![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
309 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
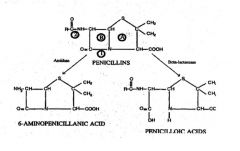
What does 1 represent?***
|
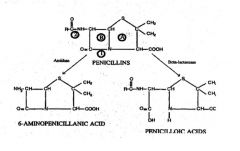
1 = Site of action of BETA-LACTAMASE
|
|
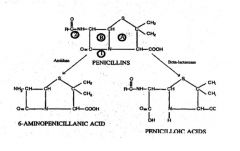
What does 2 represent?***
|
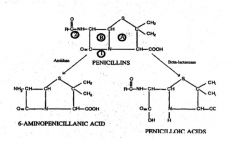
2= Site of action of AMIDASE
|
|
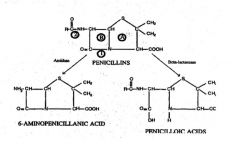
What does A represent?***
|
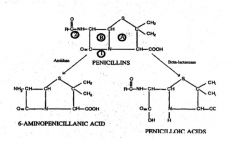
Thiazolidine ring
|
|
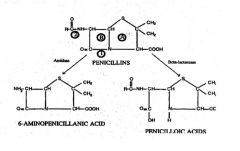
What does B represent?***
|
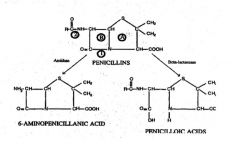
B = BETA-LACTAM RING
|
|
|
What are the 4 major problems w/ Penicillin G?
|
1. Destroyed by stomach acid
2. Narrow spectrum- Mainly Gram (+) 3. Suspectible to beta-lactamase 4. Not active against Pseudomonas |
|
|
Since Penicillin G is destroyed at low pH it could only be given by injection, how was this problem solved?
|
Penicillin V = acid stable form & can be given orally
|
|
|
Penicillin G was not able to get through outer membrane of gram (-) organisms, how was is this problem solved?
|
AMPICILLIN & AMOXOCILLIN = Broad spectrum
-Have added amino group that can pass through pores to get access to cell wall in Gram (-) |
|
|
What are the penicillinase-resistant penicillins? (5)***
|
1. Methicillin
2. Nafcillin 3. Cloxacillin 4. Dicloxacillin 5. Oxacillin |
|
|
The penicillinase-resistant penicillins are effective against?
|
Beta-lactamase producing S. aureus
(bacteremia, endocarditis, pneumonia, osteomyelitis) |
|
|
If S. aureus is methicillin resistant what is the next drug of choice?
|
Vancomycin
|
|
|
What is the drug of choice to treat anthrax?
|
Ciprofloxacin
|
|
|
What is the drug of choice to treat syphillis?
|
Penicillin G
|
|
|
Which 3 drugs are beta-lactamase inhibitors?
|
1. Clavulanic acid
2. Sulbactam 3. Tazobactam |
|
|
Which group of penicillins must be given w/ beta-lactamase inhibitors because they are sensitive to beta-lactamase?
|
Aminopenicillins-- Ampicillin & Amoxicillin
Anti-pseudomonal penicillins |
|
|
Which penicillins are effective against Pseudomonas? (5)
|
1. Carbenicillin
2. Ticarcillin 3. Piperacillin 4. Azlocillin 5 Mezlocillin |
|
|
What is the major mechanism of the penicillins?***
|
Bind to penicillin binding proteins (TRANSPEPTIDASE) & inhibit cell wall cross-linking
-Pentaglycine bridge can't be linked to Ala |
|
|
Which drug is often given w/ penicillin because inhibits tubular secretion & elevates blood levels of penicillin?
|
Probenecid
|
|
|
What is the most common adverse reaction to penicillins?***
|
Allergic reaction
|
|
|
Rapid infusion of Penicillin G through IV may cause?
|
Hyperkalemia --> arrhythmias & cardiac arrest
|
|
|
What is the major mechanism of resistance against penicillins?
|
Increased-beta-lactamase enzymes
|
|
|
What is an important cause of resistance to penicillin in gram (+) cocci?
|
Change in penicillin binding protein (Transpeptidase)
|
|
|
How are penicillins used in dentistry?
|
-Post-extraction or post-surgical infection
-Pericoronitis -Dentoalveolar abscesses -Osteomyelitis -Cellulitis -Ulcerative gingivitis -Periodontitis -Prophylaxis (aminopenicillins) |
|
|
Thizaloidine ring of penicillins contains how many members?
|
5
|
|
|
Dihydrothiazine ring in cephalosporins contain how many members?
|
6
|
|
|
What is the main limitation of 1st generation cephalosporins?
|
FIRST GENERATION
-Narrow spectrum = Gram (+) = main limitation |
|
|
What 2 benefits do first generation cephalosporins have?
|
1. Acid stable
2. Beta-lactamase resistant |
|
|
Which 3 drugs are 1st generation cephalosporins?
|
1. Cefazolin
2. Cephalothin 3. Cephalex |
|
|
Which generation of cephalosporins have increased spectrum of action (gram + & -) due to:
-Increased affinity for transpeptidase -Increase penetration of gram - -Increase resistance to beta-lactamase |
2nd generation cephalosporins = extended spectrum
|
|
|
Which drugs are active against Bacteriodes fragilis & Serratia marcescens?
