![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
197 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
when can congenital infections occur |
at any time during pregnancy, labor and delivery |
|
|
how are congenital infections transmitted |
through placenta, amniotic fluid and vaginal canal |
|
|
infections during this period affect virtually any of the developing organ systems and you will find symmetrically growth restricted infants |
first trimester infections |
|
|
some presentations of congenital infections (broad spectrum) |
growth retardation premature delivery cns abnormalities (microcephaly, intracranial calcifications, chorioretinitis, hydrocephaly) hepatosplenomegally with possible jaundice bruising or petechiae (thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia) skin lesions pneumonitis |
|
|
the original concept of the ____ perinatal infections was to group five infections with similar presentations, including rash and ocular findings |
TORCH |
|
|
what does TORCH stand for |
toxoplasmosis other (syphilis, HIV, parvovirus B-19, varicella, hepatitis, enterovirus) rubella cytomegalovirus herpes simplex |
|
|
Clinical manifestsions suggestive of congenital cytomegalovirus (3) |
|
|
|
periventricular intracranial calcifications microcephaly thrombocytopenia are suggestive of this congenital infection in the neonate |
congenital cytomegalovirus |
|
|
Clinical manifestsions suggestive of congenital herpes simplex virus (5) |
|
|
|
mucocutaneous vesicles or scarring CSF pleocytosis thrombocytopenia elevated liver transaminases conjunctivitis or keratoconjunctivitis are suggestive of this congenital infection in the neonate |
Congenital Herpes Simplex Virus |
|
|
Clinical manifestsions suggestive of congenital syphilis (4) |
|
|
|
skeletal abnormalities (osteochondritis and periostitis) pseudoparalysis persistent rhinitis maculopapular rash (particularly on palms and soles or in diaper area) are suggestive of this congenital infection in the neonate |
congenital syphilis |
|
|
Clinical manifestsions suggestive of congenital toxoplasmosis (4) |
|
|
|
itracranial calcifications (diffuse) hydrocephalus chorioretinitis otherwise unexplained mononuclear CSF pleocytosis or elevated CSF protein are suggestive of this congenital infection in the neonate |
congenital toxoplasmosis |
|
|
Clinical manifestsions suggestive of congenital varicella (2) |
cicatricial or vesicular skin lesions limb hypoplasia |
|
|
cicatricial or vesicular skin lesions limb hypoplasia are suggestive of this congenital infection in the neonate |
congenital varicella |
|
|
what is choreoretinitis and with which congenital infection is it associated |
choroid is in the back of the eye...pigmented vascular coat. toxoplasmosis inflames this snd it necrotizes |
|
|
what organism is responsible for toxoplasmosis |
toxoplasma gondii |
|
|
where is toxoplasma gondii found |
cat feces, raw or undercooked meat, contaminated soil or water |
|
|
what are the maternal sx of toxoplasmosis in pregnance |
nonspecific: fatigue, fever, HA, malaise, and myalgia |
|
|
what are the neonate sx of congenital toxoplasmosis |
fever, maculopapular rash, hepatosplenomegaly, microcephaly, seizures, jaundice, thrombocytopenia, generalize lymphadenopathy |
|
|
classic triad of toxoplasmosis |
chorioretinitis hydrocephalus intracranial calcifications (diffuse) |
|
|
chorioretinitis hydrocephalus intracranial calcifications (diffuse) |
classic triad of toxoplasmosis |
|
|
primary focus of toxoplasmosis in the neonate CNS |
necrotic, calcified cystic lesions dispersed within th brain (can find similar lesions in the liver, lungs, heart, skeletal muscle, spleen) |
|
|
long term complications of congenital toxoplasmosis |
seizures, mental retardation, spasticity, relapsing chorioretinitis |
|
|
85% of toxoplasmosis babies |
asymptomatic |
|
|
Dx of congenital toxoplasmosis |
IgM anti-toxoplasma antibody at 20-26 weeks (mother) isolation of the parasite in fetal blood or amniotic fluid postnatal: IgM antibodies in baby serum prenatal US: symmetric ventricular dilation, intracranial calcifications, increased placental thickness, hepatomegaly, ascites |
