![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
155 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does PARENTERAL mean?
|
-admin by any route other than the enteral, or GI tract.
|
|
|
PARENTERAL refers to?
|
-Intradermal
-subcut -IM -IV |
|
|
3 differences in given a drug Parenterally rather than orally?
|
Parenterally
**1. onset of drug action is generally more RAPID, But of SHORTER duration 2. dose is smaller b/c drug potency tends Not to be Immediately altered by the stomach or live 3. Drug cost is greater |
|
|
4 Uses of Parenteral Route?
|
1. to provide a rapid onset of action
2. to ensure a high blood level of the drug (Bioavailabity < 100%) 3. Not able to take meds orally (NPO, N/V, commatose, No PEG tube) 4. Med can only be given parenterally |
|
|
What are 4 reasons why the injections of drugs require skill and special care?
|
1. trauma at injection site
2. possibility of infection 3. chance of allergic reaction 4. drug is Irretrievable |
|
|
ASPEPTIC Technique is used to?
|
-avoid infection
-accurate drug dosing, along w/ correct rate and site of injection, is followed to avoid injury |
|
|
Injuries that could occur at the site of Injection?
|
-abscess formation
-necrosis -skin sloughing -nerve injuries -prolonged pain -periostitis |
|
|
Periostitis?
|
Inflammation of the periosteum, a dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue that closely wraps (invests) all bone, except the bone of articulating surfaces in joints which are covered by synovial membranes
|
|
|
1/3 of All "sharps" injuries are related to?
|
-The disposal process
|
|
|
What are the 3 primary safety concerns, nursing have?
|
1. patient
2. themselves 3. other healthcare workers |
|
|
What must be practiced to avoid "sharpes" injuries?
|
-Safety
|
|
|
PLUNGER:
|
-Inner cylindrical portion the fits snugly into the barrel
-Used to draw up and eject the solution from the syringe |
|
|
TIP of syringes?
|
-portion that holds Needle
|
|
|
BARREL of a syringe?
|
-outer portion
-where the calibrations ofor the measurement of the drug volume are located |
|
|
PLUNGER:
|
-Inner cylindrical portion the fits snugly into the barrel
-Used to draw up and eject the solution from the syringe |
|
|
TIP of syringes?
|
-portion that holds Needle
|
|
|
BARREL of a syringe?
|
-outer portion
-where the calibrations ofor the measurement of the drug volume are located |
|
|
All syringes are available with what type of TIP?
|
-Either a Luer Slip or a Luer Lock tip
|
|
|
What are the 2 parts of a Luer system?
|
-male tapered end
-the reverse tapered female connector flange (p147) |
|
|
TIP of syringes?
|
-portion that holds Needle
|
|
|
BARREL of a syringe?
|
-outer portion
-where the calibrations ofor the measurement of the drug volume are located |
|
|
All syringes are available with what type of TIP?
|
-Either a Luer Slip or a Luer Lock tip
|
|
|
What are the 2 parts of a Luer system?
|
-male tapered end
-the reverse tapered female connector flange (p147) |
|
|
What are the 2 types of Syringe Tips?
|
-Luer Slip= a male tapered, plain tip (connection is only relatively secure)
-Luer Lock= threaded locking collar outside the male luer slip, that will lock the flange of the female connector securely, "locking" it in place |
|
|
What are the advantages of a GLASS Syringe?
|
-economy
-easy-to-read calibrations -availability in a wide range of sizes -can be cleaned, packaged, sterilized & reused |
|
|
What are the Disadvantages of a GLASS syringe?
|
-eaily breakable
-time consuming to clean & sterilize -plunger may become loose w/ extended use, causing med to "creep" b/w plunger and barrel= Resulting in a inaccurate dose admin to pt |
|
|
What are the advantages of a PLASTIC syringe?
|
-availability in sizes
-prepackaging w/ and w/o neddles in a vareity of gauges and needle lengths -disposability -convenience |
|
|
What are the Disadvantages of a PLASTIC syringe?
|
-expense
-one-time use -sometimes, unclear calibrations |
|
|
What are the advantages of a GLASS Syringe?
|
-economy
-easy-to-read calibrations -availability in a wide range of sizes -can be cleaned, packaged, sterilized & reused |
|
|
What are the advantages of a PLASTIC syringe?
|
-availability in sizes
-prepackaging w/ and w/o neddles in a vareity of gauges and needle lengths -disposability -convenience |
|
|
Milliliter?
