![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In Otto Rank's theory, which personality type is described as "individuality to the exclusion of unity"? |
Neurotic personality: Individuality to the exclusion of unity |
|
|
Describe what a "personologist" is |
Someone who is an expert in understanding people's thought, feeling and action patterns |
|
|
Describe the disagreement of ideas between Erikson and Freud |
None, they agree on both |
|
|
Justin Bobby Jr. is a very complicated man. Sometimes, he cares very much about his physical appearance and the way he dresses. He is the life of the party and a ladies man. However, sometimes, Justin Bobby Jr. wants to be alone, calling himself ugly and fat. At what stage might he have experienced a fixation? |
Phallic stage: vanity and flirtatiousness Characteristics: vanity/self-hatred, pride/humility |
|
|
Describe "fixation" |
Body is developing, however mentally, the mind is stuck at a certain stage. The individual cannot move on to the next stage without getting over the stage that is fixated on |
|
|
Describe the core belief of Rogers and Maslow |
They believe that people are generally born good than bad |
|
|
Give an example of Otto Rank's theory of "fear of death" and how it might manifest itself |
e.g., Fear of becoming old and others needing to take care of you Fear of death: inherent tendency toward union, fusion, dependency |
|
|
As a boss, Steve Bobs is very punctual and organized, he likes things a certain way and can be very stubborn if people do not agree with him. He tells people exactly what they need to do. At what stage might have Bob experienced a fixation? |
Anal stage e.g., Early or harsh potty training can lead to the child becoming an anal-retentive personality who hates mess, is obsessively tidy, punctual and respectful of authority. They can be stubborn and tight-fisted with their cash and possessions. |
|
|
What is the most ideal personality according to Jung? |
Ideal personality: selfhood Non-ideal personality: • introversive-rational • introversive-irrational • extroversive-rational • extroversive-irrational
|
|
|
Describe Erikson's "industry vs. inferiority" stage |
This stage involves the child's feelings of competence among their peers. Those who are commended and encouraged by their parents at a young age will more likely be successful because they get a sense of belief in their skills. Those who receive little or no encouragement from their parents will doubt their skills in the future.
e.g., this stage determines how the child will set themselves up as a worker and provider |
|
|
Describe the characteristic of "rational functions" |
A person who classifies under general concepts and organize them to determine meanings |
|
|
What defense is mainly used in the phallic stage? |
Repression: unawareness of wishes/desires to avoid anxiety |
|
|
What component of personality is present at birth? |
Id: your impulsive self who basically wants sex, food, and sleep |
|
|
Describe the behaviors involved in fixation in the oral stage |
Too little or too much stimulation of the oral stage can lead to behaviors in the future, such as sucking, nail biting, thumb sucking, etc. |
|
|
In the psychosocial conflict model, what type of defense is not associated with fixation in the oral stage of development? |
Regression |
|
|
According to Jung, how does one become introverted or extroverted? |
You learn to become one over the other |
|
|
Describe the conflict-free ego sphere for Ego Psychologists |
Some of the ego's functions are carried out without energy from the id |
|
|
Describe the defense mechanism of sublimation |
The changing of a social instinct into something that's more acceptable e.g., Having anger issues, and thus joining rugby to release aggression and frustration |
|
|
What factor influences "inherent potentialities"? |
Genetics |
|
|
What factor influences the "self concept"? |
Society (environment)
|
|
|
According to the psychosocial conflict theory, the ideal personality type defends against the antisocial force |
True |
|
|
In the fulfillment models, the goal is to minimize tension in one’s life |
False No, that's part of Otto Rank's Conflict Model |
|
|
In Otto Rank’s theory, only some people develop will from counterwill |
False
The Will is an active form of the self, which is a force that shapes a person's life with different experiences, thus, everyone develops this. |
|
|
Jung’s ego is different from Freud’s in that Jung thought the ego was partially unconscious |
True |
|
|
In Maslow’s theory, “the survival instinct”includes both physical and psychological needs |
True |
|
|
Like Freud, Jung emphasizes human biology to be influential on people’s personality and behavior |
False No, his core tendency is spiritual, NOT biology |
|
|
The core and periphery of personality are expressed at the same time in everyone’s behavior |
True |
|
|
According to the psychosocial conflict model(Freud), the goal of psychotherapy is to assist the patient in satisfying the id while minimizing the influence of the ego and superego |
False You want to minimize the id (impulsive desires) and assist the ego (conscious) and superego (morality) |
|
|
For Carl Jung, the collective unconscious wasmore important than the personal unconscious |
True: collective unconscious: accumulated experience of the human species personal unconscious: like Freud, experiences that were forced out of unconscious or forgotten |
|
|
The intrapsychic version of the conflict modelclaims that there are two competing forces, one from the within individuals and the other from groups or societies |
False -That's the psychosocial version of the conflict model -Intrapsychic version only has one force and its' up the society (environment) whether that force is attained or not |
|
|
The archetypes are examples of the personal unconscious |
False Archetypes are part of the collective unconscious |
|
|
In Otto Rank’s theory, the core statement is to strike a balance between the conscious and the unconscious |
False Core statement: to minimize the fear of life while at the same timeminimizing the fear of death |
|
|
The latency stage in Freud’s theory is considered to be the ideal type in which all traits are shown in moderate degree |
False No, that's the genital stage. Genital is the combination of all the previous stages in moderate degrees |
|
|
Rogers specified defense mechanisms in his model |
True |
|
|
Freud and Jung agreed that one way to uncover the unconscious is through imaginative procedures, like art |
True Freud: "art is the expression of the collective unconscious" |
|
|
The collective unconscious can become conscious with the help of psychotherapy |
False Only personal unconscious can become conscious with he help of psychotherapy; accumulated experience of the human species cannot be forced out by psychotherapy (personal unconscious) |
|
|
According to Jung, conflict should not be defended against |
True |
|
|
Personality types are inborn characteristics and tendencies |

