![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four steps of the intitial exam?
|
1) Chief complaint
2) Medical history 3) Social history 4) Dental history |
|
|
What is the physical exam divided into?
|
1) Extraoral Examination
2) Soft Tissue Evaluation 3) Hard Tissue Evaluation |
|
|
T/F
Gingivitis in children is extremely common, but periodontal disease is not common |
True
|
|
|
What kind of problems can macroglossia present?
|
Speaking and breathing
|
|
|
What is the first thing you do in the hard tissue evaluation?
|
Count the teeth
(are there missing, impacted, congenitally missing teeth) |
|
|
During your hard tissue exam, when you are performing occlusal analysis which thing do you have to intervene with at an early age?
|
Transvers/midline/crossbites and overjet
|
|
|
What are the components of an occlusal analysis?
|
1. Alignment/crowding
2. Overbite 3. Overjet 4. Molar relation/cuspid relation 5. Transverse/midline/crossbites |
|
|
What should you use to check for caries in children?
|
Air syringe
|
|
|
What is the order of eruption for primary dentition?
|
CI
LI M1 C M2 |
|
|
What is the order of eruption of the permanent dentition?
|
Max - M1, CI, LI, PM1, PM2, C, M2, M3
Mand - M1, CI, LI, C, PM1, PM2, M2, M3 |
|
|
When talking about MICP in deciduous teeth, what are the molar relationships?
|
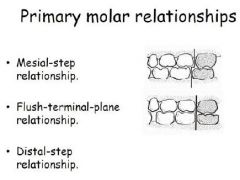
Not Class I II or III for primary molars
Flush terminal plane = class I Distal step = class II |
|
|
What is the growth pattern of the maxillary and mandibular arches?
|
Downward and Forward
|
|
|
Which molar relationship has retruded CI's?
|
Class II Div II
|
|
|
When doing orthodontic evaluation how are overbites described?
|
100% overbite = 100% covered teeth
0% = edge to edge |
|
|
What type of radiographs need to be taken on a child?
|
If child has closed contacta then take 2 Bitewings with the largest size that fits. One occlusal.
Take a Panorex at age 9 to monitor eruption of cuspids |
|
|
What is a knee to knee exam?
|
knee to knee exam allows the dentist to examine the child who is either too young or is unable to sit in the dental chair
|
|
|
On caries risk assessment what is the child's overall assessed risk for developing decay?
|
Based on the highest level of risk indicator circles
|
|
|
When treatment planning how should you plan your sequence?***EXAM QUESTION
|
Treatment by QUADRANT
1. Most serious quadrant first 2. Permanent teeth prior to primary teeth 3. Posterior teeth prior to anterior teeth The exception is if the patient is in pain, treat that area first |
|
|
What are some options for treating primary anterior teeth?
|
Interproximal stripping, just strip it away
Composite resins/Glass ionomer fillings Composite resin strip crowns |
|
|
How are primary posterior teeth restored?
|
Amalgam
Composite resins Stainless steel crowns |
|
|
Which children are candidates for pit and fissure sealants?
|
Medium-High risk children
|
|
|
What is a preventative resin restoration?
|
Enamel only lesions
Incipient lesions just into dentin Small class I lesion |
|
|
What is important about using fluoride trays for 1-4 minutes?
|
Sit the Child Upright
|
|
|
T/F
In your documentation, you should detail any instructions to the parent and note behavior of the child |
True
|
|
|
What is the Frankel Behavior Rating Scale?
|
F1 - Definitely negative (really bad screaming, kicking, a nightmare)
F2 - Negative (Almost nightmare loud, obnoxious) F3 - Positive (but whiny and anxious) F4 - Definitely positive (great patient) |
|
|
What type of local anesthesia do we use most often on children?
|
2% Lidocaine (Xylocaine) 1:100,000 epinephrine
Amide anesthetic |
|
|
How many mg of Lidocaine is in one carpule?
|
36 mg
|
|
|
What is the Maximum Recommended Dose of anesthetic?
|
4.4 mg/kg
Absolute Maximum 300 mg |
|
|
How much lidocaine can you give a pedo patient who weighs 40 lbs?