|
-measure of Volume
|
|
|
The Shorter lines on a syringe represents?
|
- O.1mL
|
|
|
The Longer lines on a syringe represents?
|
- 0.5ml
|
|
|
What size syringe is used when administering < 0.5 mL
|
** 1mL syringe
|
|
|
Longest line on a Tuberculin syringe represents?
|
- 0.1 (1/10) ml
|
|
|
Intermediate line on a tuberculin syringe represents?
|
- 0.05 (5/100)
|
|
|
Shortest line on a tuberculin syringe represents?
|
-0.01 (1/100)
|
|
|
Where are the Volumes read on a Glass syringe?
|
-at the point where the plunger is directly parallel w/ the calibration on the syringe
|
|
|
Where are the Volumes read on a Plastic syringe?
|
-rubber flange of the syringe plunger is parallel to the calibration scale
|
|
|
PREFILLED SYRINGE?
|
-premeasured amt of med in a Disposable cartridge-needle unit
-Carpuject -Tubex |
|
|
What are the Advantages of a PREFILLED SYRINGE?
|
-time saved in preparation
-diminishes chance of contamination b/w patient & nurse (the cartridge is in a sealed unit, used Once and discarded) |
|
|
What are the Disadvantages of a PREFILLED SYRINGE?
|
-additional expenses
-need for diff holders for diff cartridges -limitation of Volume of a second med that may be added to the cartridge |
|
|
Insulin is inserted in ______ tissue
|
-subcutaneous
|
|
|
INSULIN PEN
|
-pre-filled syringe
|
|
|
EPI PEN?
|
-disposable automatic injection, prefilled w/ Epinephrine
-use w/ allergy to Insect bites, food, drugs |
|
|
NEEDLE GAUGE?
|
-diameter of the hole through the needle
**the Larger the gauge number (ie. 28g), the Smaller the hole -gauge is selected based on the viscosity (thickness) of the solution |
|
|
3 parts of a Needle?
|
-hub
-shaft -beveled tip |
|
|
3 Factors that determine what size of syringe to choose?
|
-volume of med to admin
-degree of accuracy needed to measure dose -type of med to admin |
|
|
Needle Selection is based on?
|
-viscosity of the solution
-correct needle length for delivery of med to correct site |
|
|
Maximum Volume for IM injections at one site in small children and older adults?
|
-1mL
|
|
|
Max. Volume & needle length for small infants?
|
-0.5mL
-1/2 in needle |
|
|
Max. Volume for older children?
|
-Individualized
|
|
|
*Volume for INTRADERMAL (ID) route?
|
-0.01mL - 0.1mL
|
|
|
*Gauge for ID route?
|
26-29 gauge
|
|
|
*Needle Length for ID route?
|
-3/8" - 1/2"
|
|
|
*Volume for SUBCUT route?
|
-0.5mL - 1mL
|
|
|
*Gauge for SUBCUT route?
|
-25-27 gauge
|
|
|
*Needle Length for SUBCUT route
|
-individualize based on depth of appropriate tissue at site
|
|
|
*Volume for IM route?
|
-0.5mL - 3mL
|
|
|
*Gauge for IM route?
|
-20-22 gauge
|
|
|
*Needle Length for IM route?
|
-individualize based on depth of appropriate tissue at site
|
|
|
*Volume for IV route?
|
1-2000mL
|
|
|
*Gauge for IV route?
|
-20-22 gauge (solutions)
-15-19 gauge (blood) |
|
|
*Length of Needle for IV route?
|
- solutions= 1/2" -1 1/4" (butterfly)
-Blood= 1/2" - 2" (regular needles) |
|
|
How many inches remain above the the skin surface when the injection is admin.?
|
-1/4" to 1/2"
(consider this when judging the needle length) |
|
|
HYPODERMIC syringes?
|
-AKA =standard syringe
-available in 3mL - 60mL |
|
|
When does OSHA require NEEDLELESS Systems to be used? (3)
|
1. collection of body fluids or withdrawal of body fluids after initial venous arterial access is established
2. admin of meds or fluids 3. any other procedure involving the potential for occupational exposure to blood-borne pathogens as a result of percutaneous injuries for contaminated sharps |
|
|
What is an example of a needleless system?
|
-IV med delivery system that admin meds or fluids through a catheter port or connector site using a blunt cannula
|
|
|
BLUNT ACCESS DEVICE(spike)?
