![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the 5 hypothalamic-ant pituitary target axes, including:
--AP hormone --hypothalamic hormone(s) --which type of receptors are bound by AP hormones? (2) |
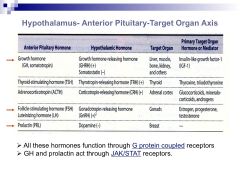
|
|
|
Describe the 3 types of target organ feedback in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis
|

|
|
|
Contrast the physiological actions of growth homone in:
1. childhood 2. adulthood |
1. promote growth of long bones (linear), cartilage, muscle, organs
2. metabolic: increase protein synth & bone density, increase lipolysis, promote gluconeogenesis, blocks insulin effects |
|
|
List features of GH axis dss in:
1. children (2) 2. adults (5) |

|
|
|
List 3 types of drugs used to tx GH deficiency and why they're used
|
1. synthetic GHRH (Sermorelin): defective GHRH release, NL AP)
2. recombinant GH (Somatropin, Somatrem) 3. Recombinant IGF1 (Mecasermin): in Laron dwarfism w/ GH receptor mutation |
|
|
6 drug indications for Somatropin & Somatrem
|
(recombinant GH)
1. documented growth failure in kids w/ GH deficiency, chr renal failure, Prader Willi, Turner's 2. small for gestational age 3. idiopathic short stature (>2.25 SD) 4. adult GH deficiency 5. AIDS wasting 6. short bowel syndrome |
|
|
5 SEs of recombinant hGH
|
1. leukemia, rapid melanocytic growth
2. hypothyroidism 3. insulin resistance 4. arthalgia 5. induce P450 enzymes |
|
|
4 contraindications and 2 tx considerations in using recombinant hGH
|

|
|
|
Name for GH excess in:
1. children 2. adults |
1. gigantism: longitudinal bone growth
2. acromegaly: bone thickening |
|
|
3 types of drugs to tx GH excess
|
1. somatostatin analogues (Octreotide)
2. GH receptor antag (Pegvisomant) 3. DA receptor ag (bromocriptine) |
|
|
1. Benefit of using octreoside over recombinant somatostatin
2. 3 drug indications for use |
1. octreoside is more potent and has longer half life
2. --control pituitary adenomas, --control carcinoid syndrome, --secretory diarrhea from VIP secreting tumor |
|
|
For octreotide, list:
1. 4 SEs 2. 1 contraindication 3. 3 tx considerations |

|
|
|
Describe the MOA of pegvisomant by comparing it to GH
|
GH: binds 2 receptor molecules causing dimerization and JAK/STAT cascade
Pegvisomant: compet antag of GH by only binding 1 receptor, preventing dimerization |
|
|
For pegvisoment, list:
1. 2 SEs 2. 1 contraindication 3. 2 tx considerations |

|
|
|
Describe the effects of GnRH in:
1. pulsatile release 2. continuous release |
1. promotes AP release of LH/FSH
2. inhibits AP |
|
|
Describe the effects of FSH in women:
1. in follicular stage of menstrual cycle 2. main fxn overall |
1. stimulates conversion of androgens to estrogens in Granulosa cells
2. ovarian follicle development |
|
|
Describe the effects of LH in women:
1. in follicular stage 2. in luteal phase |
1. stimulates androgen production in Thecal cells
2. control estrogen & progesterone production |
|
|
In men, describe the effects of:
1. FSH (2) 2. LH |
1. regulate spermatogenesis, increase Sertoli cell production of androgen binding protein
2. stims testosterone production by Leydig cells |
|
|
List types of drugs used in dss of gonadal axis:
1. stimulation (2) 2. inhibition (2) |
1. gonadotropins, GnRH/gonadorelin (analogue, pulsatile)
2. long half-life GnRH analogues, GnRH receptor antags |
|
|
3 drug indications of gonadaotropins to stimulate gonadal axis
|
1. ovulation induction
2. controlled ovarian hyperstim in assisted reproductive procedures 3. infertility in males |
|
|
Describe source of these gonadotropins:
1. menotropins 2. hCG 3. urofollitropin 4. follitropin |
1. urine of menopausal women containing FSH & LH
2. placental hormone 3. purified FSH from urine of postmenopausal women 4. recombinant human FSH |
|
|
List 5 SEs and 5 contraindications of gonadotropin stimulation of gonadal axis
|

|
|
|
3 indications of pulsatile GnRH agonists
|
1. stimulate ovulation
2. male infertility 3. dx hypogonadism |
|
|
1. MOA of inhibiting gonadal axis by using GnRH agonists
2. Describe biphasic response |
1. use analogs that are more potent and longer lasting than GnRH or gonadorelin...
2. --transient increase in gonadal hormones (7-10 day flare) from agonist effect --long-lasting suppression of gonadal hormones |
|
|
List 6 drug indications for sustained GnRH agonist inhibition of gonadal axis
|

|
|
|
1. List 3 GnRH receptor antags
2. benefit of use over sustained GnRH agonists 3. 2 indications |
1. ganirelix, cetrorelix, abarelix
2. no transient flare effect 3. --ganirelix & centrorelix: keep LH surge low in controlled ovarian hyperstim --abarelix: metastatic prostate cancer |
|
|
Regulation of PRL secretion:
1. inhibiting factor 2. releasing factor 3. describe feedback mechs |
1. DA from hypothalamus
2. TRH 3. no neg feedback since mammary glands release no hormones |
|
|
Strategy to tx hyperPRL
|
DA receptor ags (bromocriptine)
|
|
|
3 drug indications of bromocriptine
|
1. acromegaly if pit adenoma secretes PRL & GH
2. Parkinson's dz 3. hyper PRL |