|
40 lbs; lbs/kg
40 lbs = 18 kg 18 kg x 4.4 mg/kg = 79 mg 79 mg / 36 mg/carpule = 2 carpules |
|
|
How do you ensure that an area is anesthetized?
|
Ask patient for signs - Fat, funny feeling
Test area with explorer |
|
|
What are the most commonly used injections for children?
|
Maxillary
-Supraperiosteal infiltration -Intrapapillary Mandibular -Inferior alveolar block -Long buccal nerve block -Mental nerve block Intraligamentary anesthesia |
|
|
How do you use the quick method to obtain lidocaine dosing for a 50 lb child?
|
50/2 = 25
25 x 4 =100 100/36 = 2.8 |
|
|
When would you do an Infraorbital block?
|
Use only when truly needed i.e. trauma
|
|
|
Where is the height of insertion for Inferior Alveolar Block?
|
Height of insertion is about 5 mm above the mandibular occlusal plane of the primary teeth
|
|
|
What is kid for rubber dam?
|
Rain Coat
|
|
|
T/F
It is okay to leave a rubber dam on a kid if you only have to leave the room for a second |
False
|
|
|
T/F
Never leave anything in the mouth that is not visible to you at all times (i.e. leaving cotton rolls under the rubber dam) |
True
|
|
|
Where are the most common surfaces where sealants fail?
|
Maxillary molars distal to the transverse ridge
|
|
|
When performing a PRR (Preventative Resin Restoration), what should you use to remove caries?
|
SLOW SPEED round bur
|
|
|
T/F
A Tofflemire is usually not used in children |
True
Difficult to place in a child's mouth Does not adapt well to the primary tooth It can't be placed on a tooth that is clamped |
|
|
What type of Matrix band do we use in pedo?
|
T-bands - fold flaps down and tighten like a belt. May use Howe pliers.
|
|
|
What is the occlusal reduction for stainless steel crowns?
|
SSC's occlusal reduction = 1-1.5 mm flat plane reduction
|
|
|
What is the difference between a pulpotomy and a pulpectomy?
|
Pulpotomy - partial, just take out chamber
Pulpectomy - similar to root canal, take out everything |
|
|
__________ is a procedure based on the idea that the Radicular Pulp Tissue is Healthy or is Capable of Healing after amputation of the infected coronal pulp.
|
Pulpotomy
|
|
|
When is pulpotomy contraindicated?
|
Pulpal swelling
Fistula Pathologic mobility External root resorption Internal root resorption Periapical or interradicular radiolucency Pulp calcifications Excessive bleeding from radicular stumps |
|
|
What is a major cause of pulpotomy failure?
|
Bacterial contamination from the bur during the pulpotomy procedure.
NEED A CLEAN BUR |
|
|
What is countersinking?
|
countersinking down a canal using #4 slow speed round bur
It reduces the amount of surface area of pulp tissue that will be treated Hemorrhage is easier to control when there is less tissue involved |
|
|
Following hemostasis, what do you dilute the cotton pellets with over the pulp stumps?
|
1:5 dilution of Buckley's formacresol
|
|
|
What are the steps for a pulpotomy?
|
1. Access
2. Remove coronal pulpal tissue 3. Countersink to provide hemostasis 4. Moistened cotton pellet with Buckley's formacresol for 5 minutes 5. Condense pellets 6. Remove pellets 7. Place base of IRM over amputation site and condense to cover pulpal floor 8. 2nd layer of IRM to fill access completely 9. Restore with SCC |
|
|
During a pulpotomy, if you have excessive bleeding that persists, what could be going on?
|
Inflammation has extended to the radicular pulp
|
|
|
In a two-stage pulpotomy, how long should you wait before removing the formacresol pellet?
|
7-10 days
|
|
|
When would you perform a pulpectomy?
|
When the pulp is either irreversibly inflamed (hemorrhage 7-10 days after completion of a two-stage pulpotomy) or necrotic
|
|
|
When is a two-stage pulpectomy preferred?
|
If the radicular pulp is necrotic
|
|
|
Where do you want the endodontic files to stop when performing a pulpectomy?
