![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Know medication and ways it impacts Tx
|
?
|
|
|
How does perio impact treatment?
|
Smoking increases the risk of Periodontitis by 5-10x: clinical attachment loss Pocket depth
|
|
|
What is the best number for long term glucose level management?
|
HbA1c 7 or under
|
|
|
Which patients are best referred to a periodontist?
|
??
important to maintain good hygiene over a long period of time downward trend w/attachment loss |
|
|
What are risk factors for periodontal disease?
|
Smoking
Diabetes Osteoporosis Drug induced conditions: dilantin, Ca++ channel blockers, verapamil Compromised immune system Deteriorating risk profile (charting) Cancer therapy Joint replacement therapy |
|
|
What are the best radiographs to show bone height?
|
Bitewings
can't see bone loss until 30-50% decalcification |
|
|
What are Bone problems you can identify off radiographs?
|
(straight off slides)
Amount of bone loss Distribution and pattern (vertical or horizontal) |
|
|
What do you need for diagnosis of bone loss?
|
Relies on clinical attachment loss
|
|
|
How are both bone loss & clinical attachment loss classified?
|
Mild, Moderate, severe
|
|
|
When you are diagnosing bone problems, what are you using for diagnosis?
|
Diagnosing by probing depth and recession (clinical attachment level) Not the bone loss
|
|
|
T/F
Bone loss correlates with clinical attachment loss, but is not used in the diagnostic procedure |
True
|
|
|
Why do we use clinical attachment level for bone problem diagnosis?
|
If there is recession on the facial, you will not see it on x-rays so you would not know that there is bone loss
|
|
|
What is the difference between a maintenance visit and a regular cleaning?
|
Maintenance is active therapy to identify what's falling by the wayside, more frequent, more in depth. To track and identify progress and re-evaluation.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a re-evaluation appt after a scaling and root planing?
|
It's a decision making point
Determine how successful the initial periodontal therapy was. Collect data of All the clinical parameters Re-evaluate the Data Decide what to do next. More OHI?, more root planing? Perio surgery? or Truly into maintenance |
|
|
T/F
For patients that are new to you, look at the past periodontal history that is on the back of our charting |
T
|
|
|
Why is a maintenance more expensive than a prophy?
|
Takes more time because you are measuring everything
|
|
|
What's the hallmark of Aggressive periodontitis, localized & general?
|
Rapid attachment loss and bone destruction
|
|
|
What is the first step in treating localized periodontitis?
|
Antibiotics and scaling, the re-evaluate, make a decision that patient is probably best co-managed
|
|
|
What are the demographics of aggresive localized periodontitis?
|
Young <30 years old
Blacks |
|
|
Profile of a severe periodontitis patient, how far are the bone levels from the CEJ?
|
Severe is 5 or more
Moderate 3-4 Mild 1-2 |
|
|
What does loss of attachment refer to?
|
Loss of gingival connective tissue
The attachment of the gingival fibers to the cementum on the roots The gingival attachment level is the coronal fiber attachment (which is also the depth of the pocket) |
|
|
When we say Clinical Attachment Level, the word Attachment refers to?
|
to the gingival connective tissue attachment to the cementum on the root.
This should be 1-2 mm |
|
|
How do you calculate clinical attachment level?
|
Base of Pocket to CEJ
|
|
|
How is Localized CHRONIC different from Generalized?
|
If it's less than 30% it is Localized
Generalized if more than 1/3 of sites in mouth |
|
|
Histologically, how do you measure the attached gingiva?
|
Base of pocket (sulcus) to the mucogingival junction
|
|
|
What is Trauma from Occlusion?
|
Injury to the PDL
Injury to the Alveolar bone |
|
|
What are signs on radiograph from trauma?
|
Widened Periodontal Membrane
Loss of Resorption of the root surface Vertical or angular Bony Defects (CANNOT BE REGARDED AS AN EXCLUSIVE SIGN OF TRAUMA FROM OCCLUSION) You do not see radiographic signs of trauma from occlusion often |
|
|
Chronic trauma from occlusion can be caused by?
|
Bruxing or clenching
|
|
|
Occlusion & periodontitis...Does the presence of inflammation change the rate of attachment loss? Bone loss?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Chronic inflammatory periodontal disease is classified into how many different types of lesions?
