![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is functionally homologous to sympathetic ganglion, innervated by preganglionic fibers from spinal cord, does not have does not have postsynaptic neuron?
what does it secrete? |
adrenal medulla
Secretory chromaffin cells are present to release norepinephrine and epinephrine |
|
|
Where do preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine on to?
|
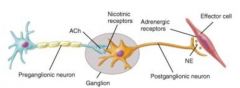
nicotinic receptors of the postganglionic neurons or adrenal medulla
|
|
|
Postganglionic neurons release norepinephrine onto what?
|
adrenergic receptors in the effector tissue
|
|
|
What are adrenergic receptors?
|
alpha
beta |
|
|
Normally the postganglionic fiber of parasympathetic nerve terminal releases ACH, whats the exception?
|
erectile tissue of genitalia
|
|
|
PS preganglionic neuron is short or long?
PS postganglionic neuron is short or long? |
long
short |
|
|
sympathetic preganglionic neuron is short or long?
sympathetic postganglionic neuron is short or long? |
short
long |
|
|
Neurotransmitter for Sympathetic
preganglion Sympathetic neuroeffector junctions release what neurotransmitter EXCEPTION?? |
Acetylcholine
norepinephrine is the neurotransmitter >exception: sweat glands in humans (acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter) |
|
|
What originates from the midbrain, medulla oblongata, and sacral spinal cord?
|
Preganglionic neurons originates from the midbrain, medulla oblongata and sacral spinal cord (craniosacral out flow).
|
|
|
What is the neurotransmitter responsible for penile erection?
|
Nitric oxide
|
|
|
What is the principal supraspinal site which involves the modulation of both sympathetic and PS out flow traffic such as blood pressure, body temperature, sleep-awake responses, carb metabolism, and emotions?
|
hypothalmus
|
|
|
What are the drugs that can provoke the physiological responses as that of endogenous adrenergic mediators, epinephrine and norepinephrine?
|
adrenergic agonists or sympathomimetics
|
|
|
stimulating adrenergic receptors
indirectly by release of catecholamines from adrenergic neurons |
adrenergic agonists or sympathomimetics work
|
|
|
What is the rate limiting step for the synthesis of norepinephrine?
|
tyrosine if transported by a Na+ linked carrier into the axoplasm of adrenergic neuron, where is it hydroxylated by tyrosine hydroxylase enzyme to DOPA
|
|
|
Where does the synthesis of norepinephrine occur?
|
in the cytoplasm of adrenergic neuron
|
|
|
Dopamine is transported into the synaptic vesicle by ______ and is then converted to what? BY WHAT ENZYME?
|
transported into the synaptic vesicle by <anion transported system>
then converted to <norepinephrine> by dopamine beta hydroxylase enzyme |
|
|
Action potential arriving at the nerve terminal triggers an influx of what?
|
calcium ions from the extracellular fluid into the cytoplasm of neurons
|
|
|
The increase of calcium in the extracellular fluid into the cytoplasm of neurons causes vesicles to fuse with the adrenergic cell membrane and to release what?
|
norepinephrine by exocytosis
|
|
|
Which receptor is present on post synaptic membrane?
|
alpha 1 receptors
|
|
|
Nitric Oxide has effects in: (3)
What part of neuron released from? |
* responsible for penile erection is nitric oxide.
* also has GI and vascular effects. (Note: these autonomic nerves release Nitric oxide from postganglionic terminal end at effector junction.) |
|
|
Most important components of ANS are _____ nerve tracts
|
EFFERENT out flow tracts nerve tracts which supply motor innervation to visceral structure.
|
|
|
Catecholamines
|
epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and dopamine,
|
|
|
What class of drugs are not effective orally because they undergo metabolism by conjugation and oxidation in the GI mucosa and liver?
|
Catecholamines
|
|
|
When should administering dopamine be avoided?
|
in patients recieving MAO inhibitors or taking tricyclic antidipressants
|
|
|
What should happen before dopamine is given to patients in shock?
|
hypovolemia should be corrected by transfusion of whole blood, plasma, etc.
|
|
|
Why is absorption of catecholamines very slow subQ?
|
Causes local vasoconstriction
|
|
|
What two enzymes metabolize epinephrine?
|
COMT (catechol O-methyl transferase)
MAO (mono amine oxidase) excreted in the urine |
|
|
Epinephrine injection is available in what concentrations?
|
1:1,000
1:10,000 |
|
|
What are some therapeutic uses of catecholamines?
|
Relieve respiratory distress due to bronchospasm
Hypotension Cardiac effects Rapid relief of hypersensitivity rxn to drugs PROLONGS the action of *local anesthetic drugs* (b/c of vasoconstrictiing affect) Topical hemostatic agent on bleeding surfaces |
|
|
What are some adverse effects of catecholamines?
|
fear, anxiety
Hypertension with headache Cerebral haemorrhage Cardiac arrhythmia Necrosis of tissue |
|
|
When are catecholamines contraindicated?
|
In pregnancies (incuces contraction of uterus)
|
|
|
What neurotransmitter is responsible for regulation of movement (motor activity) and is a substrate for both MAO and COMT?
|
Dopamine
|
|
|
At low concentrations what receptor does dopamine interact with?
|
D1-dopaminergic receptors
|
|
|
What effect does dopamine have on the body at low concentrations?
|
Increases GFR
Increases renal blood flow Increases Na excretion |
|
|
At medium-high doses what receptor does dopamine interact with?
What affect does it have on body? |
B1 receptors, exerts positive inotropic effect on myocardium
|
|
|
At very high concentrations what receptor does dopamine interact with?
|
Alpha1 adrenergic receptors, vasoconstriction
|
|
|
How is dopamine hydrochloride administered?
|
IV only
|
|
|
What are some therapeutic uses of dopamine?
|
Treatment of shock
Beneficial to patients with oliguria |
|
|
Dopamine hydrochloride is used only by what route?
|
IV only
|
|
|
At medium-high doses what receptor does dopamine interact with?
|
B1 receptors, exerts positive inotropic effect on myocardium
alpha-1 at very high |