|
Cephamycins (cefoxitin)
-2nd generation analogs w/ 7-methoxy group |
|
|
What are the 4 2nd generation cephalosporins?
|
1. Cefuroxime
2. Cefaclor 3. Cefoxitin 4. Cefotetan |
|
|
What is the main cephalosporin of the 3rd generation?
|
Ceftriaxone
|
|
|
Why do 3rd generation cephalosporins have increased activity against gram (-) organisms?
|
Aminothiazole moeity added to beta-lactam ring --> Inceased gram (-) activity
|
|
|
Which drug is a zwitterion & has enhanced ability to penetrate porin in outer membrane of gram (-) bacteria?
|
CEFEPIME= 4th generation cephalosporin
|
|
|
Which cephalosporins belong to the 3rd generation? (5)
|
1. Ceftriaxone (main one)
2. Cefotaxime 3. Ceftazidime 4. Ceftizoxime 5. Cefpodoxime proxetil |
|
|
What is the mechanism of cephalosporins?
|
Inhibit cell wall synthesis
|
|
|
Which drug contains methylthiotetrazole (MTT) side chain & can interfere w/ Vit K metabolism & cause clotting problems?
|
Cephalosporins
|
|
|
What percentage of people allergic to penicillins also have allergy to cephalosporins?
|
5-10%
|
|
|
Azetreonam is used against what type of organism?
|
Aerobic gram (-) bacteria
-Resistant to beta-lactamase |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Azetreonam?
|
Binding PBP-3 of gram (-) bacteria --> Inhibit cross-linking
|
|
|
How is Azetreonam administered?
|
Must be administered IV or IM
-Poorly absorbed by gut --> converted to inactive form by intestinal flora |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of vancomycin?
|
Inhibit cell wall synthesis--
BIND ACYL-D-ALANYL-D-ALA TERMINUS of cell wall precursor unit --> lysis |
|
|
What is the major adverse effect of vancomycin?***
|
VANCOMYCIN = RED MAN SYNDROME
-Ototoxic -Nephrotoxic |
|
|
What is the mechanism of resistance of Vancomycin?***
|
Proteins replace normal D-Ala-D-Ala peptidoglycan w/ D-Ala-D-Lactate
|
|
|
Which antibiotic contains a 5 member ring w/ only carbon (no sulfur)?
|
Carbapenems
|
|
|
Which drugs are carbapenems? (2)
|
1. Imipenem/cilastatin
2. Meropenem |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of carbapenems?
|
Bind PBP 1 & 2-
Easy penetration of gram (-) envelope through porins |
|
|
Why must cilistatin be given w/ imipenem?***
|
Imipenem hydrolyzed by dehydropeptidase I in proximal renal tubule --> Cilistatin is competitive inhibitor & prevents Imipenem from being broken down
|
|
|
What drug must be given w/ Imipenem?
|
Impipenem & cilistatin
|
|
|
What is the main adverse reaction of high doses of Imipenem?
|
Seizures
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of fosfomycin?
|
Inhibit cell wall synthesis by
BLOCKING FORMATION OF N-ACETYLMURAMIC ACID |
|
|
Cycloserine is used to treat?
|
TB
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of cycloserine?
|
Inhibit cell wall synthesis -->
INHIBIT ALANINE RACEMASE (& ALA LIGASE) --> Prevents incorporation of D-Ala into peptidoglycan pentapeptide |
|
|
Which drug is used to treat Rickettsia (Rocky mountain spotted fever, typhus & Q fever)?
|
Tetracyclines
|
|
|
Which drug is used to treat borrelia burgdoferi (Lyme disease)?***
|
Tetracyclines
|
|
|
What combination of drugs is used to treat GI ulcers?
|
1. Clarithromycin
2. Omeprazole (pepto-bismol/metronidazole) 3. Amoxicilln |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of tetracyclines?***
|
Inhibt protein synthesis by binding 30S
|
|
|
Which antibiotic is absorbed best under acidic conditions & has impaired absorption when comined w/ milk products?
|
Tetracyclines
|
|
|
Which antibiotic has the potential to bind tissue undergoing calcification during formation of bone, dentin & enamel of unerupted teeth?
|
Tetracyclines
|
|
|
What is the major mechanism of resistance for tetracyclines?
|
Efflex pump
|
|
|
Which antibiotic inhibits MMP & leads to recession & loss of gum tissue?***
|
Tetracyclines
|
|
|
What is the main tetracycline used?
|
Doxycycline
|
|
|
Which broad spectrum antibiotic is often used for serious infections when no other drugs work?
|
Chloramphenicol
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of chloramphenicol?
|
Inhibit protein synthesis -- binds 50S
|
|
|
What are the 3 major adverse effects of chloramphenicol?***
|
1. Toxic bone marrow depression
2. Idiosyncratic aplastic anemia 3. Gray baby syndrome |
|
|
What causes Gray baby syndrome?
|
Inability to conjugate chloramphenicol --> glucuronide
|
|
|
Toxic bone marrow depression associated w/ chloramphenicol presents as?
|
Anemia w/ leukopenia or thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
What drugs are aminoglycosides? (6)
|
1. Gentamicin
2. Tobramycin 3. Amikacin 4. Streptomycin 5. Neomycin 6. Paromomycin |
|
|
Neomycin is used to treat?
|
Topical infections of skin & mucous membranes
|
|
|
Neosporin contains which 3 antibiotics?
