![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
On assessing for nystagmus a child's eye's have a slow phase back to center with a quick gaze laterally, when asked to look far up or out. What is the diagnosis? |
This is Jerk nystagmus.
|
|
|
True or False.
Jerk nystagmus is normal. |
True
|
|
|
On assessing for nystagmus a child's eye's has equally delayed or rapid to and fro movement What is the diagnosis?
|
Pendular nystagmus.
A pendulum is equally delayed. |
|
|
What happens in cover test in strabismus?
|
The eye with strabismus deviates instead of fixing on the object.
|
|
|
How do you distinguish pseudoesotropia from esotropia?
|
Pseudo esotropia will have equal light reflexes, while true esotropia will not.
See page 135 in picture worth 100 points v2. |
|
|
What is the complication of untreated strabismus?
|
Ambylopia which is loss of the non-dominant eye and permanent loss of binocular vision.
|
|
|
A child has a violaceous discoloration around his left eye and cheek. What is he at risk of?
|
Glaucoma. This is sturge webber
|
|
|
When do you have to intervene with a strawberry hemangioma?
|
When it is on or near the eyelid AND interfering with vision
|
|
|
A newborn infant has absent red reflex, and instead has leukokoria in one eye. What is your next step?
|
Consult ophthalmology.
|
|
|
What are the two most common causes of congenital cataracts?
|
Galactosemia and Rubella
|
|
|
A patient has an external hordeolum aka stye. It is red, tender and inflamed. What is the treatment?
|
Warm compresses, topical antibiotics
|
|
|
What is dacyrocystitis?
|
A blocked tear duct. Milk and massage.
|
|
|
What is aniridia? What 2 diseases is it usually seen in?
|
Aniridia is incomplete formation of the iris. It is seen in Wilms and Beckwith Widemann.
See page 295 of picture book. |
|
|
A child has a recurrent, but slow growing, non-tender mass above her eyelid. What is this and how do you treat it?
|
It is a chalazion. Treat with warm compresses, and sometimes antibiotics, but this is benign.
|
|
|
You are evaluating a 2 month old with excessive tearing of the left eye and mucoid discharge. When you evaluate the crying infant you notice that the tears pool on the left eyelid and cheek. The parents note that the child has nasal congestion and coughs occasionally. He is otherwise healthy. What is the management?
A) PO antibiotics B) Topical antibiotics C) IV antibiotics D) Observe E) Warm compress and massage. |
E.
|
|
|
A child is brought in because she fell on the playground and something got in her eye. The eye is red and painful. What is your first step?
|
Fluorescein stain. THEN TOPICAL antibiotics.
|
|
|
A 4 month old has a history of a painless nodule on her upper eyelid. What is your next step in management?
|
Refer to ophthalmology for excision as this is a chronic nodule
|
|
|
I am usually unilateral, preceded bya viral illness and cause a transient decrease in visual acuity. On funduscopic exam, the optic disc is engorged and inflammed. Who am I?
A) Papilledema B) Papillitis C) Retrobulbar optic neuropathy |
B
|
|
|
I cause loss of visual acuity but the optic discs are normal looking on funduscopic exam.
Who am I? A) Papilledema B) Papillitis C) Retrobulbar optic neuropathy |
C
|
|
|
I cause enlargement of the blind spot, but no loss in visual acuity. On funduscopic exam, you will note loss of arteriovenous pulsations.
Who am I? A) Papilledema B) Papillitis C) Retrobulbar optic neuropathy |
A
|
|
|
How do you distinguish a stye from a chalazion?
|
A stye is tender and red. A chalazion is not.
See page 299 in picture book |
|
|
I cause peripheral vision loss, then night blindness, then central visual defects. I tend to run in families and can be seen in Usher syndrome. Who am I?
|
Retinitis Pigmentosa.
See page 313 of picture book. |
|
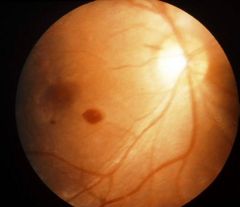
What is this?
Hint...it is seen in shaken baby syndrome. |
Retinal flame hemorrhage
See page 311 of picture book. |
|
|
Which infants should be screened for ROP?
|
Babies who are:
< 1500 grams OR < 28 weeks OR 1500-2000 grams and unstable clinical course. See page 315 of picture book |
|
|
When should you screen for ROP?
|
At 31 corrected gestational age or 4 weeks chronological age, whichever is later.
See page 315 of picture book |
|
|
Who is at greatest risk of ROP?
|
Babies < 28 weeks
See page 315 of picture book |