|
-a safey innovation created to reduce the freq of needle injuries
-spike is used when drawing liquid from a rubber diaphragm-covered-vial |
|
|
FILTER Needle?
|
-a type of blunt device
-contains an internal filter -used to draw liquid from an ampule -filter screens out glass particles from ampule |
|
|
Advantages of Blunt access devices?
|
-preventing needle sticks
-nurse can draw up larger amts of fluid volumes faster |
|
|
BD Safety-Lok Syringe provides?
|
-a sleeve that is stored around the syringe barrel p. 153
-after admin sleeve is pulled forward fully, locking the shield in place, covering needle |
|
|
BD Safety Glide shielding Hypodermic needle?
|
device attached to the needle hub
-after injection, nurse pushed hinged shield forward, covering needle |
|
|
BD SafetyGlide Syringe TIny Needle?
|
available for short needles
|
|
|
AMPULES
|
-glass container
-contain a single dose -marking on ampule is the location where the ampule is broken open P.154 |
|
|
VIALS?
|
-glass container w/ 1 or more doses
-can use spike to withdrawal med |
|
|
MIX-O-VIALS?
|
-glass container w/ 1 dose, 2 compartments
-LOWER chamber contains the drug (Solute) -UPPER chamber contains a sterile diluent (Solvent) p154(picture) |
|
|
What equipment is needed for preparation of Parenteral Meds?
|
-drug in sterile, sealing container
-syringe of the correct volume -needles of the correct gauge and length -needleless access device -antiseptic swab -MAR or Medication profile |
|
|
What is the Technique for preparing ALL Parenteral Meds?
|
1. Wash hands
-keep "sterile to sterile" & "unsterile to unsterile" when handling the syringe and needle2. 5 Rights (Patient, Drug, Route, Dose, Time) 3. check drug dose form ordered against the source you are holding 4. check compatibility chart 5. check med calcuations (heparin & insulin, hospital may require calcul. to be checked by 2 nurses) 6. Prepare drug using aseptic tech 7. check exp date |
|
|
What is the technique for preparing a med from an Ampule?
|
1. move all solution to the bottom of the ampule (by flicking side of container)
2. cover ampule neck w/ a sterile gauze or antiseptic swab while breaking the top off 3. use filter needle 4. remove needle from ampule & point Vertically 5. pull back the plunger, replace the aspiration needle w/ a new sterile needle 6. push plunger until med is at tip of needle |
|
|
Diluent?
|
Solvent
|
|
|
Solute?
|
Drug
|
|
|
*What do you label on a Reconstituted Medication Label?
|
-date/time mixed
-resulting dosage supply -date/time expired -initials/title |
|
|
*What is labeled on a multi-use vial after opeing ?
|
-date
-time -initials -check agency policy regarding when to discard |
|
|
What is the tech for preparing a med from a vial?
|
p. 156-158
|
|
|
Preparing a Drug from a Mix-O-Vial?
|
p159
|
|
|
What is the absorption rate for INTRADERMAL Sites?
|
-SLOW
-usually 0.1mL |
|
|
What layer of skin of the intradermal injection?
|
- DERMAL Layer of skin just below the epidermis
|
|
|
Intradermal is the route of choice for what injections?
|
-allergy sensitivity test
-desensitization injection -local anesthetics vaccinations |
|
|
What meds should a client NOT take within 24-48 hrs of local anesthetics and skin testing (intradermal route)
|
-Antihistamines
-anti-inflammatory -Immunosuppressant= prednisone |
|
|
Read a PPD test w/in ___ hours?
|
-48 to 72 hrs
*don't massage intradermal sites after injections |
|
|
What are the most common injection sites for Intradermal?
|
-upper chest
-scapular areas of the back -inner aspect of the forearms |
|
|
What route of injections requires site to be hairles and recive little friction from clothing?
|
-Intradermal
|
|
|
What is the gauge and length used for a Intradermal route?
|
-26-29 gauge
3/8" to 1/2" length ONLY insert bevel of needle |
|
|
Do NOT start any type of allergy testing unless _______ _____ is available in immediate area?
|
-Emergency equipment (in case of an Anaphylactic response
|
|
|
What are some examples of an Antiinflammatory agent?
|
-ASA
-Ibuprofen -corticosteroids |
|
|
PPD
|
-purified protein derivative
-ask if ever had a positive result |
|
|
Usual dose for a TB skin test?
