![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Outline the Nervous System:
|
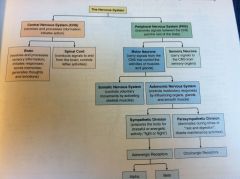
|
|
|
What are the basic functions of the nervous system?
|
Processing perceptions.
Reacting to the internal/external environment. |
|
|
What are the 4 fundamental classes of autonomic drugs?
|
Adrenergic agents, Adrenergic-blocking agents, Cholinergic agents, & Cholinergic-blocking agents.
|
|
|
In the PNS, neurons either:
|
recognize changes to the environment (sensory division), or respond to these changes by moving muscles or secreting chemicals (motor division).
|
|
|
The Somatic nervous system controls:
|
VOLUNTARY contraction of skeletal muscles.
|
|
|
The Autonomic nervous system controls:
|
INVOLUNTARY contraction of SMOOTH muscle , CARDIAC muscle, and glands.
|
|
|
Organs and tissues under autonomic nervous system control:
|
the heart & arteries; the respiratory, digestive, & reproductive tracts; the salivary glands, and portions of the eye.
|
|
|
The Autonomic NS has two divisions:
|
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic.
|
|
|
With few exceptions, organs and glands receive nerves from ______ branch(s) of the Autonomic NS.
|
Both
|
|
|
What are the physiologic responses to Sympathetic activation?
|
Increased HR and BP.
Increased Blood flow to muscles. Bronchi and pupils dilate. Liver produces glucose. |
|
|
What are the physiologic responses to Parasympathetic activation?
|
Decreased HR and BP.
Bronchi constrict. Digestion is promoted. |
|
|
HR can be increased by either:
|
Increasing sympathetic stimulation or decreasing parasympathetic stimulation.
|
|
|
Do the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic divisions always produce opposite effects?
|
NO, some things are entirely controlled by one or the other. eg.. CONSTRICTION of arterioles is controlled entirely by the Sympathetic branch. Sympathetic stimulation causes constriction of arterioles, whereas VASODILATION is caused by lack of Sympathetic stimulation.
|
|
|
What systems are controlled entirely by the Sympathetic system?
|
Arterioles and sweat glands.
|
|
|
In the Autonomic NS, communication involves the connection of:
|
two neurons in series.
|
|
|
In the Autonomic NS, as the action potential travels along the first nerve, it encounters the first ________. Because this occurs outside of the CNS it is called:
|
Synapse; a Ganglionic synapse.
|
|
|
Describe a nerve impulse sent from the CNS to the target tissue in the Autonomic NS:
|
The impulse is sent from the spinal cord down the Preganglionic neuron, through the Ganglionic synapse, then down the Postganglionic neuron which then synapses at the target tissue.
|
|
|
Are Autonomic drugs given to correct physiological defects in the autonomic nervous system?
|
NO, they are given to STIMULATE or INHIBIT TARGET ORGANS of the Autonomic NS such as the heart, lungs, glands, or digestive tract.
|
|
|
With few exceptions, disorders lies with the ____________, not the:
|
target tissue, not the ANS, which itself is remarkable free from disease compared to other systems.
|
|
|
When an Autonomic drug is administered, it does not correct an autonomic disorder, rather it:
|
corrects dysfunction of that target organ naturally stimulated by the autonomic neurotransmitter.
|
|
|
The two primary neurotransmitters of the Autonomic nervous system are:
|
norepinephrine (NE) and acetylcholine (Ach).
|
|
|
Parasympathetic division:
______________ pupils. ______________ salivation. ______________ HR. ______________bronchioles. ______________digestion. ______________gallbladder. ______________urinary bladder. ______________sex organs. |
CONSTRICTS pupils.
STIMULATES salivation. DECREASES HR. CONSTRICTS bronchioles. STIMULATES digestion. STIMULATES gallbladder. CONTRACTS urinary bladder. STIMULATES sex organs. |
|
|
Sympathetic Stimulation:
______________ pupils. ______________ salivation. ______________ HR. ______________bronchioles. ______________digestion. ______________ release of glucose. ______________urinary bladder. ______________sex organs. |
DILATES pupils.
