![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is metacognition? |
Processes involved in monitoring and controlling performance on a task |
|
|
What is monitoring? |
A process that allows us to observe and reflect on our own cognition |
|
|
What are some measures of monitoring? |
- Ease of Learning - Judgment of Learning - Feeling of Knowing - Confidence |
|
|
What is control? |
Conscious and non-conscious decisions we make based on the output of our monitoring processes |
|
|
What are some measures of control? |
- Self-paced study time - Response time - Quantity of information reported - Grain-size of information reported |
|
|
What is the accuracy of metacognitive judgements? |
They are of intermediate accuracy - above chance but far from perfect |
|
|
What are experience-based cues? |
Sheer feeling arising from some aspect of remembering, learning or failing remember - interpretation of what that means |
|
|
What are information-based cues? |
A-priori theories and analytical inferences about the impact of various factors on memory - "The longer a stimulus is present for, the more likely I will later remember it" |
|
|
What is the recall-recognition paradox? |
Recognition better in lab but recall better in eyewitness studies |
|
|
What is the model of monitoring and control in memory? |
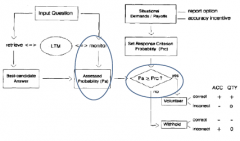
|
|
|
According to the model, what is memory based on? |
- Overall retention - Monitoring effectiveness - Control sensitivity - Report criterion setting |
|
|
What is the accessibility hypothesis? |
Effects occur because the new information (misinformation) modifies the activiation and accessibility of the original memory, which thereby becomes less accessible |
|
|
What is the memory replacement hypothesis? |
Effects occur becuase the original memory is replaced by misinformation |
|
|
What are the three steps for memory implantation? |
1. Convince people that the target event is plausible 2. Convince people they experienced target event 3. Reinterpret images and narratives as memories of target event |
|
|
Why is confidence not a good predictor of accuracy? |
- Most studies use one set of stimulus materials for all witnesses (restricting variability) - Most studies look at the confidence-accuracy relationship using point-bi-serial correlation |
|
|
What's the problem with point-bi-serial correlation? |
- Cannot 'see' the full relationship - Provides no information about extent to which participants over or under estimate the prob. that they were correct - The correlation can be low but the calibration perfect |
|
|
What is the confidence-accuracy calibration? |
Plot subjective confidence against proportiton correct |
|
|
What factors can affect the confidence-accuracy calibration? |
- Decision type: positive vs. negative - Reflection - Hypothesis disconfirmation |
|
|
When would we see a single dimension emerge from state-trace analysis? |
If confidence is based only on memory strength |
|
|
When would we see a multidimensional model from state-trace analysis? |
If another IV also affected confidence along with memory strength, such as certainity |
|
|
What is the discrepancy-reduction model? |
People study the judged-difficult items forlonger, to reduce discrepancy |
|
|
What is the under confidence-with-practice effect? |
- Participants confidence in each test cycle is lower than their actual accuracy - We aren't considering the effect of practice on our performance |
|
|
What did Son & Metcalfe find regarding the discrepancy-reduction model? |
With insufficient study time, participants actually choseto study those items judged to be easy to learn |
|
|
When is performance on tests poor? |
- Insensitive to the amount they have studied - Don't know which material will be tested - Haven't realised that spaced study is better than cramming |
|
|
What are the benefits and costs of dropping items? |
- Cost: No longer being learned and can't be revisited - Losing benefit of spacing - Benefit: spend more time on other item |
|
|
What did Kornell & Bjork find about dropping cards? |
Accuracy is impaired by allowing participants to drop cards |
|
|
When is the delay after learning effect not present? |
- When question and answer are both present - Less than 5 minutes - May not be applicable to all types of material - If the type of questions of the practice and criterion test are different |
|
|
When are practice tests useful? |
- Delay after study - Time to relearn poor material - Relate to criterion performance - Recognition less useful than recall |
|
|
What is constructive matching? |
Lookat problem, try to think of answer then inspect alternatives |
|
|
What is response elimination? |
Lookat alternatives and try to eliminate alternatives |
|
|
What are the tenets of a cognitive interview? |
- Buildrapport, foster control over report in the witness - Contextreinstatement “think back to the event” - Openended report – free recall - Followed by focussed report |