False No, personality types are learned differences and similarities among people |
|
|
The fulfillment models are more optimistic than the conflict models |
True Yes because fulfillment model are about the goodness of the people |
|
|
A tendency is an attempt to achieve one’s ideals in life |
True |
|
|
The superego strives to act in socially appropriate manner and attempts to follow norms of the society |
True Yes, that's your morality |
|
|
The rational dimensions of Jung’s personalitytypes include thinking and feeling modes |

True |
|
|
Rogers and Maslow both agree that potentialities serve the maintenance and enhancement of life |
False That's both their "core tendency" but their core characteristics are different Rogers: -inherent potentialities -need for positive regard -need for positive self regard Maslow: -deprivation motivation -growth motivation |
|
|
According the Otto Rank’s model, people who are neurotic are fixated at the level of "counterwill" |

True |
|
|
According to the intrapsychic conflict theorythe ideal personality type defends against the antisocial force |
False Ideal: -accepted both types of fears as inevitable forces and achieving -intimacy and commitment -productive and innovative |
|
|
Personality types are at the periphery level ofpersonality |

True |
|
|
One of the main similarities between Rogers and Maslow’s theories is that they both specify one true force within the person |
False No, that's just their tendencies |
|
|
Describe what an archetype is |

Universal form of, or predisposition to, characteristic thoughts or feelings -has no material existence -is a form/essense |
|
|
One of the major differences between Freud’smodel and Erikson’s model is that Freud believes personality development is complete in young adulthood, while Erikson believes personality development is never complete |
True |
|
|
According to Jung’s Theory, personality can shift to selfhood in a person’s ___ |
Early 40's |
|
|
According to the conflict model, what parenting style would lead to the ideal personality type |
Moderately, accept, reward, and punish both selfish expression and altruistic expressions |
|
|
What is Freud's core statement? |
Core characteristic: instincts
|
|
|
What are the components of instincts? |
1. source 2. energy 3. aim 4. concept |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of the Id |
Deeply self-centered wishes and emotions |
|
|
What are the three instincts hosted by Id |
1. self preservation/life 2. sexual 3. death |
|
|
Describe the source, object, & aim of the following "life instinct"
|
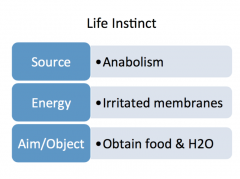
|
|
|
Describe the source, object, & aim of the following "sexual instinct" |
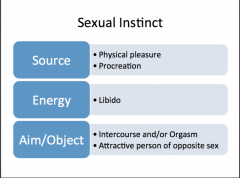
|
|
|
Describe the source, object, & aim of the following "death instinct" |
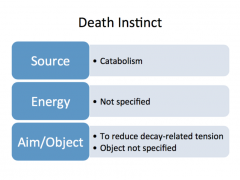
|
|
|
Describe the differences between Id and Ego |
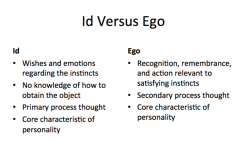
|
|
|
Describe the superego |
Morals/internalized rules of society; reality principle functioning |
|
|
What is the function of psychoanalysis? |
It helps change pleasure principle functioning to reality principle functioning |
|
|
Give an example of "repression" |
e.g., In the Oedipus complex, the unconscious desire to have sex with the parent is repressed by the conscious mind (ego)
|
|
|
Give and example of "regression"
|
e.g., a child comes home and goes into a fetal position on his/her bed because he/she did bad no his/her test. |
|
|
Give an example of "reaction formation" |
Reacting the opposite way what you're truly feeling e.g., Pretending to hate crush because she already has a boyfriend, but you like her |
|
|
Give an example of "denial" |
e.g., Boyfriend who is guilty for the termination of his relationship because he cheated on her is in denial of his mistake e.g., Smokers deny that smoking is bad for their health |
|
|
Give an example of "sublimation"
|
e.g., a person who is experiencing a lot of anger takes up kick-boxing classes as a means of venting out frustrations
