![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Ummm... |

|
|

|

|
|
|
Where is half of all water that enters the gut absorbed? |
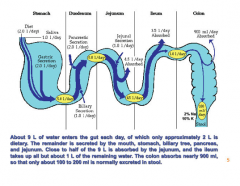
Jejunum |
|
|
What are the five groups of laxatives? |

|
|
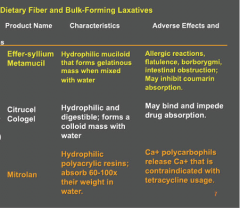
Identity the product associate with each:
Polycarbophils, semisynthetic celluloses, and psyllium husk |

|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of functional fiber? What is the net result? |

Most beneficial form of fiber is dietary |
|
|
What are the three surfactant laxatives? |
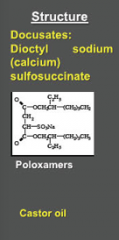
|
|

Which surfactant laxative is this? |
Ducosates: dioctyl sodium
Sulfosuccinate
Anion surfactant = salt Castor oil also increases intestinal motility |
|

Which surfactant laxative is this? |
Poloxamers |
|

Which surfactant laxative is this? |
Castor oil |
|
|
Where do stimulant laxatives act? What do they increase the permeability of? What is their effect on water and electrolytes? Effect on contractility of colon? Effect on prostaglandin synthesis and intestinal secretions? |
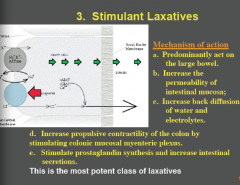
Increase the permeability of the intestinal mucosa
MOST POTENT CLASS OF LAXATIVES |
|
|
What are the two stimulant laxatives? |
Diphenymethanes Anthraquinones |
|

Which stimulant laxative is this? |
Diphenymethanes |
|

Which stimulant laxative is this? |
Antraquinones |
|
|
What are laxatives that contain magnesium cations or other non absorbable molecules? They exert an osmotic effect which does what? |

|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of the magnesium containing laxatives? What are some examples?
How are phosphate laxatives given? |

|
|
|
What are three examples of non digestible sugars and alcohols? |
Lactulose Glycerin Polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution |
|

Which osmotic laxative is this? |
Lactulose |
|

|

|
|
|
What is a mixture of hydrocarbons that penetrates and softens the stool?
What is an emulsion that irritates the mucosa and produces a cathartic effect? |

|
|
|
What is a condition of abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, and constipation of unknown etiology? What two drugs are used to treat it? |

|
|
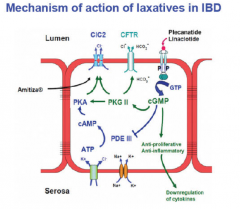
|
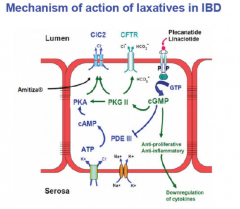
|
|
|
What can overuse of laxatives result in?
If continued, what can occur? |

|
|
|
What are the three major groups of antidiarrheal agents? |
1. Agents that absorb water 2. Absorbers of etiological factors in the lumen 3. Agents that alter intestinal motility |
|

What category of antidiarrheal agents do these belong in? |
Agents that absorb water |
|

What category of antidiarrheal agents do these belong in? |

|
|
|
What category of antidiarrheal agents do opiates belong in?
What is the effect of opiates on the following: Secretions, motility, muscle tone, sphincter tone, cramping, SUMMATIVE EFFECTS? |

|
|
|
What are three opiate antidiarrheal agents?
Which one is marketed with atropine?
Which one interacts with intestinal opioid receptors and binds to and inhibits the calcium-binding protein calmodulin? |

|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of anticholinergics? |

|
|
|
What are two examples of anticholinergics? Do they cross the BBB? Any CNS effects? What are useful in eliminating? Does atropine cross BBB and cause CNS effects?
Which drug is more suited to alleviate cramps? |

