![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
2 corticosteroids used in immunopharmacology
|
1. Prednisone
2. Methylprednisone |
|
|
|
Prednisone & Methylprednisone:
-inhibition of __1__ and __2__ synthesis -Cytotoxic to certain __3__ subpopulations -Suppress both __4__ and __5__ immunity -inhibition of __6__ at the site of inflammation -interference in the function of __7__ of inflammatory response |
1. prostaglandin
2. leukotriene 3. T-cell subpopulations = helper and suppressor 4. cellular 5. humoral 6. leukocyte infiltration 7. mediators ***inhibit Phospholipase A2 |
|
|
|
What is the major advantage of Prednisone over other drugs such as Methotrexate and Cyclophosphamides
|
Not toxic to Myeloid and Erythroid stem cells = no anemias
|
|
|
|
ADR of this immunosuppressive agent can cause Adrenal gland suppression = Cushing-like side effects = weight gain, HTN
|
Prednisone
|
|
|
|
Prednisone is used as immunosuppressive agent for these 3 things
|
1. Organ transplantation
2. Autoimmune diseases 3. Bronchial asthma |
|
|
|
Azathioprine is converted to __1__ by __2__ and then to __3__ by __4__
|
1. 6-mercaptopurine
2. Glutathione-S-transferase 3. 6-thiouric acid 4. Xanthine Oxidase |
|
|
|
You must reduce the dose of Azathioprine in patients with this deficiency
|
Thiopurine Methyltransferase deficiency
*also Glutathione-S-transferase deficiency |
|
|
|
Antimetabolite derivative of 6-mercaptopurine that interferes with the METABOLISM and SYNTHESIS of Nucleic Acids → inhibits cell proliferation
|
Azathioprine
|
|
|
|
Azathioprine is toxic to __1__ following __2__ exposure
|
1. proliferating lymphocytes
2. antigen |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of Azathioprine?
|
1. Leukopenia
2. Anemia 3. Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of Azathioprine at high doses?
|
1. Skin rashes
2. Fever 3. NVD 4. GI disturbances |
|
|
|
What 2 things increase the adverse effects of Azathioprine?
|
1. Kidney disease
2. Allopurinol (Xanthine oxidase inhibitor) |
|
|
|
What are the 2 uses of Azathioprine?
|
1. Kidney transplantation
2. Autoimmune diseases |
|
|
|
This is the most potent immunosuppressive agent
|
Cyclophosphamide
|
|
|
|
What does Cyclophosphamide destroy?
|
Proliferating lymphoid cells in addition to some quiescent cells
|
|
|
|
What are the uses of Cyclophosphamide?
|
1. Organ transplantation
2. Autoimmune diseases |
|
|
|
What is Methotrexate's mechanism of action?
|
inhibits Dihydrofolate reductase = blocks folate requiring rxns in the biosynthesis of nucleotides needed for cell proliferation
|
|
|
|
Immunopharmacologic drug that is toxic to proliferating lymphocytes following antigen exposure
|
Methotrexate = DHFRI
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 clinical uses of Methotrexate?
|
1. Prophylaxis for graft vs. host syndrome for BM transplantation in Leukemia patients
2. Active RA 3. Psoriasis |
|
|
|
What is the source of Cyclosporine?
|
Polypeptide antibiotic produced by certain fungi
|
|
|
|
Complexes with Cyclophilin → inhibits Calcineurin = blocks production of CYTOKINES by ANTIGEN-STIMULATED T-HELPER CELLS that otherwise stimulate T-cell growth and differentiation
|
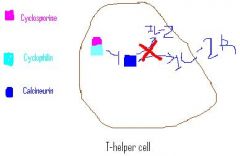
Cyclosporine
|
|
|
|
What does Cyclosporine not affect?