|
|
|
Give an example of "projection" |
e.g., you get mad at your girlfriend and you scream at her and say that she's the one mad at you e.g., if you have a strong dislike for someone and you instead believe that he/she does not like you |
|
|
Give an example of "isolation" |
e.g., acting aloof and indifferent towards someone who you really dislike |
|
|
Give an example of "undoing" |
Trying to reverse a feeling by doing an action that signifies the opposite feeling e.g., you have feelings of dislike for someone so you decide to give them a gift |
|
|
Give an example of "intellectualization" |
e.g., a person who has just learned that he has cancer decides to learn everything about the disease in order to avoid distress and remain distant from the reality of the situation |
|
|
Describe Freud's "oral stage" |
Actions: taking and receiving
Conflict: being selfish Character: • optimism/pessimism • gullible/suspicious • manipulative/passive • admiration/envy • cockiness/self-belittlement Defenses: projection, denial, introjection |
|
|
Describe Freud's "anal stage" |
Action: giving and withholding
Conflict: hygiene Character: • stinginess/over-generosity • constricted/expanded • stubborn/acquiescence • orderly/messy • punctual/tardy Defenses: intellectualization, reaction formation, isolation, undoing |
|
|
Describe Freud's "phallic stage" |
Action: Oedipus/Electra complex
Conflict: castration/seperation anxiety Character: • vanity/self-hatred • pride/humility • courage/timid • brash/bashful • stylish/plain • gaiety/sadness • flirtatiousness/homosexuality • chastity/promiscuity Defenses: repression |
|
|
Describe Freud's "genital stage" |
-Full development and maturity -Still some social conflicts regarding expression -Defense: sublimation |
|
|
Describe the similarity and differences between Freud and Erikson's theories |

First four stages of Erikson is related to Freud - oral stage = trust vs. mistrust - anal stage = autonomy vs. shame/doubt - phallic = initiative & responsibility vs. guilty functioning - latent = industry vs. inferiority Later four stages drops the emphasis on biology - identity vs. confusion (early adolescence) - intimacy (bf/gf) vs. isolation (leaving parents) (end of adolescence) - generativity (guiding next generation) vs. stagnation (establishing) (young adulthood) - integrity vs. despair (mid-life) |
|
|
What is "benevolent electricism" |
The approach of using different theories, methods, models and perspectives, which can be used in "personality" to understand individual differences. However, this approach cannot make theoretical contributions to the field |
|
|
What is "partisan zealotry"? |
Basically the reviewing and analyzing of theory which involves dependence on other theories in order to criticize and show the superiority of the theory they focus on |
|
|
What is "comparative analysis"? |
Combines the breadth of analysis in "benevolent electricism and the conviction that some theories are better than others in partisan zealotry
|
|
|
What is "personality"? |
A stable set of tendencies and characteristics that determine those commonalities and differences in people's psychological behavior (thoughts, feelings, and actions) that have continuity in time and that may not be easily understood as the sole results of the social and biological pressures of the moment |
|
|
What do "personologists" do? |
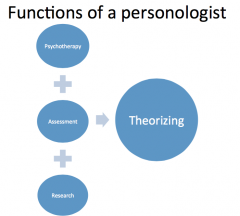
Study patterns in thoughts, feelings and actions of individuals -psychotherapy -assessment -research They also: -study groups of people to identify commonalities among them -identify and classify differences among people -attends specifically to all behaviors that seem to have psychological importance (doesn't focus on physiology) |
|
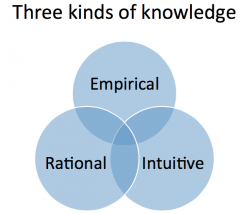
Describe the three kinds of knowledge of personologists |

|
|
|
Describe the difference between "periphery personality" and "core personality" |