|
1. Neomycin
2. Polymyxin B 3. Bacitracin |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of the aminoglycosides?***
|
Inhibit protein synthesis -- Bind 30S
|
|
|
What are the major adverse effects of aminoglycosides?
|
1. Renal damage
2. Ototoxicity |
|
|
The macrolides consist of which drugs? (4)
|
1. Erythromycin
2. Clarithromycin 3. Azithromycin 4. Dirithromycin |
|
|
Which drug is to treat chlamydial urogenital infections during pregnancy?
|
Erythromycin or Azithromycin-- Macrolides
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of macrolides?
|
Inhibit protein synthesis -- Bind 50S
|
|
|
Erythromycin is best absorbed under what conditions?
|
Erythromycin best absorbed by alkaline conditions
-Unstable to stomach acid |
|
|
What is one important benefit of azithromycin compared to other macrolides?
|
Has long half-life therefore can be given once daily
|
|
|
What are the most serious side effects of taking macrolides?
|
1. Cholestatic hepatitis
2. Allergic reactions |
|
|
Aminoglycosides are active against which type of organism?
|
Aerobic gram (-) & some gram (+)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Clindamycin?
|
Inhibit protein synthesis -- Bind 50S
|
|
|
What is the main adverse effect of Clindamycin?***
|
Severe psuedomembranous colitis due to superinfection of C. dificile
|
|
|
Which drug is highly effective against gram (-) anaerobic acute orofacial infects & chronic periodontitis?
|
Metronidazole
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of metronidazole?
|
Diffuses into cell & produces reactive metabolites that kill cell
CONCENTRATION DEPENDENT |
|
|
What adverse effect is present w/ metronidazole?
|
Disulfiram reaction w/ ethanol --> Severe flushing
|
|
|
Which drugs are sulfonamides? (6)
|
1. Sulfisoxazole
2. Sulfamethoxazole 3. Sulfacetamide 4. Sulfadiazine 5. Succinylsulfathiazole 6. Mefanide |
|
|
What is Co-trimoxazole TMP-SMX?
|
Trimethropim w/ Sulfamethoxazole
|
|
|
What antibiotic is often used for pneumocystis carinii infection in AIDS pt?***
|
Co-trimoxazole (trimethroprim w/ sulfamethoxazole)
|
|
|
What is the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis?
|
Pyrimethamine & Sulfadiazine
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action for sulfonamides?***
|
Competitive inhibitors of dihydropteroate synthetase -- synthesis of Folic acid from PABA
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Trimethoprim?***
|
Inhbits dihydrofolate reductase
(Methotrexate also inhibits) |
|
|
Sulfonamides are metabolized by acetylation to form?
|
Inactive toxic N-hydroxy metabolites
|
|
|
N-hydroxy metabolites formed by metabolism of sulfonamides can cause?
|
Hemolytic anemias in people w/ G-6-P DH deficiency
|
|
|
What effects can sulfonamides have on infants?
|
Kernicterus
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects present when taking sulfonamides? (5)***
|
1. Hemolytic anemia (G6PDH def)
2. Allergic reactions 3. Kernicterus 4. Bone marrow suppression 5. Renal damage -- crystalluria (if inadequate urine flow) |
|
|
Why do N-hydroxy metabolites cause hemolytic anemia in G6PDH deficient pts?
|
Don't have enough NADPH --> can't reduce oxidized gluthathione & oxidative metabolites can't react w/ oxidized glutathione
|
|
|
Although sulfonamides can have various adverse reactions, which drugs were developed on the basis of these reactions?
|
1. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
2. Sulfonylurea antidiabetics 3. Thiouracil group of antithyroid drugs |
|
|
Which 2 classes of antibiotics are effective against mainly aerobic gram (-) bacteria?
|
1. Aminoglycosides
2. Fluoroquinolones |
|
|
What is the treatment of choice for anthrax?
|
Ciprofloxacin
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Fluoroquinolones?***
|
Inactivate DNA gyrase (Topoisomerase II) & Topoisomerase IV
|
|
|
How are fluoroquinolones used in dentistry?
|
Ciprofloxacin --> orodental infection caused by Pseudomonas
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Isoniazid?***
|
Inhibit synthesis of mycolic acids --> components of mycobacterial cell wall
|
|
|
What is Isoniazid used to treat?***
|
Tuberoculosis
|
|
|
How is Isoniazid metabolized?
|
Acetylated in liver --> Genetic heterogenicity in rate of acetylation
|
|
|
What is the most serious adverse effect of Isoniazid?
|
Peripheral neuritis
|
|
|
How are pt protected from peripheral neuritis when taking Isoniazid?
|
10 mg Pyridoxine
|
|
|
What dentally related adverse effect can occur w/ use of Isoniazid?
|
Xerostomia
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Rifampin?
|
Inhibits RNA synthesis -- inhibits DNA-dependent-RNA-polyermase
|
|
|
What is the 4 drug regimen used for HIV patients?
|
1. Isoniazid
2. Rifampin 3. Pyrazinamide 4. Ethambutol or Streptomycin |
|
|
What effect does Rifampin have on P450 system?
|
Rifampin = P450 Activator --> Decreases half life of many drugs
|
|
|
Which 2 drugs are P450 Activators?
|
1. Rifampin
2. Barbituates (phenobarbital) |
|
|
Pyrazinamide is used to treat?
|
TB
|
|
|
Ethambutol is used to treat?
