![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is Personal Financial Planning? |
The process of managing your money to achieve personal economic satisfaction. |
|
|
|
Financial Planning Process steps? |
1. Determine your current financial situation. 2. Develop financial goals. 3. Identify alternatives (continue, expand, change, or take new action). 4. Evaluate alternatives. 5. Create and implement a financial action plan. 6. Reevaluate and revise your plan. |
DDIECR |
|
|
What are some economic risks? |
Liquidity risk (difficult converting to cash) Interest rate risk Inflation risk Product risk |
LIIP |
|
|
What are some personal risks? |
Health risks Asset and liability risk Risk of death Risk of income lost |
|
|
|
Factors that influence financial goals |
Time frame (short < 1 year, intermediate 2-5, long term > 5 years) Goals for different financial needs (consumable product goals Vs durable product goals) |
|
|
|
Consumable product goals |
Items that are quickly used up (food, clothes, entertainment) |
|
|
|
Durable-product goals |
Expensive, infrequently purchased items Tangible: appliances, cars, equipment Intangible: relationships, health, education, leisure |
|
|
|
Life Situations that affect financial goals |
-Marital Status -Employment situation -Age -Number & age of household members |
MEAN |
|
|
Financial goals should... |
1. be realistic
2. be stated in specific, measurable terms. 3. have a time frame. 4. Indicate the type of action to take. |
|
|
|
What economic forces influence personal financial planning? |
Market forces Supply and Demand, Production costs and competition Financial institutions Influence from the Bank of Canada Global influences Level of exports, foreign investors, competition Economic Conditions Consumer prices Consumer Spending Interest Rates Money Supply Unemployment Rate GDP Trade Balance & S&P/TSX |
|
|
|
What are the Personal Opportunity Costs? |
Time & Health (lack of sleep, exercise, etc...) |
|
|
|
What are the Financial Opportunity Costs? |
The Time Value of Money: Which is the increase of money due to interest earned. |
|
|
|
What is Simple Interest?
|
Interest from the principal, but it excludes previously earned interest. |
P x r x n = I P = Amount in savings r = annual interest rate n = time period I = Interest |
|
|
What is Compound Interest? |
Interest that is earned on principal + previously earned interest.. |

|
|
|
Annuity Equations?
|
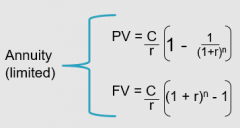
|
|