|
|
labs may show these things for congenital toxoplasmosis |
anemia, thrombocytopenia, eosinopilia, abnormal CSF |
|
|
Treatment of congenital toxoplasmosis |
pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine or Spiramycin |
|
|
in toxoplasmosis, this immunoglobulin is acute and this is old |
IgM is acute IgG is old |
|
|
if mother has toxoplasmosis in first trimesters, there is a 5% chance of |
loss of pregnancy |
|
|
if mother has acute toxoplasmosis infection in the third trimester, there is a ____% chance of transferring it to the baby |
60% |
|
|
can you treat toxoplasmosis during pregnancy? |
yes |
|
|
list the OTHER infections in TORCH |
HIV, enterovirus, parvovirus B-19, Varicella hepatitis B syphilis |
|
|
When is the enterovirus acquired and what is the prognosis |
around the time of birth good prognosis |
|
|
what is associated with parvovirus b-19 |
possible fetal hemolytic crisis associated |
|
|
varicella perinatal exposure, prognosis and tx |
can be very severe, treat with immune globulin if suspected |
|
|
treatment of congenital hepB |
HBIG and vaccine if the mom is positive |
|
|
if mom is primary or secondary stage of syphilis, transmission rate |
100% |
|
|
what organism causes syphilis |
treponema pallidum |
|
|
syphilis infection during pregnancy can result in (9) |
stillbirth hydrops fetalis prematurity and associated long-term morbidity hepatomegaly edema thrombocytopenia anemia skeletal abnormalities, saddle nose deformity rash (maculopapular, vesicular) |
|
|
what congenital infection can produce a saddle nose |
syphilis |
|
|
when does transplacental infection of syphilis occur |
second half of pregnancy |
|
|
are infected syphilis babies symptomatic |
half are |
|
|
early symptoms of congenital syphilis |
hepatosplenomegaly, skin rash, anemia, jaundice, metaphyseal dystrophy, periostitis, sf with increased protein and PMNs |
|
|
what congenital infections produce hepatosplenomegaly? |
syphilis toxoplasmosis |
|
|
Clinical manifestsions suggestive of congenital rubella (4) |
|
|
|
cataracts, congenital glaucoma, pigmentary retinopathy congenital heart disease (most common PDA or peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis) radiolucent bone disease sensorineural hearing loss are suggestive of this congenital infection in the neonate |
congenital rubella |
|
|
congenital syphilis manifestations |
late abortion or stillbirth infantile: rash, osteochondritis, periostisis, liver & lung fibrosis childhood: interstitial keratitis, hutchinson teeth, eigth nerve deafness |
|
|
what is interstitial keratitis, and with which congenital infection is it associated |
corneal scarring due to chronic inflammation of the corneal stroma. Interstitial means space between cells, i.e. corneal storm which lies between the epithelium and the endothelium. keratitis means corneal inflammation |
|
|
with which congenital infection are hutchinson teeth associated |
congenital syphilis |
|
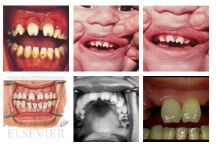
what are these? with what congenital infection are they associated? |
hutchinson teeth associated with congenital syphilis |
|
|
what does sanguineous discharge mean |
clear discharge with pink tinge |
|
|
snuffles |
associated with congenital syphilis nasal obstruction, initially clear drainage then puruluent or sanguineous discharge |
|
|
Dx of congenital syphilis |
IgM FTA-ABS (fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption) in newborn blood not always positive at first, recheck in 3-4 weeks |
|
|
use IgM FTA-ABS (fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption) to diagnose |
congenital syphilis |
|
|
treatment of congenital syphilis |
PCN G |
|
|
monitor newborns with congenital syphilis for |
vision changes, hearing, developmental abnormalities |
|
|
Dx of Rubella |
increased anti-rubella IgM titer in perinatal period increased anti-rubella IgG titer in the first few years of life isolate virus from throat swab, CSF or urine |