|
TB
|
|
|
What is the main adverse effect of ethambutol?
|
Optic neuritis
|
|
|
Which drugs are used to treat TB? (8)
|
1. Isoniazid
2. Rifampin 3. Pyrazinamide 4. Ethambutol 5. Streptomycin 6. Aminosalicylic acid 7. Ethionamide 8. Cycloserine |
|
|
What is the drug of choice to treat leprosy?***
|
Dapsone
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of dapsone?
|
Inhibits synthesis of PABA --> folic acid by competitively inhibiting dihydropteroate synthetase
|
|
|
Which 2 drugs are metabolized to N-hydroxy metabolites that can cause severe oxidative stress in RBC of G6PDH deficient patients?
|
1. Sulfonamides
2. Dapsone |
|
|
What are the major adverse effects of Dapsone? (2)
|
1. Hemolytic anemia (G6PDH def)
2. Methemoglobinemia |
|
|
Which drug colors urine, feces, sputum & sweat RED?
|
Clofazimine
|
|
|
What is clofazimine used to treat?
|
Leprosy
|
|
|
Which drugs are used to treat leprosy (5)
|
1. Dapsone
2. Clofazimine 3. Rifampin 4. Thalidomide 5. Ethonamide |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Amphotericin B & Nystatin?***
|
Binds to sterols in cell membranes forming pores
|
|
|
What is antagonistic w/ amphotericin B & inhibit synthesis of sterols?
|
Imidazoles
|
|
|
What is the drug of choice for treatment of candida infection in mouth?
|
Nystatin
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Flucytosine?
|
Thymidylate synthetase is inhibited
|
|
|
Why does Flucytosine cause bone marrow depression?
|
intestinal flora converts some Flucytosine --> 5-Fluorouracil = anti-cancer drug
|
|
|
Imidazoles contain how many N in azole ring?
|
2 nitrogen = Imidazoles
|
|
|
Triazoles contain how many N in azole ring?
|
3 nitrogen = Triazoles
|
|
|
Which azoles are Imidazoles? (3)
|
1. Clotrimazole
2. Miconazole 3. Ketoconazole |
|
|
Which azoles are Triazoles? (3)
|
1. Fluconazole
2. Itraconazole 3. Terconazole |
|
|
What are the adverse effects caused by Ketoconazole? (3)***
|
1. Fatal hepatic necrosis
2. Gynecomastia 3. Menstrual irregularities |
|
|
Iodide can be used to treat?
|
Fungal infections
|
|
|
Griseofulvin is used to treat?
|
Infections of skin, hair & nails caused by dermatophytes = GRISEOFULVIN
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Griseosulvin?
|
Inhibits fungal mitosis by binding tubulin
|
|
|
Why must Griseofulvin be used for 2-6 weeks?
|
Deposits in keratin precursor cells & persists after differentiation --> makes keratin resistant to fungal infection
|
|
|
What are the adverse affects of Griseofulvin?
|
1.Headache
2. Lapses of memory 3. Impairment of judgement Do NOT use for pilots/bus drivers |
|
|
what is the mechanism of Pneumocandins & papulocandins?
|
Inhibit cell wall synthesis by inhibint beta-1,3-glucan synthetase
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Nikkomycins?
|
Inhibit chitin synthase
|
|
|
Which antifungal agent is NOT effective against Candida infection?
|
Tolnaftate
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Allylamines?
|
Inhibit fungal ergosterol synthesis by inhibition of Squalene-2,3-epoxidase
|
|
|
What drugs are allylamines? (3)
|
ANTIFUNGALS
1. Naftifine 2. Terbinafine (lamisil) 3. Butenafine |
|
|
Which drugs are Nuceloside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors? (6)
|
1. Zidovudine (AZT)
2. Didanosine 3. Zalcitabine 4. Stavudine 5. Lamivudine 6. Abacavir |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of the Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors?
|
Lack 3' OH group --> Incorporated into DNA --> Terminates chain elongation
|
|
|
What adverse effects are commonly found when taking Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors? (3)
|
1. Peripheral neuropathy
2. Pancreatitis 3. Lactic acidosis |
|
|
Which drugs are Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors? (3)
|
1. Nevirapine
2. Delaviridine 3. Efavirenz |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors?
|
Bind directly to HIV Reverse Transcriptase --> inducing conformational changes
-Don not require phosphorylation |
|
|
What drugs are HIV Protease Inhibitors? (5)***
|
1. Saquinavir
2. Ritonavir 3. Indinavir 4. Nelfinavir 5. Amprenavir |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of HIV protease inhibitors?
|
Inhibit HIV protease --> essential enzyme for final step of viral formation
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of HIV Protease Inhibitors? (3)
|
1. Buffalo hump
2. Hyperglycemia 3. Hyperlipidemia |
|
|
Amantadine & Rimantadine are used to treat?
|
VIral Respiratory infections (Influenze)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Amantadine & Rimantadine?
|
Prevent fusion of viral membrane w/ host cell
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Zanamivir & Oseltamivir?
|
Neuraminidase inhibitor
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Ribavirin?
|
Phosphorylated intracellulary --> Inhibits repiication of RNA & DNA viruses by interfering w/ GTP formation & viral mRNA capping
|
|
|
Which drugs end in "pam"
Diazepam Chlordiazepoxide Midazolam Flurazepam Lorazepam.. |
Benzodiapezipines
|
|
|
Do benzodiapezines cause dependence?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Most of the benzodiazepines do not have antidepressant effect, which one is the exception?
