![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define drug selectivity
|
the ability of a drug to affect one tissue, cell type or organ and not others
|
|
|
what determines the drug concentration required to form a significant number of drug-receptor complexes
|
receptor affinity
|
|
|
___________ bind to receptors but do not activate them
|
antagonists
|
|
|
what is the role of non-competitive antagonists?
|
change the receptor to decrease the efficacy of the binding ligand
|
|
|
what determines the duration of action of an irreversible antagonist?
|
receptor turnover rate
|
|
|
How do physiological antagonists work?
|
2 drugs produce opposite effects through different receptor systems
|
|
|
Define intrinsic activity. Do competitive antagonists have high or low intrinsic activity?
|
extent to which a bound ligand activates a receptor. no intrinsic activity
|
|
|
Define Vmax
|
the point at which a reaction has reached its maximum velocity
|
|
|
define Km
|
the concentration of a substrate required to reach 1/2 Vmax (the measure of the affinity of an enzyme for that specific substrate)
|
|
|
what is the difference between Kd and Km?
|
Kd is the measure of binding, Km is the measure of velocity of a reaction
|
|
|
what is the equation for the law of mass action?
|
[DR] = [D][R] / [D] + Kd
|
|
|
drug _________ is related to its binding affinity
|
potency
|
|
|
drug __________ is related to the rate and extent of the receptor activation after binding
|
efficacy
|
|
|
what is the equation for drug effect?
|
intrinsic activity(alpha) x [DR] (number of occupied receptors)
|
|
|
what is the equation for Ka?
|
1/Kd
|
|
|
What is Emax?
|
the maximum effect on a dose response curve that can be produced (also referred to as efficacy)
|
|
|
what is EC50?
|
The dose concentration at which 50% of the maximal effect is produced (also referred to as potency)
|
|
|
What is the difference between full and partial agonists?
|
full agonists produce a full effect (alpha = 1) partial agonists cannot produce the maximal effect ( 0 < alpha < 1)
|
|
|
what is the threshold dose?
|
the minimal dose required to produce the desired effect
|
|
|
What does clinical effectiveness depend on?
|
a drugs ability to reach the relevant receptors combined with its efficacy
|
|
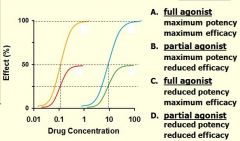
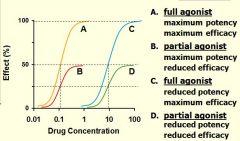
Label each curve
|
|
|
|
which type of antagonist does not require a receptor?
|
chemical
|
|
|
what are the effects of a competitive antagonist on potency and efficacy?
|
reduced potency, no effect on maximum efficacy
|
|
|
what do irreversible competitive antagonists do to ED50?
|
no change
|
|
|
what do irreversible competitive antagonists do to maximum efficacy?
|
decrease
|
|
|
what do non-competitive antagonists do to potency and efficacy?
|
decreased efficacy, no change in potency (ED50 remains)
|
|
|
increased spare receptors have what effect on potency and efficacy?
|
efficacy remains the same, potency increases
|
|
|
What is a graded dose-response curve?
|
graph of increasing response to increasing dose
|
|
|
What is a quantal dose-response curve
|
Graph of the fraction of a population that shows a specified response at progressively increasing doses
|
|
|
What is the LD50
|
dose concentration that is lethal for 50% of the population
|
|
|
What is the therapeutic index?
|
LD50/ ED50 (margin of a drug's safety - higher ratio = more safe)
|
|
|
What is the minimum TI value for a drug to be usable?
|
> 1
|
|
|
What is the certain safety factor?
|
LD1 / ED99
|