|
|
long term complications of congenital rubella |
communication disorders, hearing defects, mental or motor retardation, microcephaly, learning deficits, balance and gait disturbances, behavioral problems |
|
|
treatment of congenital rubella |
prevention with vaccination (MMR) |
|
|
most common congenital viral infection |
CMV |
|
|
how is CMV transmitted |
saliva, urine or bodily fluids |
|
|
mortality rate of CMV |
30% |
|
|
_____% of CMV sx are neurologic |
80% |
|
|
if cmv was acquired prior to conception how can the fetus get the infection? |
if the mother has secondary reactivation |
|
|
if CMV is transmitted from a newly acquired maternal infection, is the infection more severe or less severe than if it's a secondary reactivation |
more severe with worse prognosis |
|
|
what is the leading cause of sensorineural hearing loss in infants |
CMV |
|
|
what is the leading cause of sensorineural hearing loss, mental retardation, retinal disease and cerebral palsy |
CMV |
|
|
sx of congenital CMV |
SGA, microcephaly, thrombocytopenia, hepatosplenomegaly, hepatitis, intracranial calcifications |
|
|
how is herpes simplex most commonly acquired |
at the time of birth during transit through the infected birth canal |
|
|
transmission of more likely if |
mom is having a primary outbreak |
|
|
how is herpes simplex transmission prevented |
cesarean section |
|
|
how to treat congenital herpes simplex |
acyclovir |
|
|
is the mortality rate of herpes simplex low or high |
high |
|
|
what is the transmission rate of HSV in reactivated infections of the mother
|
5% |
|
|
sx of neonatal HSV |
disseminated disease (sepsis, liver 'elevated liver enzymes', lungs localized (CNS, 'seizures, encephalopathy', skin, eyes, mouth) treatment - acyclovir |
|
|
clinical manifestations of congenital varicella (8) |
|
|
|
what is an option for imaging a baby's head in order to avoid CT |
US, since the skull isn't ossified |
|
|
work up for perinatal infections |
review maternal hx assessment of physical stigmata consistent with various intrauterine infections CBC, LFTs long bone x-rays opthalmologic evaluation audiologic evaluation neuroimaging lumbar puncture |
|
|
these 4 congenital infections are asymptomatic |
toxoplasmosis, syphilis, CMV, HSV |
|
|
which infectious disease causes deafness at birth and later |
rubella |
|
|
which infections cause chorioretinitis and possible blindness? |
toxoplasmosis |
|
|
which infection has elevated LFTs? |
HSV |
|
|
which infections can be associated with thrombocytopenia and purpura or petechiae? |
CMV |
|
|
which infections cause deafness at birth and later? |
rubella and CMV |
|
|
5 maternal conditions that may cause birth defects |
|
|
|
Maternal medication use that cause birth defects (7) |
|
|
|
8 maternal medical disorders that can cause birth defects |
|
|
|
how does maternal diabetes cause birth defects |
Makes baby big After delivery, babysubject to having severe hypoglycemic episode in first day and can bedangerously low. Need to be checked frequently. Also require csection, which offers more problems (due to size) |
|
|
how does maternal PKU cause birth defects |
PKU: not able toprocess amino acids and have too much penenyl alanine At risk for latedevelopment, head growth, heart defects, intellectual developmental delay |
|
|
how does maternal androgen producing tumor of adrenal glands or ovaries cause birth defects |
Androgen producingtumors of adrenal glands or overies:Whatever hormonesthe tumor is secreting will affect the babyEg cortisol willaffect growth of baby |
|
|
how does maternal SLE cause birth defects |
SLE:Antiphospholipidantibody syndrom can cause pregnancy loss in first trimesterIf they make itpast, at risk for preterm labor due to preeclampsia or premature rupture of themembranesPreeclampsia issevere HTN during pg that can lead to fetal death if baby isn't delivered…andthe tx is delivery |
|
|
how does maternal obesity cause birth defects |