|
1. suppressor T-cells
2. T-cell independent, antibody-mediated immunity |
|
|
|
inhibit the production and/or release of various lymphokines including IL-1 and IL-2; in turn, the actions of T-helper cells, the agents of cellular immunity and tissue rejection, are impaired
|
Cyclosporine
|
|
|
|
How is Cyclosporine administered?
|
Orally
Intravenously |
|
|
|
Cyclosporine:
-after oral administration, roughly __1__% is absorbed due to __2__ |
1. 20-50%
2. "first-pass" metabolism |
|
|
|
What CYP is Cyclosporine metabolized extensively by?
|
CYP 3A4
*metabolized to at least 25 metabolites, some of which are biologically active |
|
|
|
What are the 9 drugs that decrease the clearance of Cyclosporine via inhibition of hepatic microsomal enzymes (hint)
|
1. Androgens
2. Clarithromycin 3. Diltiazem 4. Erythromycin 5. Estrogens 6. Nefazodone 7. Nicardipine 8. Verapamil 9. Azole antifungal drugs |
DAVE CANEN increases Cyclosporine
|
|
|
Drugs that increase the clearance of Cyclosporine by stimulating its metabolism may lead to what?
|
Graft rejection
|
|
|
|
What are 4 drugs / groups of drugs that may lead to increased Cyclosporine clearance? (hint)
|
1. Nafcillin
2. Omeprazole 3. Rifampin 4. Anticonvulsants - Carbamazepine - Phenytoin - Phenobarbital - Primidone - St. John's Wort |
"NORA" clears Cyclosporine and causes Graft Rejection
|
|
|
What is the most common adverse effect of Cyclosporine?
What is a less common effect? |
Nephrotoxicity
Seizures |
|
|
|
What is used to minimize the Nephrotoxicity of Cyclosporine?
Explain its mechanism of action |
Clonidine
Alpha-2 agonist -> decreases sympathetic outflow = decrease in vasoconstriction of the kidney vessels = decreases Ischemic Kidney |
|
|
|
Additive nephrotoxicity of Cyclosporine occurs if it is administered with what other nephrotoxic agents? (6) (Hint)
|
1. Amphotericin B
2. Acyclovir 3. Aminoglycosides 4. Foscarnet 5. NSAIDs 6. Vancomycin |
Cyclosporine is A FAN of VAns that hurt the kidneys
|
|
|
What is the main use of Cyclosporine?
What other things is it used for? |
Main: to prevent Allograft rejection
Others: autoimmune conditions - Uveitis - Psoriasis - Type 1 Diabetes - RA - IBD - certain Nephropathies |
|
|
|
Macrolide derived from a fungus with similar pharmacokinetics to Cyclosporine
|
Tacrolimus
|
|
|
|
More effective in ACUTE REJECTION than in chronic rejection and is a MORE POTENT immunosuppressant than cyclosporine
|
Tacrolimus
|
|
|
|
Compare the Tacrolimus adverse effects in relation to Cyclosporine
|
Overall Tacrolimus adverse effects are greater than Cyclosporine
BUT, kidney toxicity is less than cyclosporine |
|
|
|
Tacrolimus:
1. Administration? 2. Uses |
1. Oral & Parenteral
2. Prophylaxis of Liver allograft rejection -effective for other organ transplants as well |
|
|
|
This is a prodrug for the immunosuppressive agent Mycophenolic acid
|
Mycophenolate Mofetil
|
|
|
|
Inhibits the "de novo" PURINE pathway and Is used in conjunction with cyclosporine and corticosteroids for the prevention of rejection in patients with a renal allograft
|
Mycophenolate Mofetil
|
|
|
|
Used in conjunction with Cyclosporine and Corticosteroids for the prevention of rejection in patients with a Renal Allograft
Allows usage of LOWER doses of Cyclosporine = lessens adverse effects on kidneys |
Mycophenolate Mofetil
|
|
|
|
-Is a dimeric fusion protein produced by recombinant DNA technology that binds TNF
-It is a soluble TNF receptor -It is given by injection -Is effective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and works by decreasing the effects of TNF |
Etanercept (Enbrel)
|
|
|
|
What is Infliximab?