|
4
1. Initial - 2-4 days plaque accumulation, gingival crevicular fluid increases 2. Early - LYMPHOID cells accumulate 3. Established 4. Advanced - AKA Chronic periodontitis, histology of chronic lesion you see Plasma cells |
|
|
In advanced stage of Chronic inflammatory periodontal disease, what cells are present?
|
Plasma cells
|
|
|
In Early Chronic inflammatory periodontal disease what cells accumulate?
|
Lymphoid cells
|
|
|
What kind of cells are found in Acute Periodontal Abscess?
|
PMNs
|
|
|
What is the depth of a Moderate perio pocket?
|
4-6 mm
|
|
|
Different types of bone loss?
|
Vertical
Horizontal Combination (most likely) |
|
|
How many walls are in an interdental crater?
|
2 walls
|
|
|
A shallow defect with one wall, (wide shallow with 1 wall, deep and narrower with 3 walls) Which has a better prognosis?
|
Narrower deep with 3 walls has better pognosis
|
|
|
How do you differentiate clinically between chronic periodontitis vs plaque induced gingivitis?
|
Periodontal Attachment Loss
|
|
|
What causes tooth mobility?
|
Trauma from occlusion
Clinical attachment loss (bone loss) Abscess lesion |
|
|
On a 3 walled boney defect, what is the 4th wall?
|
tooth
Biofilm/calculus will hurt the prognosis of that tooth |
|
|
What is Reverse architecture?
|
Interproximals are lower than normal
It is bad |
|
|
Which disease occurs only in an acute form?
|
Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of an acute periodontitis abscess?
|
Swollen
Throbbing pain Tooth mobility (with chronic due to hydraulic forces) Sensitivity to percussion NO sensitivity to thermal changes |
|
|
When is the correct time to start definitive treatment when a patient presents with an acute periodontal abscess?
|
Manage symptoms (abx and pain control) when the acute form has left, then you can diagnose the chronic problem and be able to treat the real problem
|
|
|
How does ANUG manifest?
|
Smells horrible
Painful Bleeding Inflammation Tissue looks pink, red & white White is Necrotizing tissue |
|
|
When NUG or NUP heals what are you left with?
|
Punched out lesions, deformed gingival tissue
|
|
|
What are you left with after acute pericoronitis?
|
Gingiva looks exactly how it did before, no deformities or changes
|
|
|
What is left after Desquamative gingivitis is out of the acute phase?
|
It should return to normal
|
|
|
Biologic width is measured from the?
|
Bottom of the gingival sulcus to the alveolar crest
|
|
|
Periodontal vertical osseous defects can be classified according to Goldman and Cohen by?
|
Identifying the number of walls remaining
|
|
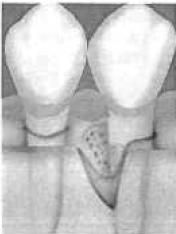
Based on the Goldman and Cohen defect classification, this represents a?
|
3 wall defect
|
|
|
Attachment level is measured from?
|
CEJ to base of pocket
|
|
|
The components of a complete periodontal diagnosis include?
|
Type of perio disease
Severity of perio disease Distribution of periodisease |
|
|
Re-evaluation after initial therapy is performed to evaluate?
|
Oral hygiene
Medical history Attachment level Patient's compliance |
|
|
During initial examination, a patient has a red, edematous gingiva with generalized 4-5 mm pockets which bleed very easily upon probing. Apical boundaries of the pockets are located at or near the cementoenamel junction. What is the most appropriate treatment?
|
Scaling and root planing
|
|
|
Which of the following types of periodontal pockets offers the best possibility for bone regeneration?
a) suprabony pocket b) one wall infrabony pocket c) two wall infrabony pocket c) three wall bony pocket |
Three wall
|
|
|
Which of the following changes is clinically observed during the initial phase of inflammatory periodontal disease?
a) Gingival margin in red b) Gingival margin is swollen c) Bleeding on probing d) A & C e) None of the above |
None of the above
|
|
|
In a healthy periodontium, how long does it take for the clinical features of the early lesion of inflammatory periodontal disease to appear from the time of stopping all oral hygiene measures?
|
4-7 days
|
|
|
Radiographically, alveolar bone loss is seen in which of the following stages of inflammatory periodontal disease?
a) Early lesion b) Advanced lesion c) Established lesion d) B& C e) None of the above |
Advanced lesion
|
|
|
The established lesion of perio disease is clinically synonymous with?
