![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the measurements of ABPI (ankle brachial press index) in normality and disease?
|
Normal = 1
Intermittant claudication = 0.5-0.9 Critical ischaemia = <0.5 |
|
|
What is intermittant claudication?
|
Obstruction of arteries by artherosclerosis (usually lower limb)- atherosclerosis of simple segment
Affects 5% middle aged men Presents: Calf m pain (if superior femoral artery affected) Buttock and thigh pain = iliac artery affected |
|
|
Rx IC:
|
Cilostazol (peripheral VD)
|
|
|
What is critical ischaemia?
|
Atherosclerotic plaques at multiple levels
Rest/night pain Gangrene/ulcerative foot >2 wks ABPI < 50mmHg NB Called subcritical ischaemia if symptoms but pressure > 50 30-40% DM |
|
|
Cause night pain in CI?
|
Occurs 1-2hrs after lying down
Lose gravitational effect on perfusion Drop BP + CO Pain relieved hanging foot outside bed Sleep in chair leads to oedema |
|
|
Features of diabetic vascular disease?
|
Arterial calcification
Immunocomprimised therefore = gangrene and cellulitis Charcot joint due to poor proprioception so present late |
|
|
What is buergers disease?
|
AKA Thromangiitis obliterans
Assoc male smokers 20-30yr Inflam obliterative arterial disease Symptoms: claudication, rest pain, fingers and toes affected Also affects VV Genetic element |
|
|
How does peripheral vasc disease affect the upper limb?
|
Subclavian artery common site for disease
Arm claudication rare Mainly due to atheroembolism as small emboli lodge in the digital aa Blue finger (easily confused raynauds) Subclavian steal - blood diverted/stolen from brain via vertebral artery As a result - dizziness, cortical blindness or collapse |
|
|
What is Raynauds phenomenom?
|
It is the description of the 3 colour changes in isch
1. White = pallor due to vasospasm 2. Blue = cyanosis secondary to deoxygenated blood 3. Red = rubor due to reactive hyperaemia |
|
|
What is Raynauds disease - primary raynauds?
|
Where the cause of the phenomenom is unknown
Rx nifedipine Affects yound females 15-30 (5-10% pop) |
|
|
What is secondary raynauds?
|
Older patients secondary to:
1. Connective tissue disease (e.g. crest syndrome) 2. Vibration injury e.g. pneumatic drill 3. Thoracic outlet obstruction - obstructing flow to arm? |
|
|
Symptoms of ischaemia? (6)
|
6 P's ischaemia
1. Pain 2. Paraesthesia 3. Paralysis 4. Perishing cold 5. Pulseless 6. Pallor |
|
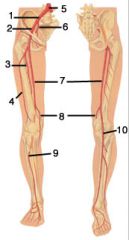
Label the diagram shown.
|
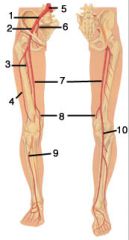
1. Right common iliac artery
2. External iliac 3. Deep femoral artery / profunda femoris 4. Lateral femoral artery 5. Abd aorta 6. Internal iliac 7. Femoral artery 8. Deep Genicular artery 9. Ant tibial artery 10. Popliteal artery |