Idea of nature vs. nurture
Periphery of personality: the type of personality that you develop depending on your society and environment (learned) Core personality: the type of personality that you are predisposed with because of genetics (unlearned) |
|
|
Schematic representation of the parts of a personality theory |
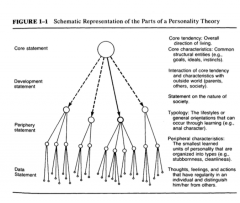
|
|
|
Describe the "conflict model" |
e.g., Erikson's stages, however this also applies to Freud's stages Periphery -ideal: compromise between the two opposing forces -non-ideal: favor one force at the expense of the other Development -ideal: parent/child interactions that are balanced -non-ideal: parent/child interactions that are too much or too little |
|
|
Describe the two versions of the "conflict model" |

-psychosocial version: •both forces of conflict (whether it be nature or nurture) will differ in where they come from -intrapsychic version: •both forcers of conflict (whether it be nature or nurture) comes from a predisposition of the individual •this version believes people are somewhat aware of their conflict and might suffer over these inconsistencies |
|
|
Describe the "fulfillment model" |
Idea that only one force in the core of personality exists within the individual and life in general allows for more and more ways to express this core aspect of personality Periphery -ideal: that which fully expresses the one force -non-ideal: those which block full expression of the one force Development -idea: individual/society interactions that facilitate full expression of the one force -non-ideal: individual/society interactions that block full expression of the one force |
|
|
Describe the two versions of the "fulfillment model" |

-Actualization version: genetic influence
-Perfection version: environmental influence |
|
|
Describe the "consistency model" |
Purpose: assumes consistency between environment and the individual is needed Cognitive dissonance version: resolves inconsistency by altering expectation of what should happen Activation version: consistencies between the tension that should happen in the body and the tension that actually occurs in the body |
|
|
Otto Rank Conflict Model: Intrapsychic |

|
|
|
Otto Rank Describe the "core statement" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

-To minimize the fear of life at the same time minimizing the fear of death -Aim is to reduce tension/anxiety caused by the two fears |
|
|
Otto Rank Describe the "developmental statement" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

-From the moment of birth, life is about a series of separation s and differentiation |
|
|
Otto Rank Describe the "peripheral statement" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

-Non-ideal: neurotic, average -Idea: artist |
|
|
Jung Describe the "core statement" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

-Tendency towards attainment of selfhood |
|
|
Jung Describe the "core characteristics" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

1. ego 2. personal unconscious 3. collective unconscious |
|
|
Jung Describe the "archetypes" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

Archetype: universal form of, or predisposition to, characteristic thoughts or feelings |
|
|
Jung Describe the "energy concepts" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

|
|
|
Jung Describe the "developmental statement" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

-More positive outlook -In your 30s and 40s orientations by the external, material word are replaced by an inward-turning spirituality. -principle of synchronicity: events that indicate commonality of collective unconscious; expressions of archetypes; highly spiritual |
|
|
Jung Describe the "peripheral statement" of the intrapscyhic version of the conflict model |

-Attitudes: one becomes more dominant -Functional modes: one is conscious, then the other isn't •rational (intro/extro) •irrational (intro/extro) |
|
|
Rogers Describe the "core statement & characteristics" of the actualization version of the fulfillment model |

|
|
|
Rogers Describe the "developmental statement" of the actualization version of the fulfillment model |

|
|
|
Rogers Describe the "peripheral statement" of the actualization version of the fulfillment model |
Ideal: "fully functioning person" -openness to experience (opposite of defensiveness): emotional, reflective, etc. -existential living: living fully at every moment; flexibility, adaptability, spontaneity, inductive thinking -organismic trusting: listening to your body's signals -experiential freedom: sense that one is free to choose among alternative courses of action -creativity: penchant for producing new and effective thoughts and things Nonideal: maladjusted -maintaining life rather than enhancing it -defensive -live according to a preconceived plan -disregard their organism -feel manipulated -are conforming and common |
|
|
Maslow Describe the "core statement" of the actualization version of the fulfillment model |

|
|
|
Describe the "core characteristic" of the actualization version of the fulfillment model |

-Depravation motivations -Growth motivations |
|
|
Describe the "developmental statement" of the actualization version of the fulfillment model |

|
|
|
Describe the "peripheral statement" of the actualization version of the fulfillment model |

|

