![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the principal monoamines? What are they most often associated with?
|
norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin, 5HT), histamine
|
|
|
What is the order of Catecholamine synthesis?
|
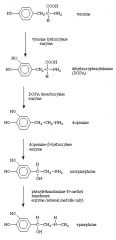
|
|
|
What does the locus ceruleus contain? Where do these neurons project?
|
cell bodies of NE cells, which have diffuse projections for activating the CNS (cortex, cerebellum, hippocampus, amygdala)
|
|
|
What roles does norepinephrine play in psych drugs?
|
affect—trycyclic antidepressant efficacy, arousal, reward (Dopamine also key for reward. )
|
|
|
What is involved in the nigrostriatal pathway?
|
DA neurons: originate in substantia nigra (pars compacta)
|
|
|
What is L-DOPA used to Rx? What is the presumed mechanism?
|
in parkinsons presumably replaces DA to striatal cells
|
|
|
What does the mesolimbic & mesocortical system contain? What are the projections?
|
DA neurons: from midbrain via medial forebrain bundle (MFB) to limbic & neocortical areas
|
|
|
What route does dopamine antagonists Rx schizophrenia?
|
mesolimbic and mesocortical system
|
|
|
What roles does dopamine play in the CNS?
|
motor—deficiencies associated with Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, Tourette’s
sexual behavior—DA agonists (apomorphine) ↑mounting behavior in rats DA antagonists ↓ anti-psychotic drugs—suggests DA has role in normal mentation reward properties of street drugs |
|
|
Describe the D1 dopamine receptor. Inhibitory or Excitatory? Post or Presynaptic?
|
post synaptic (& "D5" a subtype)—excitatory
|
|
|
Describe the D2 dopamine receptor. Inhibitory or Excitatory? Post or Presynaptic? Subtypes?
|
both post & pre synaptic—inhibitory.
"D2" subtypes: D2a, D2b—classical antipsychotics D3 D4—site of action of atypical antipsychotics, but this isn't consistent & 5HT2 blockade is probably more what distinguishes atypical from typical antipsychotics & what makes atypicals good for neg Sx |
|
|
What is the distinguishing factor between typical and atypical antipsychotics?
|
5HT2 blockade is probably more what distinguishes atypical from typical antipsychotics & what makes atypicals good for neg Sx
|
|
|
What is contained in the midbrain raphe? Where do the neurons project?
|
cell bodies of most serotonergic neurons. project to cerebrum (rostral raphe nuclei) & spinal cord (caudal raphe nuclei)—more widely than DA but not as widely as NE
|
|
|
Describe serotonin synthesis.
|
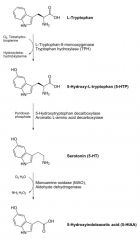
tryptophan → 5-hydroxytryptophan via tryptophan hydroxylase (rate limiting)
5-hydroxytryptophan→ 5-hydroxy tryptamine (5HT, serotonin) via aromatic amino acid decarboxylase |
|
|
Describe serotonin metabolism.
|
5HT → melatonin via N-acetylase & FOH indole O-methyltransferas → 5-HIAA via MAO (Monoamine Oxidase) & Aldehyde dehydrogenase
hence MAO Inhibitor antidepressants affect serotonin levels (as well as DA & NE) |
|
|
How many classes of serotonin receptors are there?
|
7 classes
|
|
|
What is the effector, location, and pharmaceuticals acting (and actions) at the 5HT1a isoform of the serotonin receptor?
|
Effector: Gi ↓cAMP
Location: somatic autoreceptor Drug actions: Buspirone an agonist (weak anxiolytic) |
|
|
What is the effector, location, and pharmaceuticals acting (and actions) at the 5HT1B/D isoform of the serotonin receptor?
|
Effector: Gi ↓cAMP
Location: presynaptic autoreceptor Drug actions: Sumatriptan an agonist (antimigraine) |
|
|
What is the effector, location, and pharmaceuticals acting (and actions) at the 5HT3 isoform of the serotonin receptor?
|
Effector: ↑ ion channel
Location: smooth muscle Drug actions: ondansetron, granisetron antagonists (anti-emetics) |
|
|
What roles does serotonin play in the CNS?
|
sleep (melatonin a mild hypnotic), sexual behavior (anorgasmia side effect of SSRIs), psychosis (LSD), appetite & eating disorders (weight change side effect of SSRIs), depression (SSRIs Rx), anxiety (SSRIs Rx), obsession-compulsion (SSRIs Rx), migraine (Rx: Sumatriptan), emesis (Rx: Ondansetron, Granisetron)
|
|
|
What is melatonin? What is its role? What is it synthesized from? How is it used? What is its half life?
|
Pineal hormone involved in reproduction with light/dark secretion (also involved in sleep), synthesized from serotonin, Used as a mild sedative in hi doses, T1/2 – 20-30min, Jet lag, shift work
|
|
|
What is Ramelteon? How is it used?
|
is a melatonin agonist used as a hypnotic drug
|
|
|
What is Ondansetron (Zofran)? What is it used for? What are its side-effects?
|
5HT-3 antagonist
Antinausea and antiemetic in medical oncology SE – headache, const, flush, altered taste |
|
|
What are Sumatriptan, Naratriptan, Zolmitriptan, and Rizatriptan? What are they used for? What are the side effects? What are they contraindicated in?
|
5HT-1B/D agonist
Effective in migraine, relief in two hours SE – tingling, flushing, burning, dysphoria, dizziness, non-CV chest pain. Contraindicated in ischemic heart disease |
|
|
What is the mechanism of a migraine?
|
5HT1B/D receptors are on the smooth muscle cells of extracerebral blood vessels and at the terminals of the trigeminal sensory fibers. swollen blood vessels activate trigeminal pain fibers
5HT acting on 5HT1b receptors produce vasoconstriction 5HT acting on 5HT1d receptors inhibit pain signals at spinal cord and also inhibit pain-mediated vasodilation |
|
|
What drug treats migraines? What is the mechanism of action?
|
sumatriptan agonist of both 5HT1b and 5HT1d receptors
|
|
|
What are Ergot alkaloids? What are they used for? Contraindicated in? Side-effects?
|
Nonselective partial agonists of 5HT, DA, NE
Anti-migraine - Not well tolerated Contraindicated in pregnancy SE – n/v, vasoconstriction |
|
|
What are some prophylactic Rx's for migraine?
|
ergot alkaloids, Topiramate, Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline, Propranolol
|

