![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Drug that'll cause Parkinson’s-like symptoms |
antipsychotics i.e. haloperidol [halo - not real parkinson] phenothiazines [causes parkinson 'phenothype'
|
|
|
Parkinsonism is a Component of which other disorders ? |
Shy-Drager syndrome (disease is shy, but it doesnt' stop it from "dragging" someone into this whole parkinson-like thing) |
|
|
levodopa Neurological symptoms |
choreoathetosis/involuntary movements of face & distal extremities most common |
|
|
levodopa given in combo with? |
in combo with carbidopa |
|
|
why is carbidopa used? |
It inhibits only the PERIPHERAL dopa-decarboxylase |
|
|
difference between CNS vs peripheral metabolism of dopamine |
In CNS, dopamine does nto go to NE and Epi
In periphery, dopamine is further transformed to NE and Epi |
|
|
amantidine |
stabilizes dopamine in the synapse/increases synaptic dopamine |
|
|
anticholinergics used in parkinson-ISM for antipsychotics toxicity |
Trihexyphenidyl, Benztropine |
|
|
peripheral levodopa toxicity |
G.I. Tract: nausea, vomiting, anorexia • Cardiovascular: postural hypotension |
|
|
Trihexyphenidyl moa |
muscarinic blockade restores imbalance of neurotransmitter activity |
|
|
Benztropine moa |
muscarinic blockade restores imbalance of neurotransmitter activity |
|
|
Trihexyphenidyl, Benztropine Toxicity |
1. peripheral atropine-like effects (dilates the pupils, increases heart rate, and reduces salivation and other secretions)
2. CNS toxicity (delirium, confusion) |
|
|
anticholinergics primary use in movement disorders |
parkinson-ISM mostly |
|
|
dopamine agonists |
bromocriptine pergolide Pramipexole (D3 agonist) Ropinirole (D2 agonist)
|
|
|
bromocriptine moa |
dopamine agonists - acts directly on DA receptor |
|
|
pergolide moa |
dopamine agonists - acts directly on DA receptor |
|
|
Dopamine Receptor Agonists |
Bromocriptine (D2 agonist) Pergolide (D1 & D2 agonist) Pramipexole (D3 agonist) [Premium] Ropinirole (D2 agonist) [Rope - role] Apomorphine
Pergolide associated with valvular heart disease & no longer available |
|
|
Ergot Alkaloids |
Bromocriptine (D2 agonist) [ cryptic bromine acts as dopamine] Pergolide (D1 & D2 agonist) [give pearje for dopamine]
Pergolide associated with valvular heart disease & no longer available |
|
|
bromocriptine pergolide toxicity |
Toxicity: hypotension, nausea, hallucinations |
|
|
which drug interferes with ropinirole metabolism? |
ciprofloxacin inhibits CYP1A2, inhibits ropinirole metabolism
ropinirole is dopamine agonist |
|
|
Pramipexole and ropinirole rare side effect |
Pramipexole and ropinirole linked to compulsive gambling as rare side effect
dopamine agonists
ropinirole - it's like you're tied with a rope to gambling |
|
|
Apomorphine • Mechanism of action |
dopamine agonist
Used for rescue of akinesia in “off” periods
|
|
|
How to manage apomorphine side effects? |
Side effects include nausea -pretreat with trimethobenzamide to prevent
apomorphine is dopamine agonist |
|
|
Selegiline moa |
Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors
Rasagiline is a newer MAO-B inhibitor in glia
Selegiline may block progressive neurodegeneration - only in rats though |
|
|
Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors |
Selegiline [selects for the MAO B]
Rasagiline |
|
|
mao-b vs mao-a |
mao-b = mao-brain |
|
|
relationship between carbidopa and COMT |
COMT is metabolic pathway for dopamine that's only activated when we use carbidopa (and inactivate dopa decarboxylase)
COMT Metabolizes levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa • 3-OMD inhibits DOPA transport across gut & BBB |
|
|
why don't we want to activate COMT pathway? |
COMT Metabolizes levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa • 3-OMD inhibits DOPA transport across gut & BBB |
|
|
Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT) Inhibitors |
Entacapone, Tolcapone (risk of liver injury)
[if you want to inhibit COMT, call on Al Capone] |
|
|
carbidopa/L-dopa |
Sinemet |
|
|
carbidopa/L-dopa/entacapone |
Stalevo
[Stall Parkinson's] |
|
|
Huntington’s Prominent selective neuronal loss in : |
Prominent selective neuronal loss in striatum (caudate/putamen)
Decrease in striatal GABA |
|
|
drugs used to treat large-amplitude chorea that causes falling injuries - huntington's |
Tetrabenazine, reserpine [tetrabenazine - used to stop uncontrolled movements of your 4, AKA "tetra" limbs Reserpine will make a huntington pt look like a 'reserved pine' in their movements] |
|
|
drugs used to treat huntington depression |
fluoxetine or carbamazepine [flowers and carbs will always help against depression] |
|
|
which parkinson meds cause gambling addiction |
Pramipexole and ropinirole |
|
|
SUMMARY SLIDE |
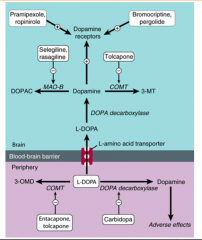
|
|
|
parkinson's drug associated with valvular disease and no longer available |
Pergolide associated with valvular heart disease & no longer available |