|
-5 units
|
|
|
When reading a TB skin test what is the nursing observing for?
|
-erythema (redness)
-induration ((a hard, raised area with clearly defined margins at and around the injection site) record area in mm |
|
|
Longer absorption/longer duration?
|
-Subcut
|
|
|
Faster absorption/shorter duration?
|
-Intramuscular
|
|
|
What is the degree of the angle for Intradermal injection?
|
15
|
|
|
No reaction to the allergens, especially the positive control is know as ?
|
-ANERGIC reaction
|
|
|
Injections are made into the loose connective tissue b/w the Dermis and Muscle Layer?
|
-SUBCUTANEOUS (subcut)
|
|
|
Common drugs that are injected into the subcu tissue?
|
-insulin
-heparin |
|
|
Commom sites for Subcut injections?
|
-upper arm
-anterior thighs -abdomen Less common areas buttocks upper back scapular region |
|
|
Never admin greater than ___ ml at subcut site?
|
-1mL
|
|
|
What gauge and length needle used used w/ SUBCUTANEOUS ROUTE?
|
-25-27 g
- 3/8", 1/2", 5/8" |
|
|
Angle of injection for SUBCUTANEOUS ROUTE?
|
- 45-90 degree angle
|
|
|
With subcutaneous route, what is the angle of injection, if able to pitch 2" of skin?
|
-insert needle at 90 degree angle
|
|
|
With subcutaneous route, what is the angle of injection, if able to pitch 1" of skin?
|
-insert at 45 degree angle
if pitch < 2", insert at 45 degree angle |
|
|
Where is the only injection site for HEPARIN?
|
-Stomach (2" away from umbilicus & scars)
|
|
|
Where is the ONLY injection site for LOVENOX?
|
-Love handles
|
|
|
Injection site for INSULIN?
|
-abdomen
-legs -back -any subcut sites |
|
|
Subcutaneous Injection sites?
|
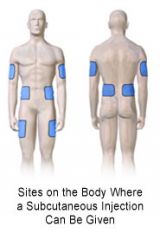
-upper arms (outer aspect)
-anterior thighs -abdomen (from below the costal margin to the iliac crests) -Less Common- buttocks upper back scapular region of upper back |
|
|
Absorption is slower and drug action is longer?
|
-SUBCUT
|
|
|
Where is the drug absorbed w/ SUCUT injection?
|
if circulation is adequate, the drug is completely absorbed from the TISSUE
|
|
|
What is the Pre-Assessment before administering HEPARIN?
|
-draw PTT levels and INR
INR-international ratio level *Never admin w/o checking lab values DAILY* |
|
|
What do you NOT do when administering HEPARIN (2)?
|
-Do NOT aspirate
-Do NOT MASSAGE (may cause hematoma, bruise=contusion) |
|
|
What function class is HEPARIN?
|
-anticoagulant
-anti-thrombotic |
|
|
What pre-assessment is performed before administering INSULIN?
|
-blood glucose
-check order on chart *always check blood glucose levels before administering insulin* |
|
|
What do you NOT do when administering INSULIN?
|
-do NOT aspirate
-do NOT massage (may form hematoma, bruising) |
|
|
a collection of blood outside of a blood vessel. It occurs because the wall of a blood vessel wall, artery, vein or capillary, has been damaged and blood has leaked into tissues where it does not belong.
|
HEMATOMA
|
|
|
When adminstering Insulin, it is important to _____ _____.
Why? |
-rotate sites
*admin to prevent lipohypertrophy or lipoatrophy, slows the absorption rate of insulin |
|
|
How should insulin injection sites be rotated?
|
-rotate SYSTEMATICALLY, w/in 1 area before progressing to a new site
|
|
|
When injecting insulin, why rotate sites systematically?
|
-to decrease variations in absorption
|
|
|
Absorption of INSULIN is known to be fastest if absorbed, Where?
|
-abdomen followed by arms, thighs, and buttocks
|
|
|
What will affect absorption rate of INSULIN?
|
-Exercise (site selection should take this factor into consideration)
|
|
|
Why rotating sites of injection for INSULIN important?
|
-Enhance drug absorption
-prevent LipoDystrophy -prevent LipoHypertrophy -preserve tissue integrity -promote comfort |
|
|
LipoDystrophy?
