![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
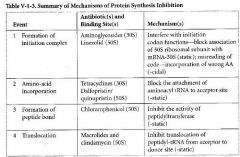
What drugs work on the 30S subunit?
|
Aminoglycosides
Tetracyclines Spectinomycin |
|
|
What drugs work on the 50S subunit?
|
Everything else:
- Chloramphenicol - Macrolides - Lincosamides (clindamycin) - Telithromycin - Quinupristin/Dalfopristin - Linezolid |
|
|
-thromycin =
|
Macrolide
|
|
|
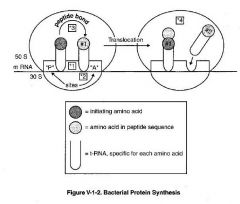
What are the 4 main events in Bacterial Protein synthesis?
|
1.) Formation if Initiation Complex
2.) AA incorporation 3.) Formation of peptide bond 4.) Translocation |
|
|
MOA of Clindamycin and Protein synthesis event it affects
|
*Formation of peptide bond*
(-static) Inhibits peptidyl-transferase, thus transpeptidation, blocking the binding of the aa-moitey of the tRNA to the acceptor site on ribosomal mRNA |
|
|
MOA and P-synthesis event involved with MACROLIDES, TELITHROMYCIN, and CLINDAMYCIN
|
*Translocation*
(-static) Block transpeptidation and inhibit translocation of peptidyl-tRNA from acceptor to donor 50S |
|
|
MOA and P-synthesis event involved with TETRACYCLINES
|
*Amino acid Incorporation*
(-static) Prevent binding of aminoacyl-charged tRNA to the acceptor site of the ribosome mRNA complex 30S |
|
|
MOA and P-synthesis event involved with STREPTOGRAMINS
|
(-cidal)
- Inhibits tRNA synthetase activity - Constrict the exit channel on the ribosome where nascent polypeptides are extruded. 50S |
|
|
MOA and P-synthesis event involved with LINEZOLID
|
*Formation of initation complex*
(-static) blockes form'n of the tRNA-ribosome-mRNA ternanry complex 50S |
|
|
Which drug doesn't bind to 80S rRNA, but CAN inhibit hte fxn of mitochondrial ribosomes with 70S rRNA?
|
Chloramphenicol
|
|
|
What structures does Chloramphenicl cross?
|
Placenta
BBB Good tissue distribution "-phen" = phenyl group! = LIPID soluble! |
|
|
What hepatic enzyme inactivates most of Chloramphenicol?
|
hepatic glucuronosyltransferase
|
|
|
What 2 groups of ppl should you watch out for with Chloramphenicol
(need dose dependent reductions) |
Neonates (incomlete maturation of the liver-> toxicity)
Pt's with liver damage/dysfunction |
|
|
What causes Gray baby syndrome?
|
Chloramphenicol
|
|
|
What causes dose-dependent bone marrow suppression?
|
Chloriamphenicol
|
|
|
What is the spectrum of chloramphenicol's action?
|
*Wide spectrum (-static)*
(-cidal against) Works really good against H.INFLUENZAE, N,mengitidis, and bacteroides. |
|
|
Choramphenicol is NOT active against which bug?
|
Chlamydia sp.
|
|
|
Clinical uses for Chloramphenicol
|
Wide-spectrum
+ Rickettsia H. influenzae - esp. in neonatal meningitis Neisseria meningitidis Bacteroides But not used often b/c of serious side effects |
|
|
Chloramphenicol is a back up drug for what?
|
Severe SALMONELLA sp.
|
|
|
How does resistance to chloramphenicol develop?
|
bacteria make acetyltransferase which inactivates the drug
|
|
|
Does Chloramphenicol inhibit p450?
|
YES!
