![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a pest |
"An undesirable organism" Ex: -insects -pathogens -plants -animals |
|
|
Pesticide resistance |
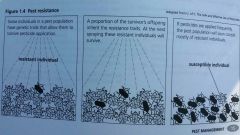
|
|
|
Ways to identify pets |
-reference materials -field guides (pictures and bio info) -have pest examined by management specialist
|
|
|
Biomagnification |

The process whereby some organisms accumulate chemical residue in higher concentration than those found in the organisms they consume. Ex: because the bird in this figure ends up eating directly or indirectly all the organisms, it has the highest concentration pesticide residue. |
|
|
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) |
The use of all suitable pest control methods to keep pest populations below the economic injury level. Two ways: Naturally or Applied |
|
|
Biological Control |
A Management Method This form often involves using a foreign enemy for the foreign pest. This process takes time because you have to locate the pest, inport its enemy, and make sure the foreign enemy doesn't have the potential to become a pest as well. |
|
|
Mechanical Control |
A pest management method. The use of devices, machines and other physical methods to control pest controll or alter their environment. Two approaches: cultivation (plows, mowers) and Exclusion (barriers) |
|
|
Having a screen door to your home is a way of barring pests. Which type of pest management method is this an example of? |
Mechanical Control (exclusive) |
|
|
Cultural Control (pg. 7) |
A pest management method. The goal of cultural control is to alter the environment. Disrupt the normal relationship between the pest and the host. This makes the pest less likely to survive, grow, or reproduce. Two approaches: Cultural practices, Sanitation. |
|
|
As a lawn care specialist, you utilize aeration, fertilization, mowing, and irrigation. Which form of pest management method is this? |
Cultural Control (Cultural Practices) |
|
|
Sanitation |
An approach of cultural control. Sanitation involves reducing food, water, shelter, other necessities important to the pest survival. |
|
|
Physical/Environmental Modification |
A pest managing method. Involves altering physical and environmental conditions such a as water, ever movement, temperature, light, and humidity. |
|
|
Refrigerators protect stored food products from unwanted pests. This is an example of which pest management method? |
Physical/Environmental Modification The refrigerator is altering the temperature. |
|
|
Host Resistance or Genetic Control |
Physical or psychological characteristics that prevent attack by pests. Ex: lion fish has spiked like body shape, psychologically making pests unattractive to it. |
|
|
Chemical Controls |
A Pest Management Method. Using pesticides. |
|
|
Why practice IPM? |

|
|
|
Key pests |
May cause major damage on a regular basis unless they are controlled. |
|
|
Occasional pests |
Become troublesome only once in a while because of their life cycles or environmental influences. |
|
|
Secondary pets (pg. 11) |
Become problems when the key pest is controlled. |
|
|
Components of IPM |
1. Identify the pest and understand its biology 2. Monitor the pest 3. Develop the pest management goal. 4. Implement the Integrated Pest Management Program 5. Record and evaluate results |
|
|
Economic Threshold |
Population density level where actions needs to be taken before reaching the EIL threshold. |
|
|
Economic injury level |
The pest density level that causes damages equal to the cost needed to control the population. |
|
|
Action threshold |
Test level hi enough that requires a past manager. Sometimes this it special day is the economic threshold. But sometimes and action to wash hold can be affected by other situations. Ex: mosquitos need to be eradicated because they can transmit diseases. |
|
|
Reasons for Pesticide resistance |
Continual use of pesticide from the same class Frequent applications Pests that have many generations per year and many offspring per generation. |
|
|
Under FIFRA, there are two kinds of pesticide applicators. Name them. |
Private pesticides (requires a certified Applicator to use them. Also known as Restricted-use pesticides) Commercial pesticides |
|
|
The two main classification for pesticides are? |
Unclassified use ( general-use pesticides) Restricted use |
|
|
Tolerance |
The maximum pesticide residue limit that may legally remain on or in treated crops and animals or animal products sold for food or feed. |
|
|
Which Federal agency is responsible for registering or licensing pesticide products for use in the United States? |
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) |
|
|
Which Federal law governors you selfish one of pesticide tolerance is is for food and feed products? |
FFDCA (Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act) |
|
|
Experimental use permits required under section 5 of FIFRA can be used when conducting experimental field test on new pesticides or new uses a pesticides on which minimal acres of land and water? |
5 or more acres of land or two or more acres of water |