|
Alprazolam
|
|
|
Which benzodiazepine has selective anticonvulsant action & can be used to treat epilepsy?
|
Clonazepam
|
|
|
Which drug is used to treat status epilepticus?***
|
Diazepam
|
|
|
Which class of drugs increase FREQUENCY of opening of GABA channels?***
|
Benzodiazepines-- Increase FREQUENCY
(Barbituates-- keep channel open LONGER) |
|
|
Which benzodiazepines are used in pt's with impaired P450 enzymes due to liver disease? (2)
|
1. Oxazepam
2. Lorazepam -Directly conjugated & excreted |
|
|
If there is an OD of benzodiapenes, what would they be treated with?***
|
Flumazenil
|
|
|
What should be avoided to prevent further CNS depression when taking benzodiazepines?
|
Alcohol (barbituates)
|
|
|
What inhibits CYP3A? (6)
|
1. Ca channel blockers (Verapamil & diltiazem)
2. Cimetidine 3. Erythromycin 4. Clarithromycin 5. Ketoconazole/itraconazole 6. Grapefruit juice |
|
|
Of the benzodiazepines, which has a unique profile w/ long half life of active metabolite & slow onset of tolerance?
|
Clorazepate
|
|
|
What is the most abused benzodiazepine?
|
Alprazolam
|
|
|
What are "Z drugs"
|
Benzodiazapine-like hypnotics
|
|
|
Why are Z drugs preferred for short-term insomnia?
|
Rapid onset & short duration of action --> less "hangover"
|
|
|
What is Busprione used to treat & mechanism?
|
Treat mild/moderate anxiety & panic disorder
-Serotonin selective agonist |
|
|
Barbituates depress the activity of?
|
ALL excitable tissues
|
|
|
Why are barbituates strictly contraindicated in people q/ acute intermitten porphyria?
|
Barbituates enhance porphyrin synthesis
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of barbituates?
|
Open GABA Cl channels for prolonged periods of times
(Benzodiazepines open channels more frequently) |
|
|
What is the most serious effect of barbituates?
|
Respiratory depression
|
|
|
What happens when Chloral hydrate is taken w/ alcohol?
|
Chloral hydrate inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase --> elevates blood alcohol levels --> stupor, coma or death
|
|
|
Chloral hydrate can cause increased bleeding by?
|
Interferes w/ Warfarin
|
|
|
What is the major adverse effect of Clozapine (Clozaril)?***
|
Agranulocytosis
-Must monitor blood count regularly (Constipation also) |
|
|
Which antipsychotic drug is most likely to cause seizures?
|
Clozapine
|
|
|
What is Risperiodne used to for?
|
Antipsychotic drug
|
|
|
What category of drugs are?
Chlorpromazine Thioridazine Trifluoperazine PRochlorperazine Haloperiodl Thiothixene Loxapine |
Antipsychotic drugs - Dopamine D2 receptor blockers
|
|
|
What type of drugs are these?
Risperidone Olanzapine Quetiapine Clozapine |
Antipsychotic drugs - Serotonin-Dopamine Antagonists
|
|
|
What is the major side effect of Olanzapine (Zyprexa)?
|
Diabetes
|
|
|
Which antipsychotic is used to treat manic diseases?
|
Lithium
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of tricyclic & atypical antidepressants?
|
Inhibit reuptake of norepinephrine
|
|
|
Adverse effects of tricyclic antidepressants are due to?
|
Antimuscarinic effects
|
|
|
What is the main adverse effect of tricyclic antidepressants?
|
Orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
Which drugs are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors? (3)
|
1. Fluoxetine (Prozac)
2. Paroxetine (Paxil) 3. Sertraline (Zoloft) |
|
|
Which type of drugs are these?
Imipramine Despiramine Amitriptyline Venlafaxine Buproprion Nefazodone |
Tricyclic & Atypical Antidepressants
|
|
|
What are the Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors? (3)
|
1. Isocarboxazid
2. Phenelzine 3. Tranylcypromine |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of monoamine oxidase inhibitors?
|
Inhibit breakdown of catecholamines --> elevate mood & cause orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
When taking monoamine oxdiase inhibitors what must be avoided?
|
Food w/ Tyramine--> wine, cheese, chocolate
|
|
|
What are the 2 mechanisms of action of anticonvulsants?
|
1. Limit sustained repetitive firing of neurons by promoting inactivated state of Na channel
2. Enhance GABA inhibition (Some block T-type Ca channels) |
|
|
Which barbituate is also used as an anticonvulsant?
|
Phenobarbital
|
|
|
What is the oldest nonsedative antiseizure drug?
|
Phenytoin (Dilatin)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of phenytoin?
|
Slow rate of recovery of Na channels from inactivation
|
|
|
Which anti-convulsant follows zero order kinetics at high doses?
|
Phenytoin
|
|
|
What dentally relevant adverse effect does phenytoin cause?
|
Gingival hyperplasia
|
|
|
What effect does phenytoin have on P450 system?
|
Phenytoin = P450 INDUCER
-Increases metabolism of other drugs including oral contraceptives |
|
|
Which anticonvulsant was originally used to treat trigeminal neuralgia?
|
Carbamazepine
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of carbamazepine?
