![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What anatomic parts of the stomach are involved in acid secretion?
|
Fundus
Body Not the antrum |
|
|
What kinds of cells are found in the antrum of the stomach? What do they do?
|
G cells
Produce gastrin |
|
|
Broadly, what is the action of gastrin?
|
Regulation of acid secretion
|
|
|
What is the structure of a stomach gland?
|
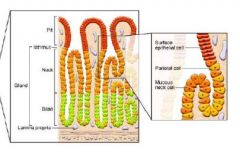
|
|
|
What do parietal cells synthesize?
|
Acid
|
|
|
Where are parietal cells found?
|
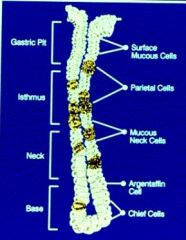
Isthmus
Neck |
|
|
Where are the chief cells located?
|
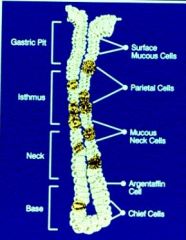
In the base of the stomach glands
|
|
|
What is the function of chief cells?
|
Synthesis of pepsinogen
|
|
|
Where are the mucous cells located?
|
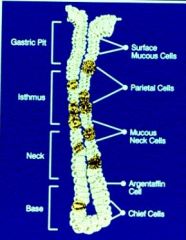
Neck
|
|
|
What is the function of mucous in the stomach?
|
Protection of the stomach epithelia from gastric acid
|
|
|
What are the three receptors on the parietal cells involved in acid production?
|
Gastrin: CCKBR
ACh: M3R Histamine: H2 |
|
|
What histamine receptor mediates acid secretion?
|
H2
|
|
|
What occurs in peptic ulcer disease?
|
A defect in mucosal integrity causes erosion of the stomach wall.
|
|
|
What is the recurrence of PUD?
|
Frequently recurs!
|
|
|
How do you control PUD?
|
Controlling the acid: no acid, no ulcer.
|
|
|
What are the important factors in the pathophysiology of PUD?
|
H. pylori
Acid |
|
|
What is the structure of H. pylori?
|
Flagella
Resistant to acid via |
|
|
What's the staining for H. pylori?
|
Silver stain
|
|
|
What is the transmission of H. pylori?
|
Fecal-oral
Oral-oral |
|
|
What factors are associated with H. pylori infection?
|
Developing countries
Inversely related to SES Age |
|
|
If you have a duodenal ulcer, what's (almost always) the cause?
|
H. pylori: 90%
|
|
|
What is the impact of eliminating H. pylori on PUD remission?
|
You decrease remission rates SIGNIFICANTLY!
|
|
|
How does the pathogenesis of H. pylori occur?
|
Motility factors: travel through the mucus layer
CagA: toxin Peptidoglycans for immune evasion Adhesive factors: can hook onto the cells. |
|
|
What does CagA do inside the cell?
|
TRKs that lead to the activation of cellular profliferation-->gastric cancer (possibly)
Also, NFB for cytokine release-->inflammation |
|
|
What is the effect of cytokines on G cells?
|
Cause gastrin release-->more acid`
|
|
|
What is the effect of cytokines on D-cells?
|
Inhibition of somatastatin release (hormone that decreases acid secretion)
|
|
|
What are the different kinds of H. pylori infection?
|
Duodenal ulcer phenotype
Simple gastritis (most common) Gastric cancer |
|
|
What is the main manifestation of H. pylori infection?
|
Simple gastritis
|
|
|
What's the most rare manifestation of H. pylori? What is this associated with?
|
Gastric cancer
Early exposure to HPV |
|
|
What changes occur in the gastric cancer phenotype of H. pylori infection?
|
High gastrin
Parietal cell atrophy |
|
|
What predisposes someone to gastric cancer from H. pylori?
|
Cytokine receptor genes:
IL-1 genes Bacteria expressing cagA, vacA |
|
|
What kind of a diet predisposes someone to gastric cancer from H. pylori?
|
Smoking
High salt diet |
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of PUD?
|
Pain: 30-40%
Mid-epigastric gnawing, burning Increaseed with fasting Decreased with meals, antacids |
|
|
What are some of the asymptomatic presentations of PUD?
|
Bleeding
Perforation Obstruction |
|
|
What's on the differential diagnosis for dyspepsia?
|
Idiopathic
GERD Pregnancy Meds Delayed gastric emptying Biliary/pancreatic diseases Mesenteric ischemia IBD: gastroduodenal Crohn's MSK |
|
|
What are some labs that you should order for someone who you suspect has PUD?
|
Labs:
CBC Chemistries Gastrin level (not routine) Acid secretory studies (hard to do - rare) Structural: Radiographic Scope |
|
|
What's the best test for an ulcer?