|
Chimeric monoclonal antibody that binds TNF-alpha
|
|
|
|
How is Infliximab administered and what is its terminal half-life?
|
IV infusion -> given at week 0, 2, 6 and thereafter, every 4-8 wks
8-12 days |
|
|
|
Infliximab is given with __1__ for the treatment of __2__
|
1. Methotrexate
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis |
|
|
|
Antibody used for Crohn's Disease when conventional therapy fails
|
Infliximab
|
|
|
|
What is the adverse effect of Infliximab?
|
may develop serious infections
|
|
|
|
monoclonal antibody that neutralizes TNF-alpha by binding to it and blocking its interaction with the p55 and p75 cell surface TNF receptors
|
Adalimumab
|
|
|
|
Neutralizes TNF-alpha and is given SUBCUTANEOUSLY every other week to patients who have had inadequate response to atleast one other DMARD
|
Adalimumab
|
|
|
|
What is Antithymocyte globulin?
|
Horse antibody against human T-lymphocytes
*also known as Lymphocyte Immune Globulin |
|
|
|
What does Antithymocyte globuin reduce the number of?
|
Circulating thymus-dependent lymphocytes, which alters T-cell function and ultimately affects cell-mediated immunity
|
|
|
|
Antibody that:
1. manages allograft rejection in Renal transplant patients 2. manages moderate to severe Aplastic Anemia in those unsuited for BM transplants |
Antithymocyte globulin
|
|
|
|
This is a parenteral monoclonal antibody of murine origin that targets CD3/TCR receptor complex
|
Muromonab-CD3
|
|
|
|
Parenteral monoclonal antibody of murine origin that targets CD3/TCR receptor complex
Treatment of ACUTE allograft rejection in patients who have undergone one of the following transplantations: 1. Kidney 2. Heart 3. Liver |
Muromonab-CD3
|
|
|
|
These 2 drugs are chimeric (murine/human) monoclonal antibodies (IgG1) produced by recombinant DNA technology that block the binding of IL-2 to its receptors (hint)
|
Daclizumab
Basiliximab |
Da-cliz and Basil inhibit IL-2
|
|
|
2 drugs that are used prophylactically in combo with Cyclosporine in patients undergoing Kidney transplantation
|
Daclizumab
Basiliximab |
|
|
|
Aside from being used in Rh-negative women, what else is Rh[D] Immune Globulin used to treat?
|
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic purpura
|
|
|
|
This is an antibody to the surface protein of RSV and is used prophylactically to prevent RSV infection
|
Palivizumab
|
"Paliv iz" RSV's enemy
|
|
|
What is used to TREAT serious RSV infections?