|
Slows rate of recovery of Na channels from inactive state
|
|
|
What are the major adverse effects of carbamazepine? (2)
|
1. Diplopia
2. Ataxia |
|
|
Carbamazepine toxicity can occur as an interaction w/ which drug?
|
Erythromycin
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Ethosuximide?
|
Blocks T-type Ca currents in thalamic neurons
|
|
|
Which anticonvulsant can be used to treat all forms of epilepsy?
|
Valproic acid
|
|
|
What is a major adverse effect caused by Valproic acid?
|
Fatal hepatitis
|
|
|
What is Gabapentin used to treat?
|
Anticonvulsant
|
|
|
Topiramate is used to treat?
|
Seizures
|
|
|
Felbamatate is used to treat?
|
Seizures
|
|
|
Lamotrigine is used to treat?
|
Seizures
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of TIagabine?
|
Inhibits GABA transporter GAT 1- Decreases GABA uptake
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Zonisamide?
|
Blocks Na & voltage gated Ca channels
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Levetiracetam?
|
Binds selectively to synaptic vesicular protein & modifies synaptic release of Glu & GABA
|
|
|
What effect does Levetiracetam have on P450 system?
|
Doesn't interact w/ it
|
|
|
Which carbonic anhydrase inhibitor has anti-seizure properties?
|
Acetazolamide
|
|
|
What do D1 dopamine receptors do?
|
D1 receptors --> stimulate synthesis of cAMP
|
|
|
What do D2 dopamine receptors do?
|
Inhibit synthesis of cAMP
|
|
|
What is the most effective agent in treating Parkinson's disease?
|
Levodopa
|
|
|
Levodopa crossing blood-brain barrier to enter CNS is mediated by?
|
Membrane transporter for aromatic amino acids
|
|
|
Which drug is given w/ Levodopa?
|
Cabidopa
|
|
|
Why is carbadopa given w/ levodopa?***
|
-Carbidopa inhibits decarboxylase peripherally to inhibit side effects
-More levodopa goes to brain w/ carbidopa --> only need half the dose |
|
|
What is the major side effect of levodopa w/o carbidopa?
|
Activate vascular dopamine receptors --> Orhtostatic Hypotension
|
|
|
What happens when levodopa is given w/ nonspecific MAO inhibitors?
|
Hypertensive crisis
|
|
|
Which MAO inhibitors can be safely given w/ levodopa?
|
MAO-B inhibitors
|
|
|
What type of drugs are these?
Bromocriptine Pergolide Ropinirol Pramipexole |
Dopamine agonists -- Parkinson's disease
|
|
|
What is the major adverse effect produced by dopamine agonists used to treat parkinson's disease?
|
Orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
Apomorphine is used as "rescue" therapy for treatment of "off" episodes in Parkinson's, but what other type of drug is required w/ it?
|
Anti-emetic therapy
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Catechol-O-Meythyltransferase Inhibitors in treatment of Parkinson's disease?
|
Inhibit metabolism of levodopa & increase half-life --> Increase amount of levodopa in CNS
|
|
|
What is the main mechanism for dopamine metabolism in the brain?
|
MAO-B
|
|
|
Which drug can be given to prolong half life of levodopa by inhibiting MAO-B?
|
Selegline
|
|
|
What type of drugs can be give to alleviate symptoms (tremor) of Parkinson's disease?
|
Muscarinic receptor antagonists
|
|
|
What are these drugs used to treat?
Phenylephrine Ephedrine (Vicks) Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) |
Nasal decongestants --> systemically active adrenergic stimulants
|
|
|
What is the main adverse effect of systemic nasal decongestants?
|
Hypertension
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of bronchodilators?***
|
Beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonists activate receptor --> raise cAMP --> relax bronchial smooth muscle
|
|
|
What are short-acting beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonists used for?***
|
Use for acute treatement of bronchospasm
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of long-acting beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonists?
|
Increased heart rate --> Cardiac arrhthymias
(due to beta 1 activity also) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of anticholinergics (Tiotropium & COP bromide) for treating asthma?***
|
Block muscarinic M3 receptors --> Prevent bronchospasm
|
|
|
How is the solubility of Theophylline enhanced?
|
Forms a complex w/ ethylenediamine & theophylline which is called aminophylline
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of methylxanthines like theophylline?***
|
Inhibit nucleotide phosphodiesterase --> Prevents breakdown of cAMP & cGMP --> bronchodilation
|
|
|
Besides inhibiting phosphodiesterase, what other 2 mechanisms does Theophylline have to decrease bronchoconstriction?
|
-Competitive inhibitor of adenosine receptors--> adenosine cause constriction & release of mediators
-Activate histone deacetylases in nucleus --> less proinflammatory genes |
|
|
Which 2 drugs can decrease clearance of theophylline?
|
Cimetidine
Erythromycin P450 INHIBITORS |
|
|
Which 3 drugs can increase clearance of theophylline?
|
Phenytoin
Barbituates Rifampin P450 INDUCERS |
|
|
What are the most effective drugs in the treatment of ashtma to to inhibiting airway inflammation?
|
Glucocorticoids
|
|
|
What is the mechnanism of glucocorticoids in the treatment of asthma?
|
-Inhibit eicosanoid production
|
|
|
What type of drugs are these?