Obesity:At risk fordeveloping gestational diabetesProblems with HTNProblems withpreeclampsia, preterm laborIf the baby is bornoverweight from excess calorie intake from the mother (she doesn't havediabetes, for example), there's a correlation with the increased birth weightleading to childhood obesity. Is this nature vs nurture |
|
|
how does maternal fever cause birth defects |
Fever:Over 103 can causethe baby to be stillbornThis is actuallylethalMom should not be inhot hottubs while pregnant |
|
|
how does maternal fever cause birth defects |
HTN: You'd think thatextra pressure would feed the placenta and get more blood flow, but it's theopposite and blood is shunted from the placenta resulting in low birth weightbabies |
|
|
how does maternal hypothyroidism cause birth defects |
hypothyroidism: ifmom is treated to normal TSH it’s okif not, babydevelopmental delays |
|
|
facial features of fetal alcohol syndrome |
skin folds at the corner of the eye low nasal bridge short nose indistinct philum small head circumference small eye opening small mid face thin upper lip |
|
|
dx of fetal alcohol syndrome |
facial features history birth weight |
|
|
5 mechanical forces that may cause congenital defects |
|
|
|
5 maternal toxins |
mercury lead ionizing radiation carbon monoxide poor nutrition |
|
|
list 5 congenital heart defects |
ventricular septal defect (VSD) atrial septal defect (ASD) patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) coarctation of the aorta tetralogy of fallot |
|
|
25% of all congenital heart defects |
VSD |
|
|
VSD symptoms |
fatigue diaphoresis with feedings poor growth pansystolic murmur may not be symptomatic at birth due to normally elevated pulmonary vascular resistance but as the PAP decreases, the amount of left to right shunt increases |
|
|
pansystolic murmur |
vsd |
|
|
soft systolic ejection murmur |
ASD |
|
|
fixed split s2 |
ASD |
|
|
machine like murmur that can be heard over the left side of the back as well |
PDA |
|
|
systolic murmur best heard on the left upper back |
coarctation of the aorta |
|
|
loud, harsh systolic ejection murmur |
tetralogy of fallot |
|
|
|
|
|
right heart becomes dilated |
atrial septal defect |
|
|
larger ASD shunts need to be closed if still present around what age |
3 years |
|
|
PDA is more likely to occur under these conditions |
high altitudes hypoxic conditions premature heart defects |
|
|
this med treats pda |
indomethacin |
|
|
risk factors for PDA |
prematurity other heart defects high altitudes >10,000 relative hypoxia (causing increased pulmonary vascular resistance) maternal rubella infection |
|
|
how to check for coarctation of the aorta on PE |
pulse in UE doesn't match femoral pulse |
|
|
sx of coarctation of the aorta |
poor feeding respiratory distress shock weak femoral pulses compared to radial or brachial pulses older children may have lower extremity claudication systolic murmur best heard on the left upper back treatment - try to keep the ductus arteriosus open until surgery |
|
|
tetralogy of fallot |
vsd pulmonary stenosis right ventricular hypertrophy overriding aorta |
|
|
tx of tof |
surgical repair at about 6 months |
|
|
sx of TOF worsen when? |
after the pda closes |
|
|
what are TET spells |
cyanosis worsens with crying, toddlers will squat to relieve symptoms, may have syncope, hemiparesis, seizures or death may occur |
|
|
what are the 5 T's of cyanotic congenital heart disease |
tetralogy of ballot transposition of the great arteries tricuspid atresia trunks arteriousus total anomalous pulmonary venous return |
|
|
what is total anomalous PVR |
Total anomalous PVRAll of theoxygenated blood is supposed to dump in LA but dumps into the SVC |
|
|
4 acyanotic congenital heart diseases |
PDA VSD ASD obstructive lesions (aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, coarctation of the aorta) |
|
|
central cyanosis is indicative of |
a significant underlying condition |
|
|
the most common cause of cyanosis in newborn |
cardiopulmonary disease (RDS, sepsis, cyanotic heart disease) |