a) chronic gingivitis b) chronic periodontitis c) aggressive periodontitis d) none of the above |
none of the above
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the advanced lesions of periodontal disease?
|
Gingival pockets
Destruction of PDL Increased tooth mobility |
|
|
The vasculitis which is present in the initial lesion of inflammatory periodontal disease is associated with?
|
Increased capillary permeability
Increased diameter of the small blood vessels |
|
|
The increase in the amount of gingival crevicular fluid starts to occur at which of the following stages of inflammatory perio disease?
|
Initial Stage
|
|
|
In chronic inflammatory periodontal disease, apical migration of the junctional epithelium along the root surface of the tooth occurs ____ the destruction of the dentogingival group of collagen fibers of the periodontium
|
After
|
|
|
The response to the presence of chronic inflammatory cellular infiltrate in the connective tissue of the periodontium is?
|
Resorption of the bone
Destruction of the collagen fibers Proliferation of the adjacent epithelium |
|
|
During the development of inflammatory periodontal disease, the following cells appear in the connective tissue of the periodontium in what order?
Plasma cells T lymphocytes B lymphocytes PMNs |
???
|
|
|
In long standing chronic inflammation, the color of the gingiva may return to the normal coral pink color due to the presence of ?
|
Excessive fibrous tissue formation
|
|
|
Radiographically, the distance between the crest of the interproximal bone and the cemento-enamel junction in patients with chronic perio is ____ than that of the healthy perio
|
Less than
|
|
|
When the alveolar bone is lost due to periodontitis around the mand 1st molar to the extent that you can probe through and through the furcation area, this condition is classified as?
|
Class III bifurcation involvement
|
|
|
The time period for the established lesion of inflammatory perio to progress to the advanced stage is?
|
???
|
|
|
In the advanced lesion of inflammatory periodontal disease bone resorption is histologically evidenced by the presence of?
|
Mast cells
Osteoclasts Howship's lacunae |
|
|
Acute periodontal disease is a clinical situation of recent onset and?
|
Associated w/pain
Related to gingivitis or periodontitis Unrelated to gingivitis or periodontitis |
|
|
Acute periodontal abscess is defined as a _____ area of inflammation
|
Localized
Circumscribed Purulent |
|
|
What clinical features are usually associated with an acute periodontal abscess?
|
Increased tooth mobility
Tooth is sensitive to percussion Connection between the periodontal pocket and the abscess |
|
|
Which of the following findings are considered to be diagnostic aids for acute periodontal abscess?
a) Sensitivity of the tooth to thermal changes b) Presence of a radiolucent area around the root c) No connection between the pocket and the abscess cavity d) None of the above e) All of the above |
None of the above
|
|
|
Clinically acute periodontal abscess is best described as?
|
Localized swelling
Purulent in nature Located at the lateral aspect of the involved root |
|
|
a 14 year old male patient has a diffuse erythema of the gingiva with scattered isolated ulcers on the tongue, oropharynx and cheek mucosa. His condition os of 3 days duration is painful and he has a fever and malaise. The most probable diagnosis is?
|
Acute herpetic Gingivostomatitis
|
|
|
The most common microorganisms implicated in the etiology of necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis are?
|
Borrelia vencenti
Fusiform bacilli |
|
|
Which of the following lesions may create gingival deformities that require gingival surgery?
a) acute pericoronitis b) desquamative gingivitis c) necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis d) acute herpetic gingivostomatitis |
Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
|
|
|
The actual position of the gingiva is determined by?
|
The level of the epithelial attachment on the tooth
|
|
|
a 14 year old male patient has a diffuse erythema of the gingiva with scattered isolated ulcers on the tongue, oropharynx and cheek mucosa. His condition os of 3 days duration is painful and he has a fever and malaise. The most probable diagnosis is?
|
Acute herpetic Gingivostomatitis
|
|
|
The most common microorganisms implicated in the etiology of necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis are?
|
Borrelia vencenti
Fusiform bacilli |
|
|
Which of the following lesions may create gingival deformities that require gingival surgery?
a) acute pericoronitis b) desquamative gingivitis c) necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis d) acute herpetic gingivostomatitis |
Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
|
|
|
The actual position of the gingiva is determined by?
|
The level of the epithelial attachment on the tooth
|