|
-disorder of adipose (fatty) tissue characterized by a selective loss of body fat. Patients with lipodystrophy have a tendency to develop insulin resistance, diabetes, a high triglyceride level (hypertriglyceridemia), and fatty liver
|
|
|
localized hypertrophy of subcutaneous fat at insulin injection sites caused by the lipogenic effect of insulin.
|
LipoHypertrophy
|
|
|
When does the nurse Check the accurracy of the drug order against the med being prepared?
|
-when 1st removing drug from storage area
-immediately after preparation storage area -immediately before administration |
|
|
What is the rational for adding air to the syringe AFTER accurately measuring the prescribed volume of drug?
|
-it will result in the needle being completely cleared of all medication at the time of injection
|
|
|
IM injections penetrate what layers of skin?
|
-epidermis
-dermis -subcutaneous -MUSCLE layer |
|
|
IM injections are more rapidly absorbed than _______ injections.
Why? |
-Subcut b/c muscle tissue has a greater blood supply
|
|
|
Why is site selection so important w/ IM injections?
|
-incorrect placement of needle may cause damage to nerves or blood vessels
|
|
|
What factors influence IM syringe size that corresponds to the: (5)
|
-volume of drug to be injected at 1 site
-type of med -site of admin' -thickness of subcut fatty tissue -age |
|
|
Gauge and Needle size for IM injection?
|
-Needle: 1 to 1 1/2" (based on pt size, needles go up to 3", ie. 400lb pt)
Gauge: 20-22 gauge |
|
|
Always inject IM at ____ degree angle?
|
-90
|
|
|
What is the max volume for deltoid muscle?
|
-no more than 1mL
|
|
|
When injecting, HOw much of the needle should be extending above the skin surface?
|
1/4"
-consider this when estimating needle length for the pt |
|
|
How is the VENTROGLUTEAL site located?
|
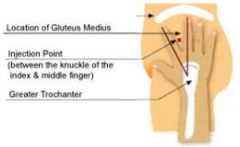
-use opposite hand (Left)
-place heal/palm of hand over greater trochanter (lateral portion) -wrist perpendicular to femur -point thumb toware groin & fingers toward client's head -index finger on the anterior superior iliac spine -extend middle finger back along the iliac crest toward the buttock -a "V" is formed b/w index & middle finger -Make injection site into center of the "V" |
|
|
Preferred injection site for infants?
|
-Vastus Lateralis
|
|
|
What injection site must NOT be used in children younger thatn 3 years old?
|
-Gluteal area b/c muscle is not well developed for walking
|
|
|
In what clients should the nurse carefully assess the sufficiency of the muscle mass before using the Vastus Lateralis site of injections?
|
-older adult
-debilitated adult -nonambulatory adult |
|
|
Where is the location of the RECTUS FEMORIS?
|
-lies medial to the Vastus lateralis but does not cross the midline of the anterior thigh
|
|
|
How is the injection site for RECTUS FEMORIS muscle located
|
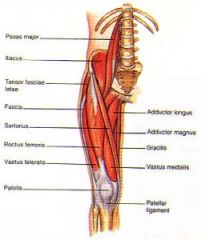
-same as vastus lateralis
(one handbreadth above the knee to 1 handbreadth below the greater trochanter) site maybe used in both children and adults when other sites are unavailable. |
|
|
What is the Primary Advantage to using the RECTUS FEMORIS site for injections?
|
-used more easily by patients for self -admin
|
|
|
What is the DISAdvantage to using the RECTUS FEMORIS site for injections?
|
-the medial border is close to the sciatic nerve and blood vessels
|
|
|
What is the MAX volume of injection for the VENTROGLUTEAL muscle?
|
-3 mL
-it's a Large muscle |
|
|
What are the Advantages for using the VENTROGLUTEAL muscle for injections?
|
-deep and away from major nerves and blood vessels
|
|
|
What is the preferred injection site for small or debilitated clients?
|
-VENTROGLUTEAL
|
|
|
Reaction readings of an allergy test
-1+ -2+ -3+ -4+ |
1+ No wheal, 3mm flare
2+ 2 to 3mm wheal w/ flare 3+ 3 to 5 mm wheal w/ flare 4+ >5 mm -a positive reaction to delayed hypersensitivity skin testing requires an induration of at least 5mm in diameter |
|
|
What is the gauge and needle length used for Pediatric IM injections?
|
25 to 26 gauge
1" to 1 1/2" needle ie 15 month old (question from book) |
|
|
Do not aspirate when giving what 2 meds, Subcut?
|
-heparin
-insulin |