|
|
workup of the cyanotic newborn |
cxr cbc, cmp (blood glucose) abg's blood cultures echocardiogram involve your supervising physician early and refer |
|
|
list 5 chromosomal abnormalities |
trisomy 21 trisomy 13 turner syndrome kleinfelter syndrome fragile x syndrome |
|
|
which is more common? trisomy 21 or 13 |
21, down syndrome |
|
|
a chromosomal deletion syndrome
|
22q11 syndrome |
|
|
numeric sex chromasomal disorders |
turner syndrome XO (1:2500 girls) klinefelter syndrome XXY (I:800 boys) |
|
|
most common abnormality of chromosomal number 1:800 |
trisomy 21, down syndrome |
|
|
increased risk for this chromosomal abnormality when the maternal ages >35 |
trisomy 21 down syndrome |
|
|
how does down syndrome result in extra chromosome |
chromosomal nondisjunction |
|
|
down syndrome characteristics |
normal size baby hypotonic brachycephaly flattened occiput hypoplastic midface flattened nasal bridge upslanting palpebral fissures epicanthal folds large protruding tongue short broad hands transverse palmar crease wide gap between 1st and 2nd toes |
|
|
what is brachycephaly |
Brachycephaly (from Greek roots meaning "short" and "head") is the shape of a skull shorter than typical for its species. |
|
|
iq of down syndrome babies |
40-50 |
|
|
medical problems associated with down syndrome |
40% congenital heart defects 10% have GI tract abnormalities 1% hypothyroidism increased risk of leukemia (20x) increased risk of infection increased risk of cataracts 10% have alantoaxial instability = predispose to spinal cord injury >age 35 may develop Alzheimer's like features |
|
|
most constant characteristic of down syndrome |
mental retardation with IQs mostly between 40-50 |
|
|
most trisomy 13 babies die of |
heart failure or infection by age 2 |
|
|
multiple dysmorphic features and complications, most die of heart failure or infection in infancy by the second year of life. marked developmental retardation |
trisomy 13 |
|
|
if a baby is born with CHF and cleft palate, think this chromosomal disorder |
deletion of 22q11 syndrome |
|
|
what body systems does deletion 22q11 syndrome affect |
virtually all of them |
|
|
deletion 22q11 syndrome is associated with these other syndromes |
velocardiofacial syndrome conotruncal anomaly face syndrome shprintzen syndrome digeorge syndrome CATCH 22 |
|
|
what chromosomal disorder presents with hypoplasia of the thymus and/or parathyroid gland |
deletion 22q11 syndrome |
|
|
conotruncal cardiac defects, what chromo disorder? |
deletion 22q11 syndrome |
|
|
facial dysmorphism what chromo disorder? |
deletion 22q11 syndrome |
|
|
what chromo disorder: clinical manifestations may include neonatal hypocalcemia, increased infections, as well as a predisposition to autoimmune diseases later in life |
deletion 22q11 syndrome |
|
|
what gender is Turner syndrome |
female |
|
|
comorbidity risks of turner syndrome |
renal anomalies 40% congenital heart defect coarctaion 20% autoimmune thyroiditis is common |
|
|
what chromosome is a turner syndrome baby missing
|
a second x |
|
|
dysmorphic features of turner syndrome |
lymphedema (hands and feet) webbing of the neck short stature multiple pigmented nevi gonadal dysgenesis (ovaries fail to respond to gonadotropin stimulation resulting in amenorrhea at puberty and failure of development of secondary sexual characteristics) hearing loss, hypothyroidism, and liver function abnormalities can occur as these women get older |
|
|
treatment of turner syndrome |
estrogen replacement therapy growth hormone therapy can be used to increase height |
|
|
what is the genome of the sex chromes for klinefelter syndrome |
XXY |
|
|
this is the most common congenital abnormality causing primary hypogonadism |
klinefelter syndrome XXY |
|
|
other than thin build and long arms, prepubertal boys with this syndrome have a normal phenotype |
klinefelter syndrome |
|
|
incidence of klinefelter syndrome XXY |
1 in 500 live male births |
|
|
when is klinefelter syndrome detected |
