![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of drugs start out as a liquid, converted in the vaporizer to gas, and inhaled and absorbed via the pulmonary capillaries?
|
Inhalational anaesthetic agents
|
|
|
___ is an indication of a liquid's evaporation rate; relates to the tendency of particles to escape from a liquid
|
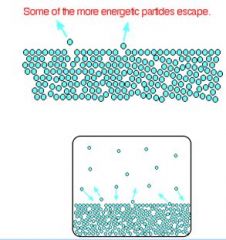
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure
|
|
|
In confined space, there equilibrium in which number of molecules entering the gaseous state equals the number leaving it.
This is called ________? |
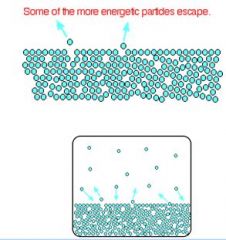
saturated vapour pressure (SVP)
At this point, vapour pressure is at a maximum for the liquid |
|
|
If an inhalational agent has a high SVP (saturated vapor pressure), then ________?
what inhalational anesthetic has highest SVP? (excluding N2O) |
Very volatile agent (SVP is also temperature dependent)
Desflurane has highest SVP |
|
|
The more insoluble an INHALATIONAL agent is, _______________?
|
The quicker you can change its concentration in the body
MORE INSOLUBLE AN INHALATIONAL ANAESTHETIC AGENT, THE FASTER IS WORKS FOR BOTH INDUCTION AND RECOVERY |
|
|
Saturated vapour pressure is the equilibrium point and is dependent on what two things?
|
SVP dep. on temperature and atmospheric pressure
SVP increases with increasing temperature |
|
|
Which inhalational agents have a large blood: gas coefficient?
|
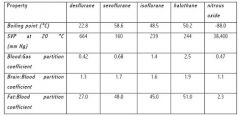
Soluble inhalational agents
|
|
|
What factors determine the extent a tissue takes up anaesthetic?
|
Depends on blood supply
and surface area of tissue |
|
|
What two effects influence the inspired concentration?
|
Concentration effect
Second gas effect |
|
|
Which inhalational agents have a LOW blood: gas coefficient: soluble or insoluble?
Example? |
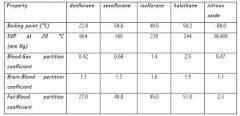
Insoluble agents = LOW blood:gas coeff.
(e.g. desflurane) Remember the more INSOLUBLE an inhalational anaesthetic agent, the FASTER it works for both induction and recovery |
|
|
What inhalational agent causes big drop in blood pressure?
Therefore you would NOT this agent in ___? |
Halothane
avoid in sick, or animals with foreign object, liver disease blas blas..because reduces organ perfusion (except cranium!) |
|
|
What inhalational agent is somewhat irritating to respiratory tract?
|
isoflourene
|
|
|
What inhalational agent are very similar to isoflourene, but more expensive?
|
sevoflurane
|
|
|
most effective absorption surface in the body?
why? |
pulmonary alveolar epithelium
huge surface area...duh |
|
|
do inhalation agents have pre- OR post-synaptic effects?
|
have BOTH pre- and post-synaptic effects
|
|
|
True or False:
* inhalation agents never interact with the neuronal plasma membrane * do not act via second messenger systems |
FALSE:
* inhalation agents DO interact with the neuronal plasma membrane * they may also act via second messenger systems |
|
|
What inhalational drug produces metabolite known as 'Compound A' on reaction with soda lime?
|
Sevoflurane
Compound A has no clinical significance...aside from causing renal necrosis in rats. |
|
|
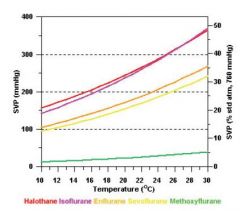
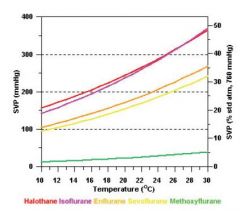
for most inhalational agents, SVP is low OR high?
|
for most inhalational agents, SVP is very HIGH – this is why vaporisers are required
|
|
|
What inhalation agent is highest?
Which is lowest? |
desflurane 664 mm Hg <-- you can pack a whole lot more of this guy into confined space, than you can sevofl.
sevoflurane 160 mm Hg |
|
|
Which 2 inhalants have ~same SVP?
|
halothane 239 mm Hg
isoflurane 240 mm Hg |
|
|
At sea level and room temperature, which can you achieve higher concentrations of : isoflurane, sevo, or desflurane?
What do vaporizers do? |
At sea level and room temperature, you can achieve concentrations of :
21% sevo 32% halothane 32% isoflurane 86% desflurane Vaporisers are used to deliver SAFE anaesthetic concentrations of inhalational agent |
|
|
If blood:gas ratio/coefficient is 2:1 or 2; which holds higher concentration - blood or gas?
|
BLOOD
this is principle behind "Solubility partition coefficients" and blood:gas solubility |
|
|
blood:gas solubility/coefficient is 0.5, what is ratio of blood:gas?
|
1:2 or 2:4, etc.
insoluble agents have a LOW Blood/Gas co-efficient; remember this means works faster! > do NOT confuse this with SVP |
|
|
body can be considered to consist of four basic groups, based on PERFUSION and PROPORTION OF BODY MASS
(determines how quickly take up drug and reach eq.) |
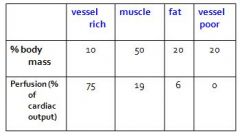
1. Vessel rich->75% perfusion (% of CO)
2. Muscle/skin->19% perfusion 3. Fat->6% 4. Vessel poor (ie. CT, bone)->0% perfusion (see next question!) |
|
|
The vessel-rich group is composed of?
Speed to eq.? Why? |
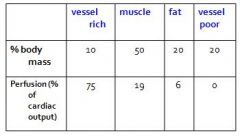
brain, heart, liver, kidneys, endocrine glands and splanchnic bed.
Perfused well, have smaller volume (like compared to muscles), so rapidly reach equilibrium |
|
|
Minimum alveolar concentration or MAC describes what ?
|
is a concept used to compare the strengths, or potency of anasthetic..at this conc. 50% patients do not respond to stimulus
|
|
|
High MAC means?
|
Drug is poor anesthetic, it is measure of potency (higher value means higher concentration needed to anesthetize animal)
Speed of onset faster?! (wrong) |
|
|
Which has higher MAC: 1. halothane
2. desflurane 3. methoxyflurane |
desflurane (MAC = 8) > halothane > methoxyflurane (0.23)
desflurane = least potent anesthetic; also fastest onset |
|
|
Key factors determining _____?:
* blood:gas solubility * Fi:FA ratio * cardiac output * partial pressure difference between alveolus and venous blood (PA - PV) |
Key factors determining anaesthetic uptake into blood
|
|
|
Fi:FA ratio is what?
|
comparing inspired concentration (Fi) to alveolar (FA) concentration of anaesthetic
uptake is determined by the rate and depth of ventilation |
|
|
What is second gas effect?
Hint: Function of nitric oxide |
Because [NO] is so insoluble, take up rapidly and concentrates other drugs in alveoli, so increases speed they're taken up as well
can use LESS of other inhalation drugs |
|
|
Why is important to minimize the amount of inhalation agents used?
|
All suppress cardiovascular and respiratory centers; so can kill animal very easily
|
|
|
What are some factors that decrease MAC?
|
Narcotics
Sedatives Tranquilizers Nitrous oxide Age Hypothermia Pregnancy |