It increases the elimination t1/5 of phenytoin, tolbutamine, and warfarin |
|
|
What are the main adverse effects of chloramphenicol?
|
Gray Baby syndrome
Bone marrow suppression Aplastic anemia (rare but fatal) Hemolytic Anemia in G6PD deficient pts. |
|
|
What characterizes Gray baby syndrome?
|
Decreased RBC's
Cyanosis Vomiting Green stools Vasomotor collapse *B/c of accumulation of the unmetabolized drug, sicne the neonateal liver is not completely mature* |
|
|
Where do Tetracyclines bind?
|
30S subunit at the acceptor site
|
|
|
What is the spectrum of tetracyclines?
|
"broad spectrum"
Good against chlamydia, mycoplasma, H.pylori, RICKETTSIA, BORRELIA (doxycycline) What I can hit with a macrolide, I can hit with a tetracycline and vice versa |
|
|
What is the DOC for infectious prostatitis?
|
Doxycycline
|
|
|
Describe the solubility of doxycycline and minocycline
|
Doxy = lipid soluble
Mino = water soluble |
|
|
Which tetracycline is used in SIADH?
|
Demeclocycline
|
|
|
Which tetracycline causes diabetes insipidus?
|
Demeclocycline
|
|
|
How do bugs develop resistance to Tetracyclines?
|
Efflux pumps
format'n of ribosomal protection proteins that interfere with drug binding These are not conferred to tigecycline (except Proteus and pseudomonas' efflux pumps) |
|
|
Which tetracycline is currently an alternative to macrolides in the initial tx of community-acquired pneumonia?
|
Doxycycline
|
|
|
Again, what the the primary species that tetracyclines are used against?
|
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae(adults)
- Chlamydia - Rickettsia - Vibrio |
|
|
What's one main difference between Chloramphenicol and Tetracyclines in terms of spectrum
|
Chloramphenicol does NOT kill Chlamydia. Tetracyclien DOES
|
|
|
Which tetracycline is used against GI ulcers cuased by h.pylori?
|
Tetracycline
|
|
|
Which tetracycline is used against Lyme disease?
|
Doxy
|
|
|
Which tetracycline is used in the meningococcal carrier state?
|
Minocycline
|
|
|
Which tetracyclineis used for prevention of malaria and in the tx of amebiasis?
|
Doxy
|
|
|
What is tigecycline derived from? and what is tige's use/spectrum?
|
From minocycline
- bugs resistant to tetracyclines - gpc resistant to methicillin and vanc: (MRSA & VRE) - B-lactamase producing gnb - anaerobes - chlamydia - mycobacteria |
|
|
How to foods and multivalent cations affect tetracycline absorption?
|
they decrease its absorption
|
|
|
What should you avoid when taking tetracycline?
|
Food, dairy, vitamins
|
|
|
Can tetracyclines be given to babies or pregnant women?
|
NO it will cause teeth enamel dysplasia (irreversible) and bone growth irregularities
|
|
|
What drugs cause cause phototoxicity?
|
Tetracyclines (demeclocycline)
Sulfonamides Quinolones |
|
|
What are ALL side effects are seen in tetracyclines?
|
- Vestibular tox: does-dependent DIZZINESS, and VERTIGO
- Fanconi's syndrome (w/outdated tetra's) - GI candidiasis, GI disturbances - Teeth enamel dysplasia - Irregular bone growth - Hepatic necrosis |
|
|
Which tetracyclines cause dizziness and vertigo?
|
doxy and minocycline
|
|
|
List of Macrolides
|
Erythromycin (prototype)
Azithromycin Clarithromycin |
|
|
Describe the structure of macrolides
|
Macro- so LARGE cyclic LACTONE ring with attached sugars
|
|
|
Which Macrolide availability is impeded by FOOD?
|
AZITHRO
|
|
|
How is Azithro's distribution in the body unique?
|
When districuted througout the body, it is in HIGHER levels in the TISSUES and PHAGOCYTES than in the plasma
|
|
|
Elimination of erythromycin =
|
biliary
|
|
|
Elimination of clarithromycin =
|
urinary
|
|
|
Elimination of Azithromycin =
|
slowly by urine
|
|
|
Spectrum of activity of Erythromycin
|
Campylobacter
Chlamydia Mycoplasma Legionella gpc some gn's |
|
|
What is erythromycin CLASSICALLY associated wiht on boards?