Fluticasone Beclomethasone Triamcinolone Budesonide Flunisolide |
Inhaled glucocorticoids for treatment of asthma
|
|
|
What is a major adverse effect of inhaled glucorticoids?
|
Oropharyngeal candidiasis due to suppressed immune system
|
|
|
Which type of a drug are these?
Cromolyn sodium Nedocromil |
Mast cell stabilizers
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of mast cell stabilizers in the treatment of asthma?
|
Inhibit release of mediators from mast cells
|
|
|
What type of drugs are...***
Zafirlukast (Accolate) Montelukast (Singulair) |
Leukotriene receptor blockers
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of leukotriene receptor blockers in the treatment of asthma?***
|
Competitive antagonist for cys-LT1 receptor
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of leukotriene-synthesis inhibitors like Zileuton in the treatment of asthma?***
|
Zileuton inhibits 5-lipoxygenase to inhibit synthesis of leukotrienes
|
|
|
What is an important adverse effect for dentists when pt are taking Iodide salts as a respiratory drug?
|
Swelling of parotid glands
|
|
|
Which type of drugs are these?
Omeprazole (Prilosec) Esomeprazole (Nexium) Lansoprazole (Prevacid) Rabeprazole (Aciphex) Pantoprazole (Protonix) |
Proton pump inhibitors
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of proton pump inhibitors?
|
Activated in acidic environment --> Bind irreversibly to H-K ATPase & inactivating molecule
-Acid secretion requires new pumps (24-48 hrs later) |
|
|
Which antibiotics can be used to treat H. pylori infection? (4)
|
1. Tetracycline
2. Clarithromycin 3. Amoxicillin 4. Metronidazole |
|
|
What is the mechanism of prostaglandin analogs such as Misoprostol in GI?
|
Reduce mucosal damage by binding EP3 receptors on parietal cells --> Inhibit acid secretion
|
|
|
Which antacid is contraindicated in pregnant women because it can increase uterine contraction?
|
Misoprostol (Prostaglandin analog)
|
|
|
Which anti-neoplastic drug has the broadest spectrum of antitumor activity of all alkylating agents?
|
Cyclophosphamide
|
|
|
Which anti-neoplastic drug does not cause alopecia?***
|
Melphalan
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Cyclophosphamide as anti-neoplastic drug?
|
Cross links DNA
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of methotrexate?
|
Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (Folic acid antagonist)
|
|
|
Which drug can be used to rescue bone marrow toxicity?***
|
Leucovorin (fully reduced folate coenzyme)
|
|
|
What are some adverse effects of methotrexate?
|
Ulceration of oropharynx & alopecia
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of 5-Fluorouracil as an anti-neoplastic drugs?
|
Inhibits synthesis of thymidylate (DNA precursor)
|
|
|
What type of drugs are?
Vincristine Vinblastine Vinorelbine |
Anti-mitotic drugs = Vinca Alkaloids
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Vinca Alkaloids?***
|
Bind beta-tubulin & block its ability to polymerize w/ alpha-tubulin into microtubules --> blocking mitosis
|
|
|
Which anti-neoplastic drug is used to treat breast cancer when estrogen receptors are present?***
|
Tamoxifen (estrogen receptor blocker)
|
|
|
What drug is a monoclonal antibody against HER-2 Ag on breast cancer cells?
|
Trastuzumab
|
|
|
What is the drug of choice to treat hypothyroidism?
|
Levothyroxine (Synthroid)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of anti-thyroid drugs?
|
Interfere w/ incorporation of iodide into tyrosyl resiudes of thyroglobulin & inactivate peroxidase
|
|
|
What type of drugs are these?
Propylthiouracil Methimazole Carbimazole |
Antithyroid drugs
|
|
|
What is the most serious side effect of antithyroid drugs?
|
Agranulocytosis
(Clozapine also causes agranulocytosis) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of steriod hormones?
|
Bind to receptor on cytoplasm --> Complex travels into nucleus --> binds specific genes on DNA
|
|
|
Dental procedures should only be done on pt w/ Addison's disease if?
|
Only do treatment on pt's with Addison's disease if they are CONTROLLED
|
|
|
Why is it important to not abrubtly withdraw from use of long-term therapy steroids?
|
Adrenal gland could shutdown w/ abrupt withdrawal
|
|
|
Ketoconazole has effect on P450 system?
|
P450 Inhibitor
|
|
|
What drug is often used to treat cushing syndrome?
|
Ketoconazole
|
|
|
What is Mifepristone (RU-486)?
|
Morning after pill
|
|
|
Spirolactone can be used to treat?
|
Primary aldosteronism
Hirsuitism in women |
|
|
What types of drugs are these?
Quinidine Procainamide Lidocaine Phenytoin |
Class I antiarrhythmic drugs
Na Channel blockers |
|
|
Mechanism of Class I anti-arrhythmic drugs?
|
Na channel blockers
|
|
|
What type of drugs are these?