INHIBITS salivation. INCREASES HR. DILATES bronchioles. INHIBITS digestion. STIMULATES release of glucose. RELAXES urinary bladder. INHIBITS sex organs. |
|
|
What transmitter is released at almost all Postganglionic nerves in the Sympathetic nervous system?
The exception is? |
NE; the exception is sweat glands, in which Ach is the neurotransmitter.
|
|
|
NE belongs to a class of agents called ____________, all of which are involved in:
|
natural Catecholamines; neurotransmission.
|
|
|
Other natural Catecholamines include:
Examples of Synthetic Catecholamines include: |
Epinephrine (adrenaline) and Dopamine.
Isoproterenol and Dobutamine. |
|
|
What are some Noncatecholamines?
Structure? |
Ephedrine, phenylephrine, and terbutaline.
They have a slightly different chemical structure than the catecholamines |
|
|
All the Noncatecholamines bind to:
|
adrenergic receptors
|
|
|
Where are Adrenergic receptors located?
|
At the ends of the Postganglionic Sympathetic neurons.
|
|
|
What are the two types of Adrenergic receptors?
|
Alpha and Beta.
|
|
|
What are the different subtypes of Alpha and beta receptors?
|
alpha₁, alpha₂ and beta₁, beta₂, & beta₃
|
|
|
In drug receptor selectivity, can drugs activate one type of receptor at low doses and begin to affect other receptor subtypes as dosage increases?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
Five Mechanisms by Which Drugs Can Affect Synaptic Transmission?
|
1) Affect the SYNTHESIS of the neurotransmitter in the
presynaptic nerve. 2) Prevent STORAGE of the neurotransmitter within the presynaptic nerve. 3) Influence RELEASE of the neurotransmitter from the presynaptic nerve. 4) Prevent the normal REUPTAKE OR DESTRUCTION of the neurotransmitter. 5) Bind to the RECEPTOR site on the postsynaptic target tissue. |
|
|
1) Drugs that Affect the synthesis of the neurotransmitter in the presynaptic nerve:
Drugs that decrease neurotransmitter synthesis will: Drugs that increase neurotransmitter synthesis will: |
Inhibit nervous system activity.
Promote nervous system activity. |
|
|
2) Drugs that Prevent storage of the neurotransmitter in vesicles within the presynaptic nerve:
Prevention of neurotransmitter storage will: |
inhibit nervous system activity.
|
|
|
3) Drugs that Influence release of the neurotransmitter from the presynaptic nerve.
Promoting neurotransmitter release will: Slowing neurotransmitter release will: |
stimulate nervous system activity.
inhibit nervous system activity. |
|
|
4) Drugs that Prevent the normal destruction or reuptake
of the neurotransmitter: Drugs that cause the neurotransmitter to remain in the synapse for a longer time will: |
stimulate nervous system activity.
|
|
|
5) Drugs that Bind to the receptor site on the postsynaptic target tissue:
Drugs that bind to the receptor site on the postsynaptic target tissue will: Drugs that attach to the postsynaptic target tissue and prevent neurotransmitter receptor interaction will: |
increase nervous system activity.
inhibit nervous system activity. |
|
|
NE is synthesized in the nerve terminal through a series of steps that require that amino acids __________________. The final step of the synthesis involves the conversion of _______________ to _________________.
|
phenylalanine and tyrosine; conversion of dopamine to NE.
|
|
|
NE is stored in the vesicles until:
|
an action potential triggers its release into the synaptic cleft. NE then diffuses across the cleft to alpha or beta receptors on the effector organ.
|
|
|
What terminates NE action?
|
The reuptake of NE back into the presynaptic neuron. Once reuptake occurs, NE may be returned to vesicles for future use or destroyed enzymatically by monoamine oxidase (MAO).