|
2 mm short of the radiographic apex of each canal
This minimizes the chance of overinstrumenting and causing periapical damage |
|
|
What do you fill the canals with after a pulpectomy?
|
ZOE paste using a lentulo mounted on a slow speed or Vitapex can be packed in using a sterile syringe
|
|
|
What are the Seven most likely Pedo emergencies you may run into?
|
1. Asthma attack
2. Allergic reaction 3. Seizure 4. Airway obstruction 5. Drug overdose 6. Hypoglycemia 7. Syncope |
|
|
What type of forceps are contraindicated for primary teeth?
|
Cow Horn Forceps - potential for injury to the developing premolars
|
|
|
If you don't use a rubber dam during extraction, what should you use?
|
A guaze guard with floss tied to it
|
|
|
When using an elevator to luxate a tooth to be extracted, what should you be careful not to do?
|
Be careful not to luxate the adjacent teeth
|
|
|
What is used to separate the epithelial attachment of the tooth prior to extraction?
|
A periosteal elevator
|
|
|
When extracting a tooth, what direction should the First Force be in?
|
First force exerted should be in the apical direction
|
|
|
What forcep is used for extraction of maxillary anterior teeth?
|
#1 forcep - labiolingual movement with slight rotation
|
|
|
How should the beaks of forceps be aligned with the tooth to be extracted?
|
Parallel to the long axis of the tooth
|
|
|
What happens if you fracture a root tip?
|
Leave root tip in there. Do not go searching for it. It may disturb the bud. Eventually the come out or resorb.
|
|
|
What forceps do you use when performin a maxillary molar extraction?
|
#150S forcep
|
|
|
When extracting maxillary molars, what is the first direction of force and then what concurrent directions?
|
Palatal movement first
Alternating palatal and buccal motions |
|
|
How do you check for signs of profound anesthesia?
|
Press the surrounding tissue with an instrument
Percuss the tooth Wiggle on the tooth slightly before to insure adequate pain control is present |
|
|
How should you split a mandibular molar to be extracted?
|
Split the tooth in its long axis and remove each root individually
|
|
|
What type of oxygen must you have on hand for emergencies?***exam question
|
Must be capable of delivering greater than 90% oxygen at flows in excess of 10L/min for a minimum of one hour
E cylinder (650 L) is minimal size required |
|
|
What is the most important piece of emergency equipment in your office?
|
oxygen
|
|
|
What is the first thing you should do when a medical emergency arises?
|
Discontinue dental treatment
The sooner you call 911 the better |
|
|
T/F
Drugs are NOT necessary for most emergencies |
True
When in doubt, use BLS, not medications |
|
|
What are the 7 most likely emergencies you may encounter?
|
1. Asthma attack
2. Allergic reaction 3. Seizure 4. Airway obstruction 5. Drug overdose 6. Hypoglycemia 7. Syncope |
|
|
What is the frequency of rescue breathing?
|
Adult >8; 10-12 breath/min
Child 12-20 breath/min |
|
|
What is the compression rate for CPR?
|
100/min
|
|
|
What is the compression to ventilation ratio for CPR?
|
30:2
|
|
|
What is used to clear airway obstructions in unconscious children?
|
Magill intubation forceps or suction
|
|
|
When should a heimlich maneuver be performed?
|
Only on a conscious child with airway obstruction
|
|
|
T/F
Dental floss could also be secured to cotton rolls and to gauze pads |
True
|
|
|
What should be administered in a sudden onset anaphylactic allergic reaction?
|
Epinephrine 1:1000 0.01 mg/kg every 5 minutes IM or subQ
|
|
|
What should you do in an acute asthmatic emergency?
|
Inhaler bronchodilator
Oxygen Sit upright ...if these aren't working administer Epinephrine 1:1000 0.01 mg/kg every 15 minutes as needed IM or SubQ |
|
|
Where should an EPIPEN be administered?***exam question
|
Anterolateral aspect of the thigh
|
|
|
What should you administer to a patient if their siezure lasts longer than 5 min?
|
IV diazepam 0.1-0.3 mg/kg to a maximum dose of 10 mg
|

