![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Isotonic contraction |
Muscles contract that results in limb movement. Muscles work in pairs to create movement, one contracts the other relaxes eg press ups |
|
|
Isometric contraction |
Muscles contesting which results in tension but length doesn't alter eg plank, yoga position |
|
|
Hypertrophy |
Increased muscle size, a result of progressive overload |
|
|
Muscle atrophy |
Loss of muscle mass and strength |
|
|
Tendons |
Connect muscle to bones |
|
|
Ligaments |
Tough elastic fibre that link bone to bone |
|
|
Cartilage |
Prevents end of bones rubbing together at joint |
|
|
Fracture |
Broken bone or cracked bone |
|
|
Name all the fractures |
Greenstick Transverse Impact Comminuted Oblique |
|
|
Bruise |
Bleeding under your skin |
|
|
Dislocation |
When bone at the joint is forced out of normal position |
|
|
Sprains |
A damaged ligament eg twisted ankle |
|
|
Tennis and golfers elbow |
Overuse injuries to the tendons at the elbow joints
Golfers on the inside, tennis on the outside |
|
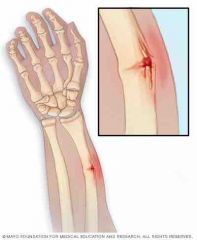
|
Greenstick - break only part way across the bone |
|
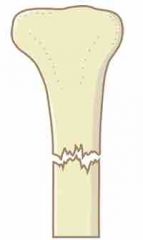
Front (Term) |
Transverse - break straight across |
|

Front (Term) |
Impacted - pieces locked into each other |
|

|
Impacted - pieces locked into each other |
|
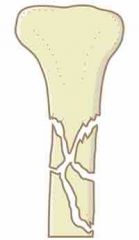
|
Comminuted - broken into more than 2 pieces |
|
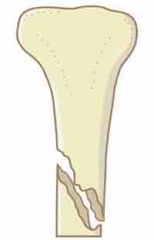
Front (Term) |
Oblique - broken at an angle |
|
|
What does the cardiovascular system consist of |
Heart, blood & blood vessels |
|
|
Long & short term benefits of exercise in the cardiovascular system |
Short term: Increased heart rate Blood pressure m
Long term: Lower resting heart rate Increases stroke volume Increased cardiac output |
|
|
Closed fracture |
Skin isn't broken |
|
|
Compound fracture |
Goes through skin |
|
|
Simple fraction |
Take place in one line with no displacement of the bone eg greenstick |
|
|
Torn cartallaige |
Cartilage is a firm elastic substance found at the end of bones of a synovial joint |
|
|
Tidal volume |
Amount of air inspired & expired with each normal breath at rest or during exercise |
|
|
Vital capacity |
Greatest amount of air that can pass in & out of your lungs by the most forceful inspiration & expiration |
|
|
What does the respiratory system consist of |
Lungs (alveoli & capillaries), ribs, diaphragm & tranches |
|
|
2 main functions of respiratory system |
1.Bring oxygen into the body 2. Remove carbon dioxide from the body |
|
|
What is oxygen debt |
Temporary oxygen shortage as a result of exercise |
|
|
Effects of smoking on alveoli & gaseous |
Makes it more difficult to get oxygen in & out of their bodies because smoking makes alveoli less stretchy, which causes smokers to be short of breath.
They're lungs have to work harder to get oxygen into their body which makes them tired |
|
|
Plantar & Dorsi flextion |
They occur around the ankle joint
Plantar flexion - increases the angle eg pointing toes
Dorsi flexion - decreases the angle eg raising & lowering heels at the edge of a step |
|
|
Effects of exercise on bones |
Stronger ligaments & tendons, increases joint flexibility and allows more power in movement
Increases bone density |
|
|
Weight bearing exercise examples |
Skipping Ball games Walking Running yo & downs stairs Junoing |
|
|
National governing bodies examples |
FA ECB |
|
|
National governing bodies examples |
FA ECB |
|
|
Government initiatives examples & purpose |
Encourages More sport participation & improves students fitness
Sport England Youth sport trust |
|
|
Mental benefits of sport |
Feel good factor Aesthetic appreciation Relieve stress & tension Mental challenge Enjoyment Increase self esteem & confidence |
|
|
Social benefits of sport |
Make new friends Improve teamwork & co operation Work with others |
|
|
Physical benefit of taking part in physical activity |
Contributes to good physical health Physical challenge Improves fitness & performance Improves health related fitness |
|
|
Systolic blood pressure |
Max pressure in the arteries when blood contracts (beats) and pushes blood to body |
|
|
Diastolic blood pressure |
Diastolic is pressure of blood during the relaxation phase between beats |
|
|
Pulse pressure |
Difference between systolic & diastolic blood pressure |
|
|
How to make it a balanced competition |
Weight Age Gender Handicap system
Playing to the rules Physical readiness - par-q |
|
|
How to prevent injuries |
Warm up & cool down Checking equipment & facilities Protective equipment & clothing
Playing to rules |
|
|
Cardiac output |
Amount of blood ejected from the heart in one minute |
|
|
Stroke volume |
Volume of blood pumped out of the heart by each ventricle during one contraction |
|
|
Cardiac output = ? X ? |
Heart rate x stroke volume |
|
|
Why is a warm up essential |
-Prevents injuries -Improves performance -Practise skill before game -Prepare psychologically for the event |
|
|
What factors effect optimum weight |
Height Gender Bone structure Muscle girth Genetics |
|
|
Long term benefits of regular exercise & physical activit |
While muscular & skeleton system improve and get stronger |
|
|
Treatment for muscular injuries |
R est I ce C ompretion E lavation |
|
|
Why set a smart targer |
To plan, record & monitor your progress |
|
|
Complex carbohydrates examples |
Starch, bread - provide long lasting energy |
|
|
Complex carbohydrates examples |
Starch, bread - provide long lasting energy |
|
|
Simple carbohydrate |
Fruits & veg - can provide enegy |