|
|
|
______________ destroys NE after reuptake inside the presynaptic neuron:
____________destroys NE at the synaptic cleft: |
monoamine oxidase (MAO).
catecholamine-O-methyl transferase (COMT). |
|
|
The primary method for termination of NE action is through:
|
reuptake.
|
|
|
As part of the sympathetic NS, the preganglionic neuron from the spinal cord terminates at the _______________ and releases:
|
Adrenal medulla and releases epinephrine directly into the blood.
|
|
|
How is the action of epinephrine terminated?
|
through hepatic metabolism, rather than reuptake.
|
|
|
Primary locations of alpha₁ receptors:
Responses: |
All sympathetic target organs except the heart.
Blood vessel constriction, pupil dilation. |
|
|
Primary locations of alpha₂ receptors:
Responses: |
Postganglionic nerve terminals in the Sympathetic division.
Inhibits release of NE. |
|
|
Primary locations of beta₁ receptors:
Responses: |
Heart and kidneys.
Increased heart rate and force of contraction; release of renin. |
|
|
Primary locations of beta₂ receptors:
Responses: |
All sympathetic target organs except the heart.
Inhibit smooth muscle. |
|
|
Primary locations of Beta₃ receptors:
Responses: |
Adipose tissue.
Lipolysis. |
|
|
Nerves releasing Ach are called:
|
Cholinergic nerves.
|
|
|
What are the two types of Cholinergic receptors?
|
Nicotinic and Muscarinic
|
|
|
Where are nicotinic receptors located?
|
at the Ganglionic synapse of both Sympathetic and Parasympathetic divisions of the Autonomic NS.
|
|
|
Where are Muscarinic receptors located?
|
On target tissues affected by Postganglionic neurons in the Parasympathetic NS.
|
|
|
Receptors for Ach at the ganglia are called:
|
Nicotinic receptors.
|
|
|
Nicotinic receptors are also located where?
|
In the Skeletal muscle, controlled by the Somatic NS.
|
|
|
Primary locations of Nicotinic receptors:
Responses: |
Postganglionic neurons; Skeletal muscle.
Stimulates smooth muscle and glands. |
|
|
Primary locations of Muscarinic receptors:
Responses: |
Heart & other organs.
Response in the heart: Decreased HR and Force of Contraction. Response in other organs: Stimulation of smooth muscle and gland secretion. |
|
|
What is the effect of drugs that act on Nicotinic receptors? Symptoms?
|
There are profound effects on both the Somatic and Autonomic nervous systems. Symptoms: Tachycardia, hypertension, and increased tone and motility in the GI tract.
|
|
|
Activation of Muscarinic receptors results in:
|
Classic Parasympathetic NS symptoms.
|
|
|
Ach is synthesized in:
|
the Preganglionic neuron of the Sympathic nerves, and both the Pre/Post-Ganglionic nerves of the Parasympathetic nerves.
|
|
|
Ach is synthesized from:
|
Acetyl coenzyme A & choline.
|
|
|
How is Ach action terminated?
|
it is rapidly destroyed in the synaptic cleft by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AchE), and Choline is reused to make more Ach.
|
|
|
How do drugs affect Ach?
|
They affect the Synthesis, Release or Destruction, and Receptor activation of Ach.
|
|
|
Autonomic drugs are classified based on:
What are they? |
one of 4 possible actions:
Stimulation/ Inhibition of the Sympathetic NS. Stimulation/ Inhibition of the Parasympathetic NS. |
|
|
Drugs that stimulate the Sympathetic NS are called:
Effects? |
adrenergic agents or Sympathomimetics.
Effects are the classic fight/flight response. |
|
|
Drugs that Inhibit the Sympathetic NS are called:
Effects? |
adrenergic-blocking agents or Adrenergic Antagonists or Sympatholytics.
Effects are the OPPOSITE of Sympathomimetics. |
|
|
Drugs that stimulate the Parasympathetic NS are called:
Effects? |
cholinergic agents or Parasympathomimetics.