age 15/16 when testes remain small and lack secondary sexual characteristics |
|
|
treatment of klinefelter syndrome |
testosterone |
|
|
dysmorphic features of klinefelter syndrome |
taller stature/wider arm span small testes, reduced testosterone, reduced spermatogenesis incomplete masculinization, decreased body hair female habits, gynecomastia |
|
|
clinical features of klinefelters syndrome XXY |
immaturity normal to borderline low IQ, some variations manifest severe mental retardation behavioral problems |
|
|
oblong face and very large ears, mental retardation, large testicles, autistic-like behavior |
fragile x syndrome |
|
|
1:4000 males, 1:8000 females |
fragile x syndrome |
|
|
mutation of DNA that codes for a protein that helps play a role in the development of synapses |
fragile x syndrome |
|
|
mutation in what gene causes marfan's syndrome |
FBN1 |
|
|
what gene determine the structure of fibrillin |
FBN1 |
|
|
what is fibrillin |
a protein that is an important part of connective tissue and elastic fibers which affect multiple parts of the body such as bones, joints, eyes, blood vessels, and heart |
|
|
who is likely to have marfan's |
inhereted and can affect men and women of any race or origin |
|
|
1 in _____ cases of marfan's are serious |
10 |
|
|
each child of a person with marina's has a ____% chance of inheriting the disease |
50% |
|
|
two unaffected parents only have a 1 in _____ chance of having a child with marfan's |
10,000 |
|
|
about ____% of all marfan cases are due to a spontaneous mutation at the time of conception |
25 |
|
|
leading cause of death in marfan patients |
aortic aneurysm |
|
|
marfan sx |
muscle weakness in legs increased risk of hernia increased risk of spontaneous pneumothorax lens dislocation ascending aortic aneurysm **** aortic valve disease vascular dissection flat feet scoliosis long and skinny fingers and toes stretch marks loose/hyperflexible joints tall, thin stature |
|
|
dx of marfan's |
aortic root aneurysm and ectopia lentis (dislocated lenses) are cardinal features genetic testing clinical signs typical of the dx |
|
|
aortic root aneurysm and ectopia lentis (dislocated lenses) are cardinal features of |
marfan syndrome |
|
|
treatment of marfan's |
beta blockers (decrease after load, taking pressure off aorta, reducing aneurysm chances) losartan? control of sx from valvular disease |
|
|
first line treatment for marfan's |
beta blockers |
|
|
life expectancy of marfan's pt |
same as average person |
|
|
the most common amino acid metabolism disorder 1 in 12,000 births |
phenylketonuria PKU |
|
|
decrease of the enzyme that converts phenylalanine to ______ |
tyrosine |
|
|
clinical presentation of pku pt without treatment |
hypopigmentation neurologic manifestations (tremors, hypertonicity, behavioral disorders, seizures) severe mental retardation |
|
|
management of PKU |
dietary restrictions (diet for life) especially during pregnancy if the mother has PKU |
|
|
foods high in phenylalanine |
red meat chicken fish eggs nuts cheese legumes milk/dairy aspartame |
|
|
can pku babies nurse |
yes |
|
|
supplementation of this for pku |
tyrosine |
|
|
what is galactosemia |
autosomal recessive disorder deficiency of galactose-1 phosphate uridyltransferase leading to buildup of unmetabolized galactose |
|
|
clinical presentation of galactosemia |
appears within days to weeks of birth hepatomegaly vomiting, anorexia growth failure (FTT) aminoaciduria |
|
|
treatement of galactosemia |
elimination of galactose from diet |
|
|
prognosis if galactosemia is untreated |
death mental and/or growth retardation cataracts |
|
|
what prevents neural tube defects |
folic acid |
|
|
two major types of neural tube defects |
anecephaly (no cranium, fatal) meningomyelocele (spina bifida) |
|
|
what is meningomyelocele |
spina bifida |
|
|
prenatal dx of neural tube defects |
elevated apha-fetoprotein |
|
|
are orofacial clefts more common in males/females |
males 2:1 |
|
|
highest incidence of orofacial clefts in this population |
asian native american |

