drug Interactions - K+ sparing duretics or supplements 5. Pregnancy, Renal artery stenosis (ATII constricts the efferent arteriole --> Maintains GFR. Remove ATII --> lose GFR) |