Effects are the classic rest/digest response. |
|
|
Drugs that Inhibit the Parasympathetic NS are called:
Effects? |
cholinergic-blocking agents or Anticholinergics or Parasympatholytics or Muscarine blockers.
Effects are the OPPOSITE of Parasympathomimetics. |
|
|
To generalize, Sympathomimetics have the same effects as _________________, and Parasympathomimetics have the same effects as ____________________.
|
Sympathomimetics have the same effects as Parasympatholytics, and Parasympathomimetics have the same effects as Sympatholytics.
|
|
|
Sympathomimetics have clinical applications in treating:
|
shock and hypotension.
|
|
|
How must catecholamines be administered?
Can non-catecholamines be administered orally? What is their duration like? |
parenterally.
Yes, and they have a longer duration of action because they are not destroyed by MAO or COMT. |
|
|
What does it mean that Sympathomimetics act directly or indirectly?
|
Sympathomimetics act directly by binding to and activating adrenergic receptors.
Sympathomimetics act Indirectly by causing the RELEASE of NE or by inhibiting the REUPTAKE or DESTRUCTION of NE. |
|
|
Sympathomimetics that act by indirect means, such as amphetamines or cocaine, are used for their ________________affects in the ______________:
|
Central effects in the brain, rather than their autonomic effects. A few agents, such as ephedrine, act by both direct and indirect mechanisms.
|
|
|
Adrenergic-blocking agents inhibit the sympathetic NS, and produce many of the same rest-and-digest symptoms as:
|
the Parasympathomimetics.
|
|
|
Adrenergic-blocking agents have wide therapeutic use in the treatment of:
|
hypertension.
|
|
|
All beta blockers are used therapeutically for their effects on:
|
the CV system
|
|
|
What do beta blockers do physiologically?
|
They decrease the rate and force of contraction of the heart and slow conduction through the AV node.
|
|
|
The primary use of beta blockers is the treatment of:
|
hypertension
|
|
|
What are the interventions for Adrenergic drugs:
|
Check Pulse, BP, BG, & pt's sensitivity to light.
|
|
|
What are the interventions for Adrenergic-blocking agents:
|
Fluid bal: weigh pt daily and report weight gain or loss of 2 lbs daily.
Do not stop abruptly (must taper down). CNS: monitor for dizziness, drowsiness, or light-headedness. Cardio: monitor for bradycardia, hypotension, reflex tachycardia, seizures Uro: monitor urinary hesitancy, incomplete bladder emptying, interrupted stream. |
|
|
What are the interventions for Parasympathomimetics:
|
Frequent monitoring of vitals, bowel sounds, urinary output, mental status, musculoskeletal function.
Promptly report bradycardia, hypotension, dysrhythmias, tremors, change in mental status. Monitor liver function tests. Carefully calculate doses to avoid toxicity. |
|
|
What are the interventions for cholinesterase inhibitors:
|
Monitor muscle strength and neuromuscular status; commonly ptosis, diplopia, and chewing and swallowing.
Schedule medication around mealtimes (unless specifically contraindicated). Schedule activities to avoid fatigue. Monitor for muscle weakness. |
|
|
What are the interventions for Anticholinergic drugs:
What is the mnemonic? |
Monitor Pulse, BP, & for Dysrhythmias.
Monitor urinary output. Monitor bowel sounds & for ABD distension. Strictly forbidden with acute glaucoma. Can’t See Can’t Pee Can’t Spit Can’t Sh*t |
|
|
Anticholinergics effect on strenuous exercise:
|
they inhibit sweating, so overheating can occur.
|
|
|
Drugs that inhibit AchE are called:
|
cholinesterase inhibitors
|
|
|
Direct acting Parasympathomimetics do this:
Indirect acting Parasympathomimetics do this: |
Bind to cholinergic receptors.
Inhibit the action of Acetylcholinesterase (AchE). |
|
|
What are some Anticholinergic drugs?
|
atropine
benztropine |
|
|
What are some Adrenergic blocking agents?
|
acebutolol
atenolol carteolol |