|
Ribavirin
|
|
|
|
This binds to CD52 antigen on normal and malignant B-lymphocytes
|
Alemtuzumab
*CD52 is also found on -T lymphocytes -NK cells -Macrophages -Platelets |
|
|
|
Antibody used to treat Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
|
Alemtuzumab
|
|
|
|
Directed towards the CD33 antigen on Leukemic cells and Myelomonocytic cells
Coupled to Calicheamicin, a cytotoxic molecule |
Gemtuzumab
|
Tangney (#33) wearing alot of Gems has just relapsed from Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
|
|
|
Antibody used to treat Acute Myelogenous Leukemia in adults over 60 years of age in first relapse and have a CD33-positive tumor
|
Gemtuzumab
|
|
|
|
What 2 drugs are used to treat Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma? (hint)
|
1. Rituximab
2. Tositumomab |
Ritu Tosits Non-Hodgkins Lymhoma
|
|
|
Antibody that binds to CD20 antigen on B-cells
|
Rituximab
|
|
|
|
Targets the CD20 antigen found on PRE-B and MATURE B-lymphocytes
|
Tositumomab
|
|
|
|
Rituximab is used in combo with __1__ to reduce the signs and symptoms of RA in adults who had inadequate responses to one or more __2__ therapies
|
1. Methotrexate
2. TNF antagonist |
|
|
|
This drug is used for the treatment of CD-20 positive follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma whose disease is refractory to Rituximab and has relapsed following chemotherapy
|
Tositumomab
|
|
|
|
Monoclonal antibody that binds to HER2 protein on the surface of tumor cells
-used for METASTATIC BREAST TUMORS that over express HER2 protein |
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
|
|
|
|
Monoclonal antibody that is an antagonist of Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor of platelets
-is used post-angioplasty and in acute coronary syndromes |
Abciximab
|
|
|
|
Monoclonal antibody that is directed towards the IgE high affinity Fc receptor on Mast cells
|
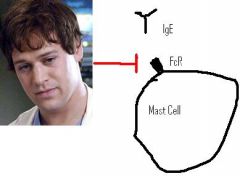
Omalizumab
|
|
|
|
Given Subcutaneously every 2-4 weeks for prophylaxis of Asthma and to control symptoms of moderate to severe Asthma not controlled by inhaled steroids
|
Omalizumab
|
|
|
|
What is Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), live intravesical used to treat? (2)
|
1. Bladder Carcinoma
2. Prophylactic against TB |
|
|
|
How does BCG treat bladder carcinoma?
|
-it is instilled into the bladder
-causes a local inflammatory rxn with histiocytic and leukocytic infiltration in the urinary bladder |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of BCG?
|
-Several urinary symptoms
-pretty much any kind of malaise |
|
|
|
Drug that is infamous for causing Phocomelia in the offspring of mothers who took it during pregnancy = arms are attached to the body
|
Thalidomide
|
|
|
|
Immunomodulator drug used to treat Leprosy
|
Thalidomide
|
|
|
|
What is IFN-alpha used to treat? (5)
|
1. Hairy-cell Leukemia
2. AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma 3. Condylomata acuminata 4. Chronic HBV 5. Chronic HCV |
|
|
|
What is IFN-beta produced by?
|
Fibroblasts
Epithelial cells |
|
|
|
What is IFN-beta used for?
Describe its mechanism |
Multiple Sclerosis
Exogenous IFN-beta offsets the activity of endogenous IFN-gamma, the agent responsible for triggering autoimmune rxn leading to Multiple Sclerosis |
|
|
|
What is recombinant IFN-gamma-1b derived from?
|
genetically engineered E. coli
|
|
|
|
What is IFN-gamma-1b used to treat?
|
Chronic Granulomatous disease
-inherited disorder of phagocytic oxidative metabolism -potent phagocyte-activating properties that result from enhancement of oxidative metabolism in tissue macrophages and enhancement of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and NK cell activity |
|
|
|
What is the most common side effect of all the IFN's?
|
Flu-like symptoms
|
|
|
|
This is a non-glycosylated biosynthetic IL-2 (hint)
|
Aldesleukin
|
Alde aisle 2
|
|
|
Immunomodulator used to treat Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
Aldesleukin (IL-2)
|
|
|
|
What 4 diseases is Aldesleukin currently being evaluated for treatment of?
|
1. Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
2. non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma 3. HIV infection 4. Leprosy |
|
|
|
Immunomodulator that is a synthetic IL-2 that induces proliferation and differentiation of B & T cells, monocytes, macrophages, and CTLs
|
Aldesleukin
|
|
|
|
How is Aldesleukin administered?
|
High dose IV bolus -> significant number of adverse rxns affecting almost every organ system
|
|
|
|
This is a recombinant version of IL-11
|
Oprelvekin (Neumega)
|
Oprah on channel 11 treats Thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
Recombinant IL-11 given subcutaneously once a day to prevent severe chemotherapy-induced Thrombocytopenia
|
Oprelvekin
|
|