Atropine does cross BBB => CNS effects |
|
|
What are the two main categories of chronic inflammatory diseases of the GI tract? |

|
|

Seriously? |

|
|
|
What two major categories of drugs are used to treat inflammatory bowel diseases? |
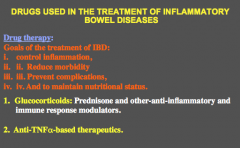
|
|
|
Is a monoclonal antibody that is a fusion against tumor necrosis factor- alpha. Given IV to patients with Crohn’s disease to mop up TNF-alpha. In most cases it is given with immunosuppressive therapy i.e with mercaptopurin).
Which drug is this? |
Infliximab |
|
|
is a fusion protein containing the ligand binding portion of TNF# receptor linked to the Fc portion of human IgG1. It binds TNF-# and prevents it from interacting with its receptor. Side effects similar to infliximab, but does not require concomitant immunosuppressive therapy.
Which drug is this? |
Enteracept |
|
|
Is a humanized mAb to TNF-alpha.
Which drug? |
Adalimumab |
|
|
It works by inhibiting certain immune cell molecules — integrins — from binding to cells in the intestinal lining.
Which drug? |
Natalizumab |
|
|
What are the components of 5-aminosalicylic acid derivatives? How does each work?
Which drug has less SE than sulfasalazine?
What drug is an immune suppressant antimetabolite? |

|
|
|
What are the three drug treatments for portal systemic encephalopathy (consequence of liver failure => increased blood ammonia)?
Which drug is a semisynthetic disaccharide metabolized by enteric bacteria to organic acids?
What type of drug is it therefore? What does acidification of the stool do? |
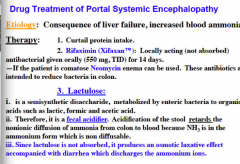
|
|
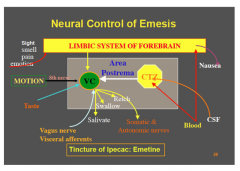
Draw this out I suppose... |

|
|
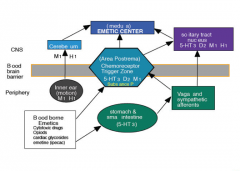
Draw this... |
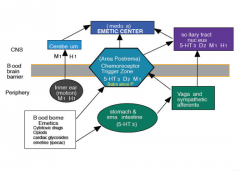
|
|
|
What is an anticholinergic prophylactic only for motion sickness arising from short or long term exposure to severe motion?
What is the mechanism of action? Any side effects? |

|
|
|
What older histamines can you use for motion sickness? |

|
|
|
How can antidopaminergics be used as anti emetics?
What is a centrally acting anticholingeric as well as antidopaminergic that is used?
Which drug is a poor antipsychotic but highly useful antiemetic?
Which drug inhibits the CTZ and VC? |
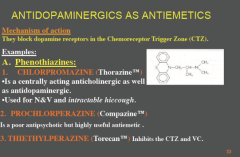
|
|
|
What drug is a butyophenone derivative that blocks dopaminergic receptors in the CTZ? Used clinically post operatively for nausea and vomiting? |
Droperidol |
|
|
What are the two benzamide derivatives? MOA of each? |

|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of the serotonin (5-HT) antagonists? What receptors do they block in the stomach and in the small intestine?
Are these agent the most effective anti emetics? |

|
|
|
What are some examples of antiemetic serotonin agonists?
Which one is effective for preventing emesis by high dose of cytotoxic drugs?
Which one is more potent? Which has a longer half life? Which available IV?
Administration of 5HT3-receptor blockers with which drug increases their potency? |

|
|
|
What drugs are used only when patients fail to respond to other anti emetics? |

|
|
|
Do corticosteroids enhance the overall antiemitic effect? How? |

|
|
|
How does Aprepitant prevent emesis induced by cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents? Does it cross the BBB?
Any CYP metabolism? |

|
|
|
What type of vomiting is benzodiazepene used for? |

|