|
Scoping the stomach`
|
|
|
What kind of a radiographic study do you order up for ulcers?
|
Double contrast barium metal with compression
|
|
|
What does an ulcer look like on plainfilm?
|
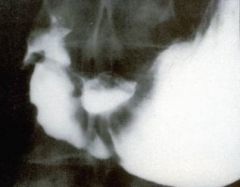
Crater with barium pooled
|
|
|
What's the best kind of study for PUD?
|
Scope!
|
|
|
How do you diagnose H. pylori?
|
Noninvasive:
Serology (Abs) Stool antigen - great Carbon-labeled urea breath test (more complicated) |
|
|
How does the carbon-labeled urea breath test work?
|
1. Give urea labeled with C14
2. H. pylori urease breaks down the urea into NH3 and CO2 3. CO2 is exhaled 4. Measure the amount of C14 in the exhaled CO2; if high, suspect H. pylori |
|
|
What are some invasive tests for H. pylori?
|
Rapid urease assay
Histology (silver stain, immunohistochemistry) Culture (RARE! tough to grow) |
|
|
How does the rapid urease assay work?
|
When you're scoping, put a piece of tissue that colors when H. pylori is present
|
|
|
What are the goals of therapy in PUD?
|
Pain relief
Ulcer healing Decreased recurrence Decreased complications |
|
|
What are the classes of drugs used for PUD?
|
Acid inhibitiing/neutralizing agents
Cytoprrotective agents |
|
|
What are some of the acid-inhibitory/neutralizing drugs for PUD?
|
Antacids
Anticholinergics H2 receptor antagonists Prostaglandins PPIs |
|
|
What are some of the cytoprotective agents used in PUD?
|
Sucralfate
Prostaglandins Not as common as the PPIs |
|
|
What are the indications for getting rid of H. pylori in ulcers?
|
Gastric ulcers: yes
Duodenal ulcers: yes Otherwise, no. If someone who's young, get rid of the H. pylori. If there's asymptomatic H. pylori infection, don't get rid of it. |
|
|
What do you do to eradicatede H. pylori?
|
2 antibiotics
PPI Basically, polypharmacy |
|
|
What are the most common side effects for therapy to H. pylori therapy?
|
Metallic taste
Nausea/vomiting Other infections Pseudomembranous colitis: <1% |
|
|
What are the indications for surgery in PUD?
|
Refractory GI bleeds
Gastric outlet obstruciton Perforation Malignancy |
|
|
Where can you get ulcers from NSAIDs?
|
Epigastric pain/dyspepsia
Gastric erosions/ulcers Duodenal ulcers Colonic and small bowel ulcers and erosions Small bowel strictures Small bowel and colonic inflammation |
|
|
How do NSAIDs cause PUD?
|
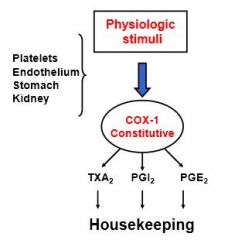
Blocking COX-1
You don't get proper housekeeping of the GI tract |
|
|
What are the mechanisms by which NSAIDs cause injury to the GI tract?
|
Prostaglandin depletion
Topical: ion trapping |
|
|
What do the prostaglandins do in the gastric mucosa?
|
Maintain good blood flow to the stomach
Promote mucus secretion Promote bicarbonate secretion All 3 are important for proper stomach functioning! |
|
|
How does ion trapping occur in the stomach?
|
NSAIDS are protonated, which makes them neutrally charged. They then are able to travel into the gastric epithelia, which brings the hydrogen ions along. Then, you get the dissociation of the NSAID and the H+ in the cell, which causes cellular damage due to an increased H+ concentration
|
|
|
What percent of people who use NSAIDS chronically get erosions? GUs? DUs?
|
Erosions: 40-60%
GUs: 10-30% DUs: 5% |
|
|
What people who use NSAIDs are at higher risk?
|
Age
Prior history of ulcers Higher NSAID doses Anticoagulant use Serious systemic injury |
|
|
What's the therapy for people with NSAID induced ulcers?
|
1. DIscontinue the NSAIDs
Other: -Sucrasulfate -Misoprostol -H2 receptor antagonists -PPI |
|
|
Do you give prophylaxis for NSAID associated ulcers?
|
Yes.
Give PPIs. Problems - noncompliance due to side effects. |
|
|
What is the side effect of misoprostol? What is the use?
|
Diarrhea, abdominal pain, uterine contraction
NSAID ulcer prophylaxis |
|
|
What are some of the selective COX-2 inhibitors?
|
Celecoxib
Rofecoxib No ulcers from the NSAIDs. |
|
|
Why aren't COX-2 inhibitors used commonly?
|
You don't want to cause heart problems.
|