|
Legionella pneumonia
|
|
|
Spectrum of Azithromycin and Clarithromycin
|
Similar as erythro-, but INCREASD activity against:
- Chlamydia - MAC!! (M.avium complex) - Toxoplasma |
|
|
Which macrolides inhibit p450?
|
erythromycin, clarithromycin
Azithro does NOT inhib. p450 |
|
|
Which macrolide is safe in pregnancy?
|
Azithro!
erythro and clarithro are UNSAFE in pregnancy |
|
|
Mechanisms of resistance against macrolides in gp's
|
- Efflux pumps
- METHYLASE that adds a methyl group to the ribosomal binding site - Drug-metaboloizing esterases (enterobateriaceae) |
|
|
Methylase-producing microbial strains that are resistant to macrolides, are also cross-resistant to what other drugs?
|
Clindamycine and streptogramins
|
|
|
Recap: which tetracycline is active against MRSA and VRE?
|
tigecycline!
|
|
|
Spectrum of action for Clarithromycin
|
Same as erythro
+ - prophylaxis for M avium complex! - H. pylori ulcers! |
|
|
What causes GI irritation wiht the use of macrolides?
|
they stimulate MOTOLIN
|
|
|
Which macrolide has the LEAST amt of GI side effect?
|
clarithromycin
|
|
|
Side effects of Macrolides in general
|
- GI irritation
- eosinophilia - reversible deafness at high doses |
|
|
Side effects of erythromycin
|
*b/c of erythromycin estolate*
- Acute cholestatic hepatitis (hypersensitivity-based) - Increased risk for Hepatitis in children - Cholestasis |
|
|
Where does Clindamycin distribute well to, and what can it be implicated for?
|
Distributes well to bone, and is used for osteomyelitis
|
|
|
Clindamycin is used as back up for -
|
gpc
|
|
|
Clindamycin is used in prophylaxis of -
|
Endocarditis in valvular disease patients who are ALLERGIC to PCN.
|
|
|
How is Clindamycin implicated in AIDS patients?
|
Its used against P. JIROVECI
& in combo w/ PYTIMETHAMINE for AIDS related TOXOPLASMOSIS |
|
|
What is the main bug associated with osteomyelitis?
|
Staph. aureus
|
|
|
Clindamycin was the first known drug (and now, not the only one) to cause
|
pseudomembranous colitis
from a superinfection of C. difficile |
|
|
MOA of linezolid
How is it different from Aminoglycosides? |
Inhibits form'n of initiation complex
Works from the 50S side instead of 30S (AG) |
|
|
Spectrum of use for Linezolid
|
1.) Drug-resistant gpc: MRSA, PRSP, VRSA, VRE
2.) L. monocytogenes & corynebacterium |
|
|
Linezolid should be reserved for tx of
|
infections caused by multidrug-resistant gpb
|
|
|
Side effects of Linezolid
|
Thrombocytopenia and neutropenia (bone marrow suppression) in immunocompromised pts.
|
|
|
Telithromycin's usage and MOA
|
Same MOA as macrolides, but is used for macrolide-resistant strains.
Binds tighter to ribosomes and is a poor susbtrate for efflux pumps Comm.-acquired pneumonia |
|
|
Side effects of Telithromycin
|
severe hepatotoxicity
visual disturbances fainting episodes |
|
|
What two Streptogramins are combined for a bactericidal effect that binds to 50S, prevents interaction with the acceptor site, stim. its dissociation from ternary complex, and prevents extrusion of completed polypeptide?
|
Quinupristin-Dalfopristin
|
|
|
Spectrum/use for Quinupristin-Dalfopristin
|
VRSA
MRSA E. faecalis |
|
|
Quinupristin-Dalfopristin side effects
|
Arthralgia-myalgia syndrome
|
|
|
Do streptogramins inhib. P450? If so, what drugs to they effect?
|
*Yes - CYP3A4*
Increase plasma levels of: astemizole cisapride cyclosporine diazepam Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhib's WARFARIN. |