Benzothiazepine Phenylaklyamine (verapamil) Dihydropyridine (Nifedipine) |
Class IV antiarrhthmic drugs
Ca channel blockers |
|
|
Mechanism of Class II antiarrhthmic drugs?**
|
Beta-receptor blocker
|
|
|
What is the most important drug used to treat congestive heart failure?
|
Cardiac glycosides (Digitalis)
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides?***
|
Increase intracellular Ca by inhibiting Na/K ATPase
|
|
|
What are the therapeutic uses of cardiac glycosides? (3)***
|
1. Congestive heart failure
2. Atrial flutter & fibrillation 3. Atrial tachycardia |
|
|
What is the main problem w/ cardiac glycosides?
|
Low therapeutic index -- danger of toxicity
|
|
|
WHAT HISTAMINE RECEPTOR IS RESPONSIBLE FOR ACID PRODUCTION?***
1. H1 2. H2 3. H3 |
H2
|
|
|
Which is an H1 BLOCKERS?***
1. Chlorpheniramine 2. Cimetidine 3. Dimaprit 4. Captopril 5. Losartan |
Chlorpheniramine
|
|
|
Which is an H2 BLOCKER?***
1. Irbesartan 2. Timolol 3. Diphenhydramine 4. Cimetidine |
Cimetidine
|
|
|
WHAT IS AN H2 AGONIST?***
1. Ranitidine 2. Dimaprit 3. Thioperamide 4. Enalapril |
Dimaprit
|
|
|
WHAT IS THE LOCATION OF THE CELL BODIES OF 5HT NEURONS?
1. Raphe Nuceli 2. Putaman 3. Medial nuclei 4. Dentate nuclei |
Raphe Nuclei
|
|
|
WHAT DRUGS INHIBIT ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME?***
1. ENALAPRIL 2. LISINOPRIL 3. RAMIPRIL 4. CAPTOPRIL 5. All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
WHAT DRUGS BLOCK ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTORS?***
1. Losartan 2. Dimaprit 3. Timolol 4. Verapamil |
Losartan
|
|
|
WHAT ARE THE ACTIONS OF PGI2?
I. Vasodilator II. Vasoconstrictor III. Antiaggregant IV. Proaggregant 1. I and III 2. II and III 3. I and IV 4. Only II |
I & II only
|
|
|
9. WHAT ARE THE ACTIONS OF TXA2?***
I. Vasodilator II. Vasoconstrictor III. Antiaggregant IV. Proaggregant 1. I and III 2. II and IV 3. I and IV 4. Only II |
II & IV
|
|
|
Which receptors mediate pain and itching?***
1. Cholinergic receptor 2. H1 receptor 3. Nicotinic receptor 4. H2 receptor |
H1 Receptor
|
|
|
TIMOLOL SHOULD NOT BE USED IN CONJUNCTION WITH WHAT OTHER DRUG?***
1. Losartan 2. Betaxolol 3. Verapamil 4. Viagra 5. Brinzolamide |
Verapamil
|
|
|
A SIDE EFFECT THAT MIGHT BE SEEN WITH A SYSTEMIC CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITOR SUCH AS ACETAZOLAMIDE WOULD BE…?***
1. Red Man Syndrome 2. Numbness and Tingling 3. Severe headache 4. Preterm birth 5. Increased libido |
Numbness & Tingling
|
|
|
WHAT DRUG ACTS ON M3 RECEPTORS ON THE CILIARY BODY?
1. Pilocarpine 2. Epinephrine 3. Verapamil 4. Prilocaine |
Pilocarpine
|
|
|
WHAT ARE THE SIDE EFFECTS ASSOCIATED WITH CHOLINERGIC AGENTS?
1. Ciliary muscle spasm and brow ache 2. Polydipsia 3. Polyuria 4. Burning mouth syndrome 5. Xerostomia |
Cliliary muscle spasm & brow ache
|
|
|
If you have a fellow dental student friend who is down and depressed about taking Boards and studying for pharmacology, what should he be prescribed?
1. Paroxetine (SSRI) 2. Physostigmine 3. Clonidine 4. Phenylephrine |
Paroxetine (SSRI)
|
|
|
What will be the effect of activation of H1 receptors on vascular endothelium?***
1. Smooth muscle relaxation 2. Smooth muscle constriction 3. There are no H1 receptors on vascular endothelium |
Smooth muscle relaxation
|
|
|
What drug is used for examination of the retina?***
1. Clonidine 2. Phenylephrine 3. Simvostatin 4. Acetylcholine |
Pheylephrine
|
|
|
. Clonidine is used for glaucoma because it functions to:***
1. Inhibit cholinesterase activity 2. Increase production of aqueous humor 3. Reduce production of aqueous humor 4. Increase release of ACh |
Reduce production of aqueous humor
|
|
|
A reversible Anticholinesterase is:***
1. Echothiophate 2. Physostigmine 3. Paroxetine 4. Betaxolol |
Physostigmine
|
|
|
What drugs are used to treat Herpes infection?*** (5)
|
1. Acyclovir
2. Valacylovir 3. Penciclovir 4. Famciclovir 5. Ganciclovir |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of anti-Herpes drugs?
|
Converted to triphosphate q/ viral thymidine kinase
Triphosphate inhibits virus DNA polymerase --> inhibiting viral DNA replication |
|
|
Which drug is useful to treat CMV in immunocompromised patients?***
|
Ganciclovir
|
|
|
Which drug can be used to treat acyclovir resistant herpes in AIDS pts?
|
Foscarnet
|
|
|
What are the short acting benzodiazepines? (2)**
|
1. Triazolam
2. Temazepam |
|
|
Which anticonvulsants are Na channel blockers? (5)***
|
1. Phenytoin
2. Carbamazepine 3. Valproic acid 4. Lamotrigine 5. Zonisamide |
|
|
Which anticonvulsants are T-type Ca channel blockers? (2)***
|
1. Exthosuximide
2. Trimethadione |

